Weiwei Wang
University of California at Davis, USA
BRIGHT: A Collaborative Generalist-Specialist Foundation Model for Breast Pathology
Mar 03, 2026Abstract:Generalist pathology foundation models (PFMs), pretrained on large-scale multi-organ datasets, have demonstrated remarkable predictive capabilities across diverse clinical applications. However, their proficiency on the full spectrum of clinically essential tasks within a specific organ system remains an open question due to the lack of large-scale validation cohorts for a single organ as well as the absence of a tailored training paradigm that can effectively translate broad histomorphological knowledge into the organ-specific expertise required for specialist-level interpretation. In this study, we propose BRIGHT, the first PFM specifically designed for breast pathology, trained on approximately 210 million histopathology tiles from over 51,000 breast whole-slide images derived from a cohort of over 40,000 patients across 19 hospitals. BRIGHT employs a collaborative generalist-specialist framework to capture both universal and organ-specific features. To comprehensively evaluate the performance of PFMs on breast oncology, we curate the largest multi-institutional cohorts to date for downstream task development and evaluation, comprising over 25,000 WSIs across 10 hospitals. The validation cohorts cover the full spectrum of breast pathology across 24 distinct clinical tasks spanning diagnosis, biomarker prediction, treatment response and survival prediction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BRIGHT outperforms three leading generalist PFMs, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in 21 of 24 internal validation tasks and in 5 of 10 external validation tasks with excellent heatmap interpretability. By evaluating on large-scale validation cohorts, this study not only demonstrates BRIGHT's clinical utility in breast oncology but also validates a collaborative generalist-specialist paradigm, providing a scalable template for developing PFMs on a specific organ system.
Fair Regression under Demographic Parity: A Unified Framework
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We propose a unified framework for fair regression tasks formulated as risk minimization problems subject to a demographic parity constraint. Unlike many existing approaches that are limited to specific loss functions or rely on challenging non-convex optimization, our framework is applicable to a broad spectrum of regression tasks. Examples include linear regression with squared loss, binary classification with cross-entropy loss, quantile regression with pinball loss, and robust regression with Huber loss. We derive a novel characterization of the fair risk minimizer, which yields a computationally efficient estimation procedure for general loss functions. Theoretically, we establish the asymptotic consistency of the proposed estimator and derive its convergence rates under mild assumptions. We illustrate the method's versatility through detailed discussions of several common loss functions. Numerical results demonstrate that our approach effectively minimizes risk while satisfying fairness constraints across various regression settings.
Searth Transformer: A Transformer Architecture Incorporating Earth's Geospheric Physical Priors for Global Mid-Range Weather Forecasting
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Accurate global medium-range weather forecasting is fundamental to Earth system science. Most existing Transformer-based forecasting models adopt vision-centric architectures that neglect the Earth's spherical geometry and zonal periodicity. In addition, conventional autoregressive training is computationally expensive and limits forecast horizons due to error accumulation. To address these challenges, we propose the Shifted Earth Transformer (Searth Transformer), a physics-informed architecture that incorporates zonal periodicity and meridional boundaries into window-based self-attention for physically consistent global information exchange. We further introduce a Relay Autoregressive (RAR) fine-tuning strategy that enables learning long-range atmospheric evolution under constrained memory and computational budgets. Based on these methods, we develop YanTian, a global medium-range weather forecasting model. YanTian achieves higher accuracy than the high-resolution forecast of the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts and performs competitively with state-of-the-art AI models at one-degree resolution, while requiring roughly 200 times lower computational cost than standard autoregressive fine-tuning. Furthermore, YanTian attains a longer skillful forecast lead time for Z500 (10.3 days) than HRES (9 days). Beyond weather forecasting, this work establishes a robust algorithmic foundation for predictive modeling of complex global-scale geophysical circulation systems, offering new pathways for Earth system science.
Feature Complementation Architecture for Visual Place Recognition
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Visual place recognition (VPR) plays a crucial role in robotic localization and navigation. The key challenge lies in constructing feature representations that are robust to environmental changes. Existing methods typically adopt convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or vision Transformers (ViTs) as feature extractors. However, these architectures excel in different aspects -- CNNs are effective at capturing local details. At the same time, ViTs are better suited for modeling global context, making it difficult to leverage the strengths of both. To address this issue, we propose a local-global feature complementation network (LGCN) for VPR which integrates a parallel CNN-ViT hybrid architecture with a dynamic feature fusion module (DFM). The DFM performs dynamic feature fusion through joint modeling of spatial and channel-wise dependencies. Furthermore, to enhance the expressiveness and adaptability of the ViT branch for VPR tasks, we introduce lightweight frequency-to-spatial fusion adapters into the frozen ViT backbone. These adapters enable task-specific adaptation with controlled parameter overhead. Extensive experiments on multiple VPR benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed LGCN consistently outperforms existing approaches in terms of localization accuracy and robustness, validating its effectiveness and generalizability.
TACO: Rethinking Semantic Communications with Task Adaptation and Context Embedding
May 16, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in generative artificial intelligence have introduced groundbreaking approaches to innovating next-generation semantic communication, which prioritizes conveying the meaning of a message rather than merely transmitting raw data. A fundamental challenge in semantic communication lies in accurately identifying and extracting the most critical semantic information while adapting to downstream tasks without degrading performance, particularly when the objective at the receiver may evolve over time. To enable flexible adaptation to multiple tasks at the receiver, this work introduces a novel semantic communication framework, which is capable of jointly capturing task-specific information to enhance downstream task performance and contextual information. Through rigorous experiments on popular image datasets and computer vision tasks, our framework shows promising improvement compared to existing work, including superior performance in downstream tasks, better generalizability, ultra-high bandwidth efficiency, and low reconstruction latency.
Task-Driven Semantic Quantization and Imitation Learning for Goal-Oriented Communications
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Semantic communication marks a new paradigm shift from bit-wise data transmission to semantic information delivery for the purpose of bandwidth reduction. To more effectively carry out specialized downstream tasks at the receiver end, it is crucial to define the most critical semantic message in the data based on the task or goal-oriented features. In this work, we propose a novel goal-oriented communication (GO-COM) framework, namely Goal-Oriented Semantic Variational Autoencoder (GOS-VAE), by focusing on the extraction of the semantics vital to the downstream tasks. Specifically, we adopt a Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder (VQ-VAE) to compress media data at the transmitter side. Instead of targeting the pixel-wise image data reconstruction, we measure the quality-of-service at the receiver end based on a pre-defined task-incentivized model. Moreover, to capture the relevant semantic features in the data reconstruction, imitation learning is adopted to measure the data regeneration quality in terms of goal-oriented semantics. Our experimental results demonstrate the power of imitation learning in characterizing goal-oriented semantics and bandwidth efficiency of our proposed GOS-VAE.
LaMI-GO: Latent Mixture Integration for Goal-Oriented Communications Achieving High Spectrum Efficiency
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:The recent rise of semantic-style communications includes the development of goal-oriented communications (GOCOMs) remarkably efficient multimedia information transmissions. The concept of GO-COMS leverages advanced artificial intelligence (AI) tools to address the rising demand for bandwidth efficiency in applications, such as edge computing and Internet-of-Things (IoT). Unlike traditional communication systems focusing on source data accuracy, GO-COMs provide intelligent message delivery catering to the special needs critical to accomplishing downstream tasks at the receiver. In this work, we present a novel GO-COM framework, namely LaMI-GO that utilizes emerging generative AI for better quality-of-service (QoS) with ultra-high communication efficiency. Specifically, we design our LaMI-GO system backbone based on a latent diffusion model followed by a vector-quantized generative adversarial network (VQGAN) for efficient latent embedding and information representation. The system trains a common feature codebook the receiver side. Our experimental results demonstrate substantial improvement in perceptual quality, accuracy of downstream tasks, and bandwidth consumption over the state-of-the-art GOCOM systems and establish the power of our proposed LaMI-GO communication framework.
Diff-GO$^\text{n}$: Enhancing Diffusion Models for Goal-Oriented Communications
Dec 09, 2024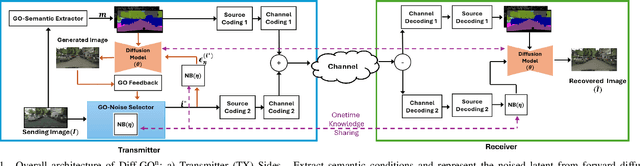
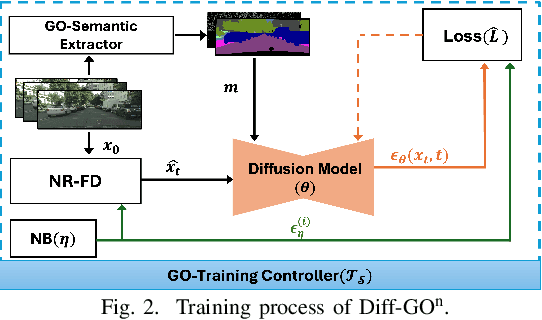
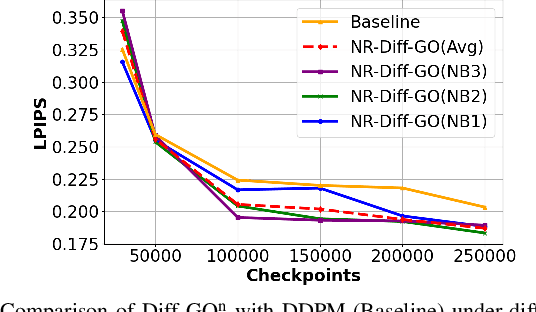

Abstract:The rapid expansion of edge devices and Internet-of-Things (IoT) continues to heighten the demand for data transport under limited spectrum resources. The goal-oriented communications (GO-COM), unlike traditional communication systems designed for bit-level accuracy, prioritizes more critical information for specific application goals at the receiver. To improve the efficiency of generative learning models for GO-COM, this work introduces a novel noise-restricted diffusion-based GO-COM (Diff-GO$^\text{n}$) framework for reducing bandwidth overhead while preserving the media quality at the receiver. Specifically, we propose an innovative Noise-Restricted Forward Diffusion (NR-FD) framework to accelerate model training and reduce the computation burden for diffusion-based GO-COMs by leveraging a pre-sampled pseudo-random noise bank (NB). Moreover, we design an early stopping criterion for improving computational efficiency and convergence speed, allowing high-quality generation in fewer training steps. Our experimental results demonstrate superior perceptual quality of data transmission at a reduced bandwidth usage and lower computation, making Diff-GO$^\text{n}$ well-suited for real-time communications and downstream applications.
Hierarchical Space-Time Attention for Micro-Expression Recognition
May 06, 2024



Abstract:Micro-expression recognition (MER) aims to recognize the short and subtle facial movements from the Micro-expression (ME) video clips, which reveal real emotions. Recent MER methods mostly only utilize special frames from ME video clips or extract optical flow from these special frames. However, they neglect the relationship between movements and space-time, while facial cues are hidden within these relationships. To solve this issue, we propose the Hierarchical Space-Time Attention (HSTA). Specifically, we first process ME video frames and special frames or data parallelly by our cascaded Unimodal Space-Time Attention (USTA) to establish connections between subtle facial movements and specific facial areas. Then, we design Crossmodal Space-Time Attention (CSTA) to achieve a higher-quality fusion for crossmodal data. Finally, we hierarchically integrate USTA and CSTA to grasp the deeper facial cues. Our model emphasizes temporal modeling without neglecting the processing of special data, and it fuses the contents in different modalities while maintaining their respective uniqueness. Extensive experiments on the four benchmarks show the effectiveness of our proposed HSTA. Specifically, compared with the latest method on the CASME3 dataset, it achieves about 3% score improvement in seven-category classification.
Deep Structure and Attention Aware Subspace Clustering
Dec 25, 2023Abstract:Clustering is a fundamental unsupervised representation learning task with wide application in computer vision and pattern recognition. Deep clustering utilizes deep neural networks to learn latent representation, which is suitable for clustering. However, previous deep clustering methods, especially image clustering, focus on the features of the data itself and ignore the relationship between the data, which is crucial for clustering. In this paper, we propose a novel Deep Structure and Attention aware Subspace Clustering (DSASC), which simultaneously considers data content and structure information. We use a vision transformer to extract features, and the extracted features are divided into two parts, structure features, and content features. The two features are used to learn a more efficient subspace structure for spectral clustering. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Our code will be available at https://github.com/cs-whh/DSASC
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge