Weichuan Zhang
Deep learning-based neurodevelopmental assessment in preterm infants
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Preterm infants (born between 28 and 37 weeks of gestation) face elevated risks of neurodevelopmental delays, making early identification crucial for timely intervention. While deep learning-based volumetric segmentation of brain MRI scans offers a promising avenue for assessing neonatal neurodevelopment, achieving accurate segmentation of white matter (WM) and gray matter (GM) in preterm infants remains challenging due to their comparable signal intensities (isointense appearance) on MRI during early brain development. To address this, we propose a novel segmentation neural network, named Hierarchical Dense Attention Network. Our architecture incorporates a 3D spatial-channel attention mechanism combined with an attention-guided dense upsampling strategy to enhance feature discrimination in low-contrast volumetric data. Quantitative experiments demonstrate that our method achieves superior segmentation performance compared to state-of-the-art baselines, effectively tackling the challenge of isointense tissue differentiation. Furthermore, application of our algorithm confirms that WM and GM volumes in preterm infants are significantly lower than those in term infants, providing additional imaging evidence of the neurodevelopmental delays associated with preterm birth. The code is available at: https://github.com/ICL-SUST/HDAN.
Second-order Gaussian directional derivative representations for image high-resolution corner detection
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Corner detection is widely used in various computer vision tasks, such as image matching and 3D reconstruction. Our research indicates that there are theoretical flaws in Zhang et al.'s use of a simple corner model to obtain a series of corner characteristics, as the grayscale information of two adjacent corners can affect each other. In order to address the above issues, a second-order Gaussian directional derivative (SOGDD) filter is used in this work to smooth two typical high-resolution angle models (i.e. END-type and L-type models). Then, the SOGDD representations of these two corner models were derived separately, and many characteristics of high-resolution corners were discovered, which enabled us to demonstrate how to select Gaussian filtering scales to obtain intensity variation information from images, accurately depicting adjacent corners. In addition, a new high-resolution corner detection method for images has been proposed for the first time, which can accurately detect adjacent corner points. The experimental results have verified that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of localization error, robustness to image blur transformation, image matching, and 3D reconstruction.
Feature Complementation Architecture for Visual Place Recognition
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Visual place recognition (VPR) plays a crucial role in robotic localization and navigation. The key challenge lies in constructing feature representations that are robust to environmental changes. Existing methods typically adopt convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or vision Transformers (ViTs) as feature extractors. However, these architectures excel in different aspects -- CNNs are effective at capturing local details. At the same time, ViTs are better suited for modeling global context, making it difficult to leverage the strengths of both. To address this issue, we propose a local-global feature complementation network (LGCN) for VPR which integrates a parallel CNN-ViT hybrid architecture with a dynamic feature fusion module (DFM). The DFM performs dynamic feature fusion through joint modeling of spatial and channel-wise dependencies. Furthermore, to enhance the expressiveness and adaptability of the ViT branch for VPR tasks, we introduce lightweight frequency-to-spatial fusion adapters into the frozen ViT backbone. These adapters enable task-specific adaptation with controlled parameter overhead. Extensive experiments on multiple VPR benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed LGCN consistently outperforms existing approaches in terms of localization accuracy and robustness, validating its effectiveness and generalizability.
Frequency-Adaptive Discrete Cosine-ViT-ResNet Architecture for Sparse-Data Vision
May 28, 2025Abstract:A major challenge in rare animal image classification is the scarcity of data, as many species usually have only a small number of labeled samples. To address this challenge, we designed a hybrid deep-learning framework comprising a novel adaptive DCT preprocessing module, ViT-B16 and ResNet50 backbones, and a Bayesian linear classification head. To our knowledge, we are the first to introduce an adaptive frequency-domain selection mechanism that learns optimal low-, mid-, and high-frequency boundaries suited to the subsequent backbones. Our network first captures image frequency-domain cues via this adaptive DCT partitioning. The adaptively filtered frequency features are then fed into ViT-B16 to model global contextual relationships, while ResNet50 concurrently extracts local, multi-scale spatial representations from the original image. A cross-level fusion strategy seamlessly integrates these frequency- and spatial-domain embeddings, and the fused features are passed through a Bayesian linear classifier to output the final category predictions. On our self-built 50-class wildlife dataset, this approach outperforms conventional CNN and fixed-band DCT pipelines, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy under extreme sample scarcity.
Dynamic Accumulated Attention Map for Interpreting Evolution of Decision-Making in Vision Transformer
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Various Vision Transformer (ViT) models have been widely used for image recognition tasks. However, existing visual explanation methods can not display the attention flow hidden inside the inner structure of ViT models, which explains how the final attention regions are formed inside a ViT for its decision-making. In this paper, a novel visual explanation approach, Dynamic Accumulated Attention Map (DAAM), is proposed to provide a tool that can visualize, for the first time, the attention flow from the top to the bottom through ViT networks. To this end, a novel decomposition module is proposed to construct and store the spatial feature information by unlocking the [class] token generated by the self-attention module of each ViT block. The module can also obtain the channel importance coefficients by decomposing the classification score for supervised ViT models. Because of the lack of classification score in self-supervised ViT models, we propose dimension-wise importance weights to compute the channel importance coefficients. Such spatial features are linearly combined with the corresponding channel importance coefficients, forming the attention map for each block. The dynamic attention flow is revealed by block-wisely accumulating each attention map. The contribution of this work focuses on visualizing the evolution dynamic of the decision-making attention for any intermediate block inside a ViT model by proposing a novel decomposition module and dimension-wise importance weights. The quantitative and qualitative analysis consistently validate the effectiveness and superior capacity of the proposed DAAM for not only interpreting ViT models with the fully-connected layers as the classifier but also self-supervised ViT models. The code is available at https://github.com/ly9802/DynamicAccumulatedAttentionMap.
Neuron Abandoning Attention Flow: Visual Explanation of Dynamics inside CNN Models
Dec 02, 2024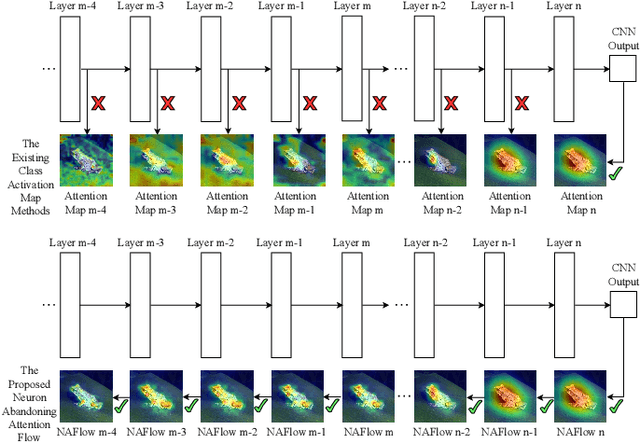
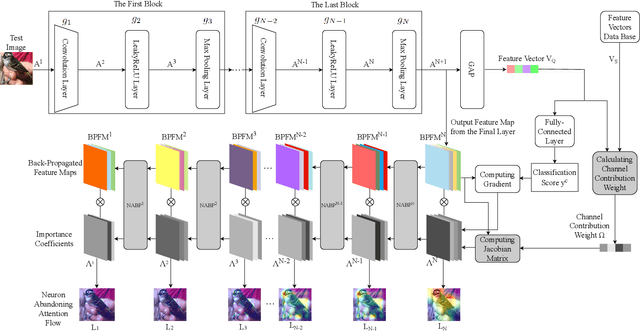
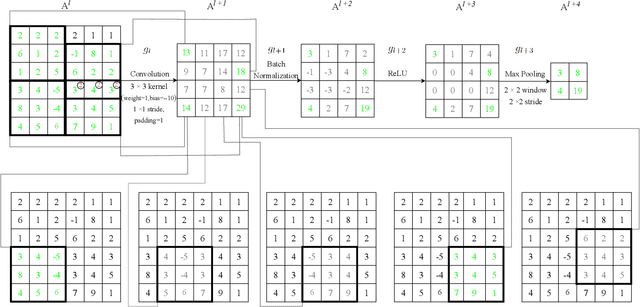
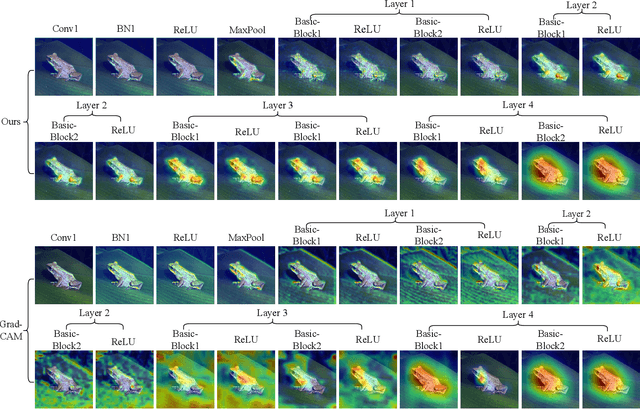
Abstract:In this paper, we present a Neuron Abandoning Attention Flow (NAFlow) method to address the open problem of visually explaining the attention evolution dynamics inside CNNs when making their classification decisions. A novel cascading neuron abandoning back-propagation algorithm is designed to trace neurons in all layers of a CNN that involve in making its prediction to address the problem of significant interference from abandoned neurons. Firstly, a Neuron Abandoning Back-Propagation (NA-BP) module is proposed to generate Back-Propagated Feature Maps (BPFM) by using the inverse function of the intermediate layers of CNN models, on which the neurons not used for decision-making are abandoned. Meanwhile, the cascading NA-BP modules calculate the tensors of importance coefficients which are linearly combined with the tensors of BPFMs to form the NAFlow. Secondly, to be able to visualize attention flow for similarity metric-based CNN models, a new channel contribution weights module is proposed to calculate the importance coefficients via Jacobian Matrix. The effectiveness of the proposed NAFlow is validated on nine widely-used CNN models for various tasks of general image classification, contrastive learning classification, few-shot image classification, and image retrieval.
A novel spatial-frequency domain network for zero-shot incremental learning
Feb 11, 2024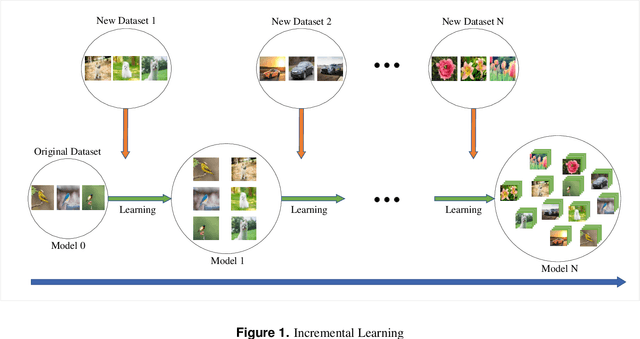
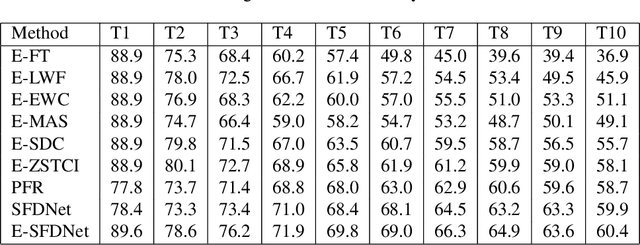
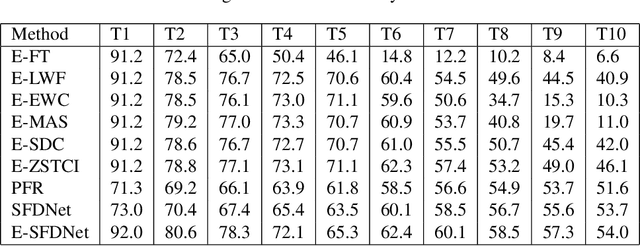
Abstract:Zero-shot incremental learning aims to enable the model to generalize to new classes without forgetting previously learned classes. However, the semantic gap between old and new sample classes can lead to catastrophic forgetting. Additionally, existing algorithms lack capturing significant information from each sample image domain, impairing models' classification performance. Therefore, this paper proposes a novel Spatial-Frequency Domain Network (SFDNet) which contains a Spatial-Frequency Feature Extraction (SFFE) module and Attention Feature Alignment (AFA) module to improve the Zero-Shot Translation for Class Incremental algorithm. Firstly, SFFE module is designed which contains a dual attention mechanism for obtaining salient spatial-frequency feature information. Secondly, a novel feature fusion module is conducted for obtaining fused spatial-frequency domain features. Thirdly, the Nearest Class Mean classifier is utilized to select the most suitable category. Finally, iteration between tasks is performed using the Zero-Shot Translation model. The proposed SFDNet has the ability to effectively extract spatial-frequency feature representation from input images, improve the accuracy of image classification, and fundamentally alleviate catastrophic forgetting. Extensive experiments on the CUB 200-2011 and CIFAR100 datasets demonstrate that our proposed algorithm outperforms state-of-the-art incremental learning algorithms.
Track-before-detect Algorithm based on Cost-reference Particle Filter Bank for Weak Target Detection
Sep 25, 2023



Abstract:Detecting weak target is an important and challenging problem in many applications such as radar, sonar etc. However, conventional detection methods are often ineffective in this case because of low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). This paper presents a track-before-detect (TBD) algorithm based on an improved particle filter, i.e. cost-reference particle filter bank (CRPFB), which turns the problem of target detection to the problem of two-layer hypothesis testing. The first layer is implemented by CRPFB for state estimation of possible target. CRPFB has entirely parallel structure, consisting amounts of cost-reference particle filters with different hypothesized prior information. The second layer is to compare a test metric with a given threshold, which is constructed from the output of the first layer and fits GEV distribution. The performance of our proposed TBD algorithm and the existed TBD algorithms are compared according to the experiments on nonlinear frequency modulated (NLFM) signal detection and tracking. Simulation results show that the proposed TBD algorithm has better performance than the state-of-the-arts in detection, tracking, and time efficiency.
Feature Activation Map: Visual Explanation of Deep Learning Models for Image Classification
Jul 11, 2023
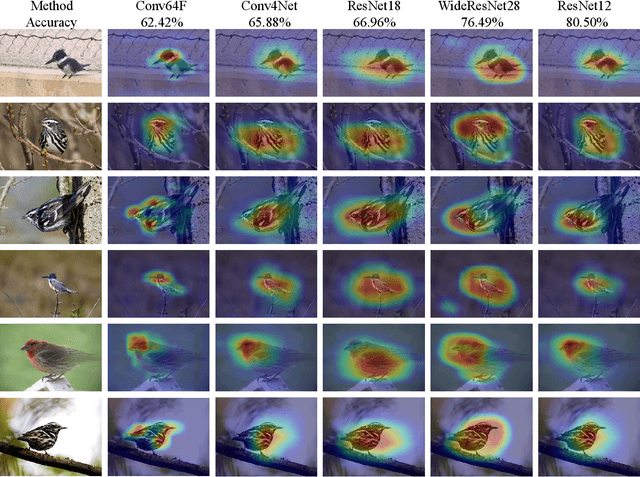
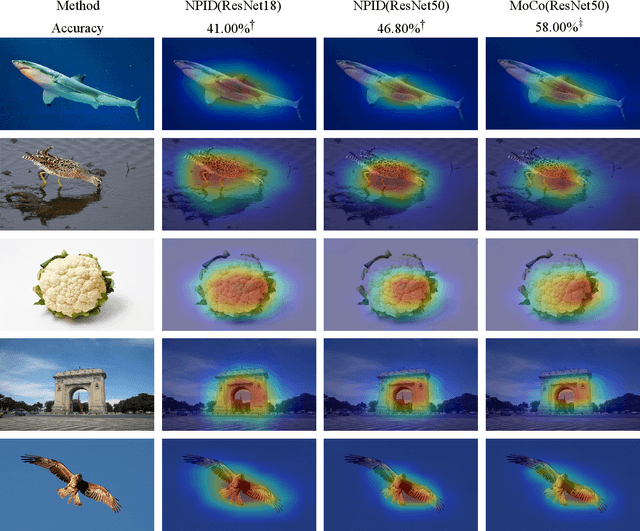
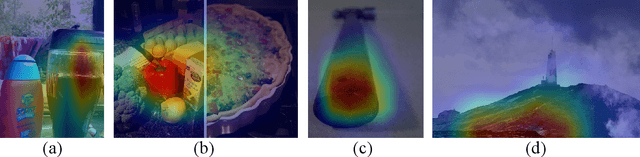
Abstract:Decisions made by convolutional neural networks(CNN) can be understood and explained by visualizing discriminative regions on images. To this end, Class Activation Map (CAM) based methods were proposed as powerful interpretation tools, making the prediction of deep learning models more explainable, transparent, and trustworthy. However, all the CAM-based methods (e.g., CAM, Grad-CAM, and Relevance-CAM) can only be used for interpreting CNN models with fully-connected (FC) layers as a classifier. It is worth noting that many deep learning models classify images without FC layers, e.g., few-shot learning image classification, contrastive learning image classification, and image retrieval tasks. In this work, a post-hoc interpretation tool named feature activation map (FAM) is proposed, which can interpret deep learning models without FC layers as a classifier. In the proposed FAM algorithm, the channel-wise contribution weights are derived from the similarity scores between two image embeddings. The activation maps are linearly combined with the corresponding normalized contribution weights, forming the explanation map for visualization. The quantitative and qualitative experiments conducted on ten deep learning models for few-shot image classification, contrastive learning image classification and image retrieval tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed FAM algorithm.
Automotive Radar Mutual Interference Mitigation Based on Hough Transform in Time-Frequency Domain
Jul 10, 2023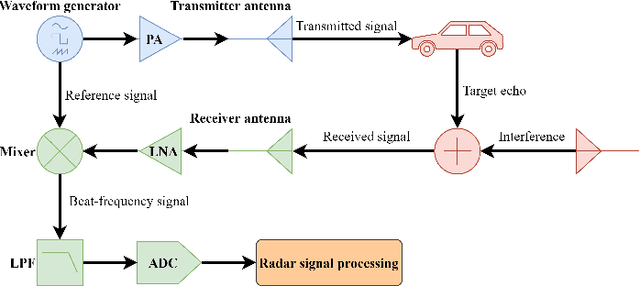

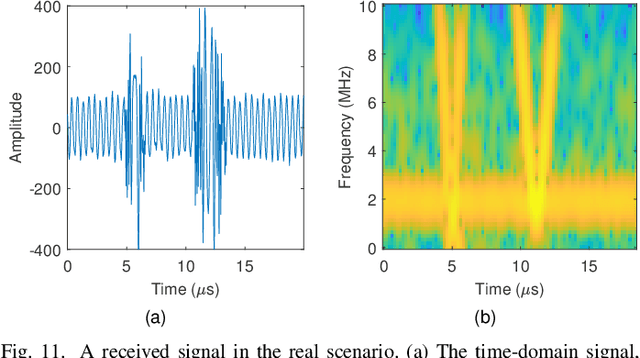
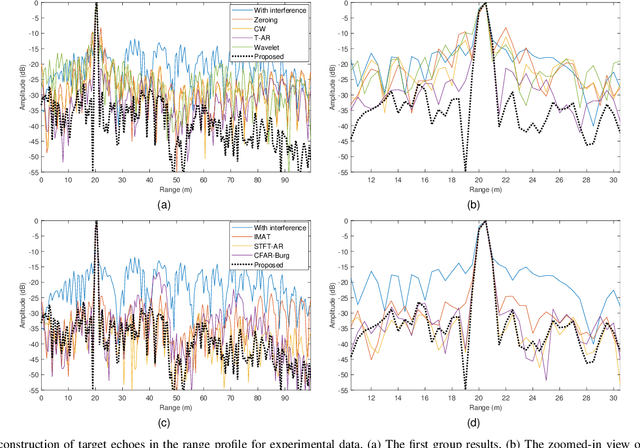
Abstract:With the development of autonomous driving technology, automotive radar has received unprecedented attention due to its day-and-night and all-weather working capability. It is worthwhile to note that more and more vehicles are equipped with automotive radars, resulting in mutual interference between radars. The interference reduces radar target detection performance, making perception information unreliable. In this paper, a novel interference mitigation method based on power-weighted Hough transform is proposed for solving the radar mutual interference and improving the safety of autonomous driving systems. Firstly, the frequency modulation characteristics of interference signals and target echo signals are analyzed, and differences between the two signals are introduced. Secondly, based on the straight line detection technique, the power of the mutual interference signal in time-frequency domain is accumulated, and the accurate position of the interference is located. Finally, the target echo is recovered by autoregressive model. Compared with existing state-of-the-art methods, the proposed method has the ability to retain more useful signals after the interference mitigation, and achieve better interference detection robustness under low signal-to-noise ratio conditions. Simulation experiments and real scenario experiments verify the effectiveness of the proposed method and show its superiority.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge