Ning Li
Exposing and Defending the Achilles' Heel of Video Mixture-of-Experts
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) has demonstrated strong performance in video understanding tasks, yet its adversarial robustness remains underexplored. Existing attack methods often treat MoE as a unified architecture, overlooking the independent and collaborative weaknesses of key components such as routers and expert modules. To fill this gap, we propose Temporal Lipschitz-Guided Attacks (TLGA) to thoroughly investigate component-level vulnerabilities in video MoE models. We first design attacks on the router, revealing its independent weaknesses. Building on this, we introduce Joint Temporal Lipschitz-Guided Attacks (J-TLGA), which collaboratively perturb both routers and experts. This joint attack significantly amplifies adversarial effects and exposes the Achilles' Heel (collaborative weaknesses) of the MoE architecture. Based on these insights, we further propose Joint Temporal Lipschitz Adversarial Training (J-TLAT). J-TLAT performs joint training to further defend against collaborative weaknesses, enhancing component-wise robustness. Our framework is plug-and-play and reduces inference cost by more than 60% compared with dense models. It consistently enhances adversarial robustness across diverse datasets and architectures, effectively mitigating both the independent and collaborative weaknesses of MoE.
Reward-Forcing: Autoregressive Video Generation with Reward Feedback
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:While most prior work in video generation relies on bidirectional architectures, recent efforts have sought to adapt these models into autoregressive variants to support near real-time generation. However, such adaptations often depend heavily on teacher models, which can limit performance, particularly in the absence of a strong autoregressive teacher, resulting in output quality that typically lags behind their bidirectional counterparts. In this paper, we explore an alternative approach that uses reward signals to guide the generation process, enabling more efficient and scalable autoregressive generation. By using reward signals to guide the model, our method simplifies training while preserving high visual fidelity and temporal consistency. Through extensive experiments on standard benchmarks, we find that our approach performs comparably to existing autoregressive models and, in some cases, surpasses similarly sized bidirectional models by avoiding constraints imposed by teacher architectures. For example, on VBench, our method achieves a total score of 84.92, closely matching state-of-the-art autoregressive methods that score 84.31 but require significant heterogeneous distillation.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Explore the Ideology of Deep Learning in ENSO Forecasts
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:The El Ni{~n}o-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) exerts profound influence on global climate variability, yet its prediction remains a grand challenge. Recent advances in deep learning have significantly improved forecasting skill, but the opacity of these models hampers scientific trust and operational deployment. Here, we introduce a mathematically grounded interpretability framework based on bounded variation function. By rescuing the "dead" neurons from the saturation zone of the activation function, we enhance the model's expressive capacity. Our analysis reveals that ENSO predictability emerges dominantly from the tropical Pacific, with contributions from the Indian and Atlantic Oceans, consistent with physical understanding. Controlled experiments affirm the robustness of our method and its alignment with established predictors. Notably, we probe the persistent Spring Predictability Barrier (SPB), finding that despite expanded sensitivity during spring, predictive performance declines-likely due to suboptimal variable selection. These results suggest that incorporating additional ocean-atmosphere variables may help transcend SPB limitations and advance long-range ENSO prediction.
MG-HGNN: A Heterogeneous GNN Framework for Indoor Wi-Fi Fingerprint-Based Localization
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Received signal strength indicator (RSSI) is the primary representation of Wi-Fi fingerprints and serves as a crucial tool for indoor localization. However, existing RSSI-based positioning methods often suffer from reduced accuracy due to environmental complexity and challenges in processing multi-source information. To address these issues, we propose a novel multi-graph heterogeneous GNN framework (MG-HGNN) to enhance spatial awareness and improve positioning performance. In this framework, two graph construction branches perform node and edge embedding, respectively, to generate informative graphs. Subsequently, a heterogeneous graph neural network is employed for graph representation learning, enabling accurate positioning. The MG-HGNN framework introduces the following key innovations: 1) multi-type task-directed graph construction that combines label estimation and feature encoding for richer graph information; 2) a heterogeneous GNN structure that enhances the performance of conventional GNN models. Evaluations on the UJIIndoorLoc and UTSIndoorLoc public datasets demonstrate that MG-HGNN not only achieves superior performance compared to several state-of-the-art methods, but also provides a novel perspective for enhancing GNN-based localization methods. Ablation studies further confirm the rationality and effectiveness of the proposed framework.
Can Agent Conquer Web? Exploring the Frontiers of ChatGPT Atlas Agent in Web Games
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:OpenAI's ChatGPT Atlas introduces new capabilities for web interaction, enabling the model to analyze webpages, process user intents, and execute cursor and keyboard inputs directly within the browser. While its capacity for information retrieval tasks has been demonstrated, its performance in dynamic, interactive environments remains less explored. In this study, we conduct an early evaluation of Atlas's web interaction capabilities using browser-based games as test scenarios, including Google's T-Rex Runner, Sudoku, Flappy Bird, and Stein.world. We employ in-game performance scores as quantitative metrics to assess performance across different task types. Our results show that Atlas performs strongly in logical reasoning tasks like Sudoku, completing puzzles significantly faster than human baselines, but struggles substantially in real-time games requiring precise timing and motor control, often failing to progress beyond initial obstacles. These findings suggest that while Atlas demonstrates capable analytical processing, there remain notable limitations in dynamic web environments requiring real-time interaction. The website of our project can be found at https://atlas-game-eval.github.io.
Synthesize, Retrieve, and Propagate: A Unified Predictive Modeling Framework for Relational Databases
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Relational databases (RDBs) have become the industry standard for storing massive and heterogeneous data. However, despite the widespread use of RDBs across various fields, the inherent structure of relational databases hinders their ability to benefit from flourishing deep learning methods. Previous research has primarily focused on exploiting the unary dependency among multiple tables in a relational database using the primary key - foreign key relationships, either joining multiple tables into a single table or constructing a graph among them, which leaves the implicit composite relations among different tables and a substantial potential of improvement for predictive modeling unexplored. In this paper, we propose SRP, a unified predictive modeling framework that synthesizes features using the unary dependency, retrieves related information to capture the composite dependency, and propagates messages across a constructed graph to learn adjacent patterns for prediction on relation databases. By introducing a new retrieval mechanism into RDB, SRP is designed to fully capture both the unary and the composite dependencies within a relational database, thereby enhancing the receptive field of tabular data prediction. In addition, we conduct a comprehensive analysis on the components of SRP, offering a nuanced understanding of model behaviors and practical guidelines for future applications. Extensive experiments on five real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of SRP and its potential applicability in industrial scenarios. The code is released at https://github.com/NingLi670/SRP.
Efficient Edge LLMs Deployment via HessianAware Quantization and CPU GPU Collaborative
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:With the breakthrough progress of large language models (LLMs) in natural language processing and multimodal tasks, efficiently deploying them on resource-constrained edge devices has become a critical challenge. The Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture enhances model capacity through sparse activation, but faces two major difficulties in practical deployment: (1) The presence of numerous outliers in activation distributions leads to severe degradation in quantization accuracy for both activations and weights, significantly impairing inference performance; (2) Under limited memory, efficient offloading and collaborative inference of expert modules struggle to balance latency and throughput. To address these issues, this paper proposes an efficient MoE edge deployment scheme based on Hessian-Aware Quantization (HAQ) and CPU-GPU collaborative inference. First, by introducing smoothed Hessian matrix quantization, we achieve joint 8-bit quantization of activations and weights, which significantly alleviates the accuracy loss caused by outliers while ensuring efficient implementation on mainstream hardware. Second, we design an expert-level collaborative offloading and inference mechanism, which, combined with expert activation path statistics, enables efficient deployment and scheduling of expert modules between CPU and GPU, greatly reducing memory footprint and inference latency. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our method on mainstream large models such as the OPT series and Mixtral 8*7B: on datasets like Wikitext2 and C4, the inference accuracy of the low-bit quantized model approaches that of the full-precision model, while GPU memory usage is reduced by about 60%, and inference latency is significantly improved.
Latent Video Dataset Distillation
Apr 23, 2025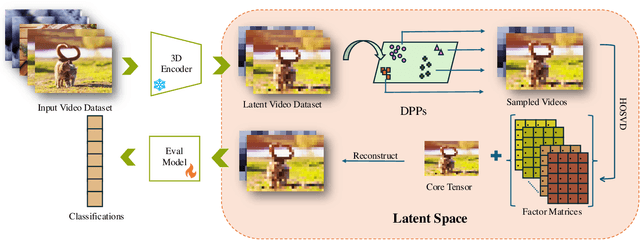

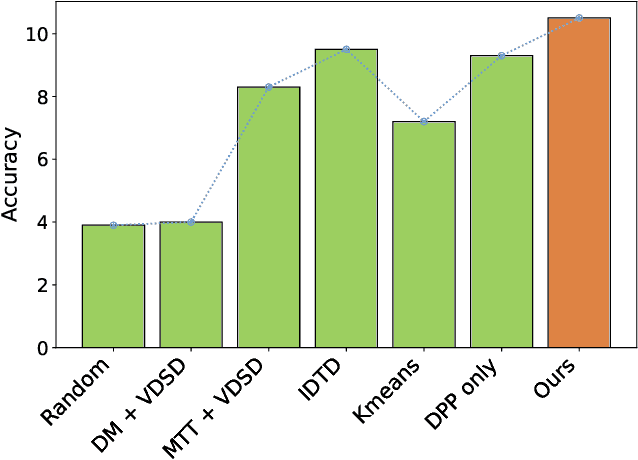

Abstract:Dataset distillation has demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in high-compression scenarios for image datasets. While video datasets inherently contain greater redundancy, existing video dataset distillation methods primarily focus on compression in the pixel space, overlooking advances in the latent space that have been widely adopted in modern text-to-image and text-to-video models. In this work, we bridge this gap by introducing a novel video dataset distillation approach that operates in the latent space using a state-of-the-art variational encoder. Furthermore, we employ a diversity-aware data selection strategy to select both representative and diverse samples. Additionally, we introduce a simple, training-free method to further compress the distilled latent dataset. By combining these techniques, our approach achieves a new state-of-the-art performance in dataset distillation, outperforming prior methods on all datasets, e.g. on HMDB51 IPC 1, we achieve a 2.6% performance increase; on MiniUCF IPC 5, we achieve a 7.8% performance increase.
A Survey of AI Agent Protocols
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of large language models (LLMs) has led to the widespread deployment of LLM agents across diverse industries, including customer service, content generation, data analysis, and even healthcare. However, as more LLM agents are deployed, a major issue has emerged: there is no standard way for these agents to communicate with external tools or data sources. This lack of standardized protocols makes it difficult for agents to work together or scale effectively, and it limits their ability to tackle complex, real-world tasks. A unified communication protocol for LLM agents could change this. It would allow agents and tools to interact more smoothly, encourage collaboration, and triggering the formation of collective intelligence. In this paper, we provide a systematic overview of existing communication protocols for LLM agents. We classify them into four main categories and make an analysis to help users and developers select the most suitable protocols for specific applications. Additionally, we conduct a comparative performance analysis of these protocols across key dimensions such as security, scalability, and latency. Finally, we explore future challenges, such as how protocols can adapt and survive in fast-evolving environments, and what qualities future protocols might need to support the next generation of LLM agent ecosystems. We expect this work to serve as a practical reference for both researchers and engineers seeking to design, evaluate, or integrate robust communication infrastructures for intelligent agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge