Zhi Ding
University of California at Davis, USA
Leveraging Bi-Directional Channel Reciprocity for Robust Ultra-Low-Rate Implicit CSI Feedback with Deep Learning
Jul 16, 2025



Abstract:Deep learning-based implicit channel state information (CSI) feedback has been introduced to enhance spectral efficiency in massive MIMO systems. Existing methods often show performance degradation in ultra-low-rate scenarios and inadaptability across diverse environments. In this paper, we propose Dual-ImRUNet, an efficient uplink-assisted deep implicit CSI feedback framework incorporating two novel plug-in preprocessing modules to achieve ultra-low feedback rates while maintaining high environmental robustness. First, a novel bi-directional correlation enhancement module is proposed to strengthen the correlation between uplink and downlink CSI eigenvector matrices. This module projects highly correlated uplink and downlink channel matrices into their respective eigenspaces, effectively reducing redundancy for ultra-low-rate feedback. Second, an innovative input format alignment module is designed to maintain consistent data distributions at both encoder and decoder sides without extra transmission overhead, thereby enhancing robustness against environmental variations. Finally, we develop an efficient transformer-based implicit CSI feedback network to exploit angular-delay domain sparsity and bi-directional correlation for ultra-low-rate CSI compression. Simulation results demonstrate successful reduction of the feedback overhead by 85% compared with the state-of-the-art method and robustness against unseen environments.
TACO: Rethinking Semantic Communications with Task Adaptation and Context Embedding
May 16, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in generative artificial intelligence have introduced groundbreaking approaches to innovating next-generation semantic communication, which prioritizes conveying the meaning of a message rather than merely transmitting raw data. A fundamental challenge in semantic communication lies in accurately identifying and extracting the most critical semantic information while adapting to downstream tasks without degrading performance, particularly when the objective at the receiver may evolve over time. To enable flexible adaptation to multiple tasks at the receiver, this work introduces a novel semantic communication framework, which is capable of jointly capturing task-specific information to enhance downstream task performance and contextual information. Through rigorous experiments on popular image datasets and computer vision tasks, our framework shows promising improvement compared to existing work, including superior performance in downstream tasks, better generalizability, ultra-high bandwidth efficiency, and low reconstruction latency.
Task-Adaptive Semantic Communications with Controllable Diffusion-based Data Regeneration
May 12, 2025Abstract:Semantic communications represent a new paradigm of next-generation networking that shifts bit-wise data delivery to conveying the semantic meanings for bandwidth efficiency. To effectively accommodate various potential downstream tasks at the receiver side, one should adaptively convey the most critical semantic information. This work presents a novel task-adaptive semantic communication framework based on diffusion models that is capable of dynamically adjusting the semantic message delivery according to various downstream tasks. Specifically, we initialize the transmission of a deep-compressed general semantic representation from the transmitter to enable diffusion-based coarse data reconstruction at the receiver. The receiver identifies the task-specific demands and generates textual prompts as feedback. Integrated with the attention mechanism, the transmitter updates the semantic transmission with more details to better align with the objectives of the intended receivers. Our test results demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed method in adaptively preserving critical task-relevant information for semantic communications while preserving high compression efficiency.
Generative Semantic Communications: Principles and Practices
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Semantic communication leverages artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to extract semantic information from data for efficient transmission, theraby significantly reducing communication cost. With the evolution towards artificial general intelligence (AGI), the increasing demands for AGI services pose new challenges to semantic communication. In response, we propose a new paradigm for AGI-driven communications, called generative semantic communication (GSC), which utilizes advanced AI technologies such as foundation models and generative models. We first describe the basic concept of GSC and its difference from existing semantic communications, and then introduce a general framework of GSC, followed by two case studies to verify the advantages of GSC in AGI-driven applications. Finally, open challenges and new research directions are discussed to stimulate this line of research and pave the way for practical applications.
Task-Driven Semantic Quantization and Imitation Learning for Goal-Oriented Communications
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Semantic communication marks a new paradigm shift from bit-wise data transmission to semantic information delivery for the purpose of bandwidth reduction. To more effectively carry out specialized downstream tasks at the receiver end, it is crucial to define the most critical semantic message in the data based on the task or goal-oriented features. In this work, we propose a novel goal-oriented communication (GO-COM) framework, namely Goal-Oriented Semantic Variational Autoencoder (GOS-VAE), by focusing on the extraction of the semantics vital to the downstream tasks. Specifically, we adopt a Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder (VQ-VAE) to compress media data at the transmitter side. Instead of targeting the pixel-wise image data reconstruction, we measure the quality-of-service at the receiver end based on a pre-defined task-incentivized model. Moreover, to capture the relevant semantic features in the data reconstruction, imitation learning is adopted to measure the data regeneration quality in terms of goal-oriented semantics. Our experimental results demonstrate the power of imitation learning in characterizing goal-oriented semantics and bandwidth efficiency of our proposed GOS-VAE.
A Unifying View of OTFS and Its Many Variants
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:High mobility environment leads to severe Doppler effects and poses serious challenges to the conventional physical layer based on the widely popular orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). The recent emergence of orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation, along with its many related variants, presents a promising solution to overcome such channel Doppler effects. This paper aims to clearly establish the relationships among the various manifestations of OTFS. Among these related modulations, we identify their connections, common features, and distinctions. Building on existing works, this work provides a general overview of various OTFS-related detection schemes and performance comparisons. We first provide an overview of OFDM and filter bank multi-carrier (FBMC) by demonstrating OTFS as a precoded FBMC through the introduction of inverse symplectic finite Fourier transform (ISFFT). We explore the relationship between OTFS and related modulation schemes with similar characteristics. We provide an effective channel model for high-mobility channels and offer a unified detection representation. We provide numerical comparisons of power spectrum density (PSD) and bit error rate (BER) to underscore the benefit of these modulation schemes in high-mobility scenarios. We also evaluate various detection schemes, revealing insights into their efficacies. We discuss opportunities and challenges for OTFS in high mobility, setting the stage for future research and development in this field.
LaMI-GO: Latent Mixture Integration for Goal-Oriented Communications Achieving High Spectrum Efficiency
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:The recent rise of semantic-style communications includes the development of goal-oriented communications (GOCOMs) remarkably efficient multimedia information transmissions. The concept of GO-COMS leverages advanced artificial intelligence (AI) tools to address the rising demand for bandwidth efficiency in applications, such as edge computing and Internet-of-Things (IoT). Unlike traditional communication systems focusing on source data accuracy, GO-COMs provide intelligent message delivery catering to the special needs critical to accomplishing downstream tasks at the receiver. In this work, we present a novel GO-COM framework, namely LaMI-GO that utilizes emerging generative AI for better quality-of-service (QoS) with ultra-high communication efficiency. Specifically, we design our LaMI-GO system backbone based on a latent diffusion model followed by a vector-quantized generative adversarial network (VQGAN) for efficient latent embedding and information representation. The system trains a common feature codebook the receiver side. Our experimental results demonstrate substantial improvement in perceptual quality, accuracy of downstream tasks, and bandwidth consumption over the state-of-the-art GOCOM systems and establish the power of our proposed LaMI-GO communication framework.
Diff-GO$^\text{n}$: Enhancing Diffusion Models for Goal-Oriented Communications
Dec 09, 2024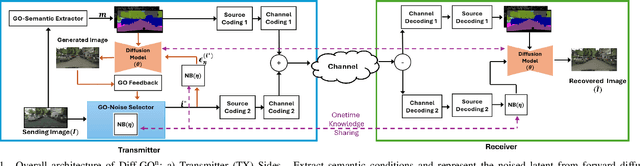
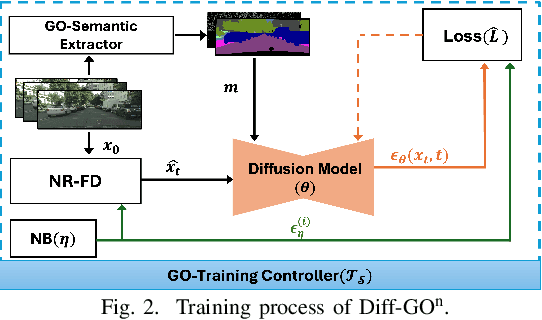
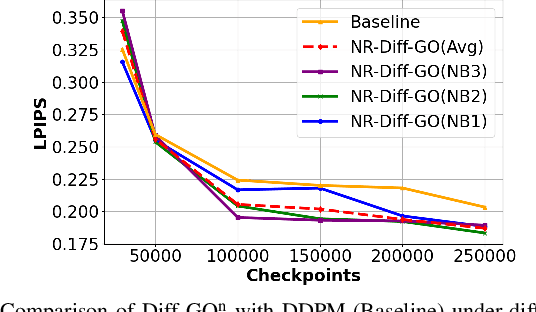

Abstract:The rapid expansion of edge devices and Internet-of-Things (IoT) continues to heighten the demand for data transport under limited spectrum resources. The goal-oriented communications (GO-COM), unlike traditional communication systems designed for bit-level accuracy, prioritizes more critical information for specific application goals at the receiver. To improve the efficiency of generative learning models for GO-COM, this work introduces a novel noise-restricted diffusion-based GO-COM (Diff-GO$^\text{n}$) framework for reducing bandwidth overhead while preserving the media quality at the receiver. Specifically, we propose an innovative Noise-Restricted Forward Diffusion (NR-FD) framework to accelerate model training and reduce the computation burden for diffusion-based GO-COMs by leveraging a pre-sampled pseudo-random noise bank (NB). Moreover, we design an early stopping criterion for improving computational efficiency and convergence speed, allowing high-quality generation in fewer training steps. Our experimental results demonstrate superior perceptual quality of data transmission at a reduced bandwidth usage and lower computation, making Diff-GO$^\text{n}$ well-suited for real-time communications and downstream applications.
Fast Adaptation for Deep Learning-based Wireless Communications
Sep 06, 2024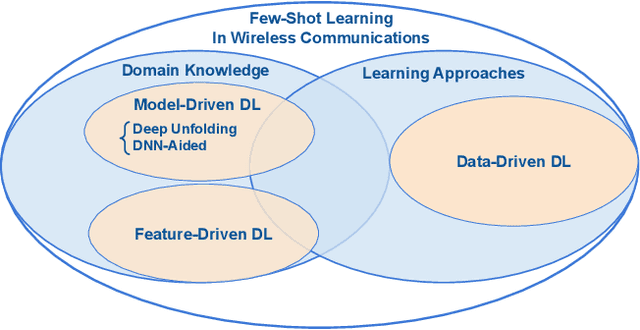



Abstract:The integration with artificial intelligence (AI) is recognized as one of the six usage scenarios in next-generation wireless communications. However, several critical challenges hinder the widespread application of deep learning (DL) techniques in wireless communications. In particular, existing DL-based wireless communications struggle to adapt to the rapidly changing wireless environments. In this paper, we discuss fast adaptation for DL-based wireless communications by using few-shot learning (FSL) techniques. We first identify the differences between fast adaptation in wireless communications and traditional AI tasks by highlighting two distinct FSL design requirements for wireless communications. To establish a wide perspective, we present a comprehensive review of the existing FSL techniques in wireless communications that satisfy these two design requirements. In particular, we emphasize the importance of applying domain knowledge in achieving fast adaptation. We specifically focus on multiuser multiple-input multiple-output (MU-MIMO) precoding as an examples to demonstrate the advantages of the FSL to achieve fast adaptation in wireless communications. Finally, we highlight several open research issues for achieving broadscope future deployment of fast adaptive DL in wireless communication applications.
Plug-in UL-CSI-Assisted Precoder Upsampling Approach in Cellular FDD Systems
May 31, 2024Abstract:Acquiring downlink channel state information (CSI) is crucial for optimizing performance in massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) systems operating under Frequency-Division Duplexing (FDD). Most cellular wireless communication systems employ codebook-based precoder designs, which offer advantages such as simpler, more efficient feedback mechanisms and reduced feedback overhead. Common codebook-based approaches include Type II and eType II precoding methods defined in the 3GPP standards. Feedback in these systems is typically standardized per subband (SB), allowing user equipment (UE) to select the optimal precoder from the codebook for each SB, thereby reducing feedback overhead. However, this subband-level feedback resolution may not suffice for frequency-selective channels. This paper addresses this issue by introducing an uplink CSI-assisted precoder upsampling module deployed at the gNodeB. This module upsamples SB-level precoders to resource block (RB)-level precoders, acting as a plug-in compatible with existing gNodeB or base stations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge