Bineng Zhong
UBATrack: Spatio-Temporal State Space Model for General Multi-Modal Tracking
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Multi-modal object tracking has attracted considerable attention by integrating multiple complementary inputs (e.g., thermal, depth, and event data) to achieve outstanding performance. Although current general-purpose multi-modal trackers primarily unify various modal tracking tasks (i.e., RGB-Thermal infrared, RGB-Depth or RGB-Event tracking) through prompt learning, they still overlook the effective capture of spatio-temporal cues. In this work, we introduce a novel multi-modal tracking framework based on a mamba-style state space model, termed UBATrack. Our UBATrack comprises two simple yet effective modules: a Spatio-temporal Mamba Adapter (STMA) and a Dynamic Multi-modal Feature Mixer. The former leverages Mamba's long-sequence modeling capability to jointly model cross-modal dependencies and spatio-temporal visual cues in an adapter-tuning manner. The latter further enhances multi-modal representation capacity across multiple feature dimensions to improve tracking robustness. In this way, UBATrack eliminates the need for costly full-parameter fine-tuning, thereby improving the training efficiency of multi-modal tracking algorithms. Experiments show that UBATrack outperforms state-of-the-art methods on RGB-T, RGB-D, and RGB-E tracking benchmarks, achieving outstanding results on the LasHeR, RGBT234, RGBT210, DepthTrack, VOT-RGBD22, and VisEvent datasets.
Towards Universal Modal Tracking with Online Dense Temporal Token Learning
Jul 27, 2025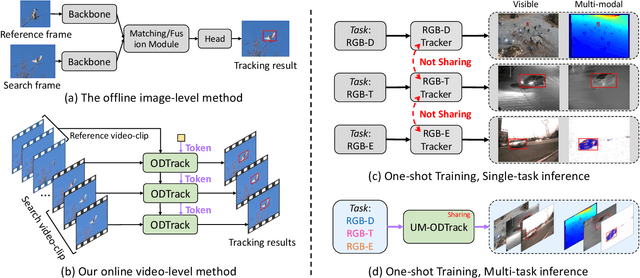
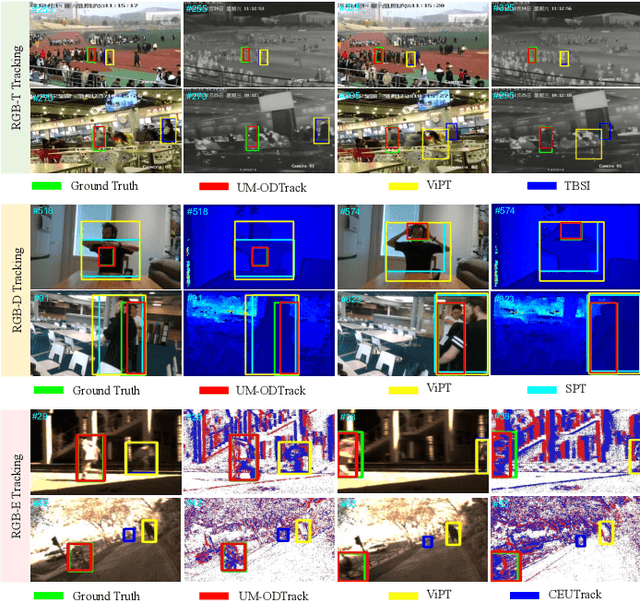


Abstract:We propose a universal video-level modality-awareness tracking model with online dense temporal token learning (called {\modaltracker}). It is designed to support various tracking tasks, including RGB, RGB+Thermal, RGB+Depth, and RGB+Event, utilizing the same model architecture and parameters. Specifically, our model is designed with three core goals: \textbf{Video-level Sampling}. We expand the model's inputs to a video sequence level, aiming to see a richer video context from an near-global perspective. \textbf{Video-level Association}. Furthermore, we introduce two simple yet effective online dense temporal token association mechanisms to propagate the appearance and motion trajectory information of target via a video stream manner. \textbf{Modality Scalable}. We propose two novel gated perceivers that adaptively learn cross-modal representations via a gated attention mechanism, and subsequently compress them into the same set of model parameters via a one-shot training manner for multi-task inference. This new solution brings the following benefits: (i) The purified token sequences can serve as temporal prompts for the inference in the next video frames, whereby previous information is leveraged to guide future inference. (ii) Unlike multi-modal trackers that require independent training, our one-shot training scheme not only alleviates the training burden, but also improves model representation. Extensive experiments on visible and multi-modal benchmarks show that our {\modaltracker} achieves a new \textit{SOTA} performance. The code will be available at https://github.com/GXNU-ZhongLab/ODTrack.
Dynamic Updates for Language Adaptation in Visual-Language Tracking
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:The consistency between the semantic information provided by the multi-modal reference and the tracked object is crucial for visual-language (VL) tracking. However, existing VL tracking frameworks rely on static multi-modal references to locate dynamic objects, which can lead to semantic discrepancies and reduce the robustness of the tracker. To address this issue, we propose a novel vision-language tracking framework, named DUTrack, which captures the latest state of the target by dynamically updating multi-modal references to maintain consistency. Specifically, we introduce a Dynamic Language Update Module, which leverages a large language model to generate dynamic language descriptions for the object based on visual features and object category information. Then, we design a Dynamic Template Capture Module, which captures the regions in the image that highly match the dynamic language descriptions. Furthermore, to ensure the efficiency of description generation, we design an update strategy that assesses changes in target displacement, scale, and other factors to decide on updates. Finally, the dynamic template and language descriptions that record the latest state of the target are used to update the multi-modal references, providing more accurate reference information for subsequent inference and enhancing the robustness of the tracker. DUTrack achieves new state-of-the-art performance on four mainstream vision-language and two vision-only tracking benchmarks, including LaSOT, LaSOT$_{\rm{ext}}$, TNL2K, OTB99-Lang, GOT-10K, and UAV123. Code and models are available at https://github.com/GXNU-ZhongLab/DUTrack.
Similarity-Guided Layer-Adaptive Vision Transformer for UAV Tracking
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Vision transformers (ViTs) have emerged as a popular backbone for visual tracking. However, complete ViT architectures are too cumbersome to deploy for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) tracking which extremely emphasizes efficiency. In this study, we discover that many layers within lightweight ViT-based trackers tend to learn relatively redundant and repetitive target representations. Based on this observation, we propose a similarity-guided layer adaptation approach to optimize the structure of ViTs. Our approach dynamically disables a large number of representation-similar layers and selectively retains only a single optimal layer among them, aiming to achieve a better accuracy-speed trade-off. By incorporating this approach into existing ViTs, we tailor previously complete ViT architectures into an efficient similarity-guided layer-adaptive framework, namely SGLATrack, for real-time UAV tracking. Extensive experiments on six tracking benchmarks verify the effectiveness of the proposed approach, and show that our SGLATrack achieves a state-of-the-art real-time speed while maintaining competitive tracking precision. Codes and models are available at https://github.com/GXNU-ZhongLab/SGLATrack.
Adaptive Perception for Unified Visual Multi-modal Object Tracking
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:Recently, many multi-modal trackers prioritize RGB as the dominant modality, treating other modalities as auxiliary, and fine-tuning separately various multi-modal tasks. This imbalance in modality dependence limits the ability of methods to dynamically utilize complementary information from each modality in complex scenarios, making it challenging to fully perceive the advantages of multi-modal. As a result, a unified parameter model often underperforms in various multi-modal tracking tasks. To address this issue, we propose APTrack, a novel unified tracker designed for multi-modal adaptive perception. Unlike previous methods, APTrack explores a unified representation through an equal modeling strategy. This strategy allows the model to dynamically adapt to various modalities and tasks without requiring additional fine-tuning between different tasks. Moreover, our tracker integrates an adaptive modality interaction (AMI) module that efficiently bridges cross-modality interactions by generating learnable tokens. Experiments conducted on five diverse multi-modal datasets (RGBT234, LasHeR, VisEvent, DepthTrack, and VOT-RGBD2022) demonstrate that APTrack not only surpasses existing state-of-the-art unified multi-modal trackers but also outperforms trackers designed for specific multi-modal tasks.
Less is More: Token Context-aware Learning for Object Tracking
Jan 01, 2025Abstract:Recently, several studies have shown that utilizing contextual information to perceive target states is crucial for object tracking. They typically capture context by incorporating multiple video frames. However, these naive frame-context methods fail to consider the importance of each patch within a reference frame, making them susceptible to noise and redundant tokens, which deteriorates tracking performance. To address this challenge, we propose a new token context-aware tracking pipeline named LMTrack, designed to automatically learn high-quality reference tokens for efficient visual tracking. Embracing the principle of Less is More, the core idea of LMTrack is to analyze the importance distribution of all reference tokens, where important tokens are collected, continually attended to, and updated. Specifically, a novel Token Context Memory module is designed to dynamically collect high-quality spatio-temporal information of a target in an autoregressive manner, eliminating redundant background tokens from the reference frames. Furthermore, an effective Unidirectional Token Attention mechanism is designed to establish dependencies between reference tokens and search frame, enabling robust cross-frame association and target localization. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our tracker, achieving state-of-the-art results on tracking benchmarks such as GOT-10K, TrackingNet, and LaSOT.
Exploiting Multimodal Spatial-temporal Patterns for Video Object Tracking
Dec 20, 2024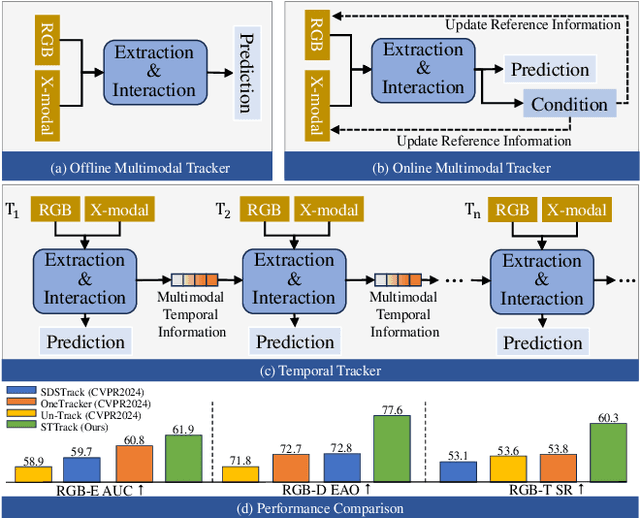
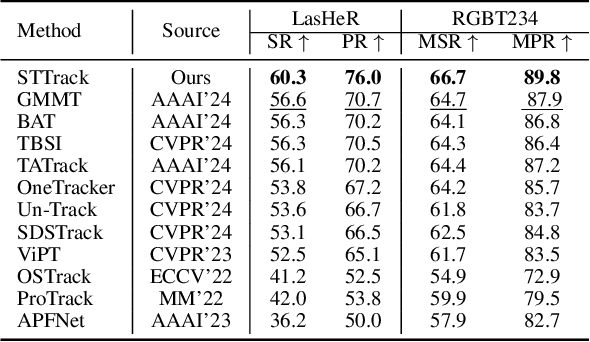
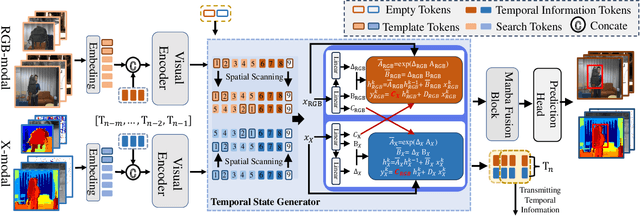
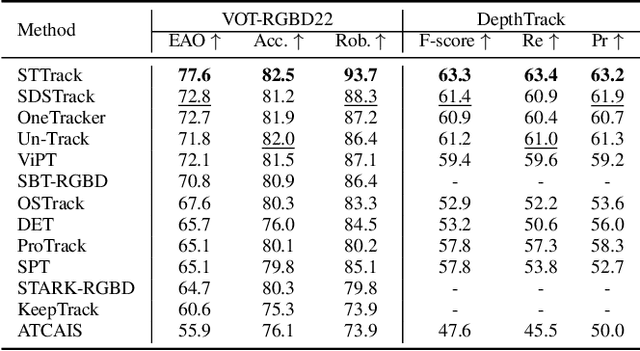
Abstract:Multimodal tracking has garnered widespread attention as a result of its ability to effectively address the inherent limitations of traditional RGB tracking. However, existing multimodal trackers mainly focus on the fusion and enhancement of spatial features or merely leverage the sparse temporal relationships between video frames. These approaches do not fully exploit the temporal correlations in multimodal videos, making it difficult to capture the dynamic changes and motion information of targets in complex scenarios. To alleviate this problem, we propose a unified multimodal spatial-temporal tracking approach named STTrack. In contrast to previous paradigms that solely relied on updating reference information, we introduced a temporal state generator (TSG) that continuously generates a sequence of tokens containing multimodal temporal information. These temporal information tokens are used to guide the localization of the target in the next time state, establish long-range contextual relationships between video frames, and capture the temporal trajectory of the target. Furthermore, at the spatial level, we introduced the mamba fusion and background suppression interactive (BSI) modules. These modules establish a dual-stage mechanism for coordinating information interaction and fusion between modalities. Extensive comparisons on five benchmark datasets illustrate that STTrack achieves state-of-the-art performance across various multimodal tracking scenarios. Code is available at: https://github.com/NJU-PCALab/STTrack.
Robust Tracking via Mamba-based Context-aware Token Learning
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:How to make a good trade-off between performance and computational cost is crucial for a tracker. However, current famous methods typically focus on complicated and time-consuming learning that combining temporal and appearance information by input more and more images (or features). Consequently, these methods not only increase the model's computational source and learning burden but also introduce much useless and potentially interfering information. To alleviate the above issues, we propose a simple yet robust tracker that separates temporal information learning from appearance modeling and extracts temporal relations from a set of representative tokens rather than several images (or features). Specifically, we introduce one track token for each frame to collect the target's appearance information in the backbone. Then, we design a mamba-based Temporal Module for track tokens to be aware of context by interacting with other track tokens within a sliding window. This module consists of a mamba layer with autoregressive characteristic and a cross-attention layer with strong global perception ability, ensuring sufficient interaction for track tokens to perceive the appearance changes and movement trends of the target. Finally, track tokens serve as a guidance to adjust the appearance feature for the final prediction in the head. Experiments show our method is effective and achieves competitive performance on multiple benchmarks at a real-time speed. Code and trained models will be available at https://github.com/GXNU-ZhongLab/TemTrack.
MambaLCT: Boosting Tracking via Long-term Context State Space Model
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Effectively constructing context information with long-term dependencies from video sequences is crucial for object tracking. However, the context length constructed by existing work is limited, only considering object information from adjacent frames or video clips, leading to insufficient utilization of contextual information. To address this issue, we propose MambaLCT, which constructs and utilizes target variation cues from the first frame to the current frame for robust tracking. First, a novel unidirectional Context Mamba module is designed to scan frame features along the temporal dimension, gathering target change cues throughout the entire sequence. Specifically, target-related information in frame features is compressed into a hidden state space through selective scanning mechanism. The target information across the entire video is continuously aggregated into target variation cues. Next, we inject the target change cues into the attention mechanism, providing temporal information for modeling the relationship between the template and search frames. The advantage of MambaLCT is its ability to continuously extend the length of the context, capturing complete target change cues, which enhances the stability and robustness of the tracker. Extensive experiments show that long-term context information enhances the model's ability to perceive targets in complex scenarios. MambaLCT achieves new SOTA performance on six benchmarks while maintaining real-time running speeds.
Autoregressive Queries for Adaptive Tracking with Spatio-TemporalTransformers
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:The rich spatio-temporal information is crucial to capture the complicated target appearance variations in visual tracking. However, most top-performing tracking algorithms rely on many hand-crafted components for spatio-temporal information aggregation. Consequently, the spatio-temporal information is far away from being fully explored. To alleviate this issue, we propose an adaptive tracker with spatio-temporal transformers (named AQATrack), which adopts simple autoregressive queries to effectively learn spatio-temporal information without many hand-designed components. Firstly, we introduce a set of learnable and autoregressive queries to capture the instantaneous target appearance changes in a sliding window fashion. Then, we design a novel attention mechanism for the interaction of existing queries to generate a new query in current frame. Finally, based on the initial target template and learnt autoregressive queries, a spatio-temporal information fusion module (STM) is designed for spatiotemporal formation aggregation to locate a target object. Benefiting from the STM, we can effectively combine the static appearance and instantaneous changes to guide robust tracking. Extensive experiments show that our method significantly improves the tracker's performance on six popular tracking benchmarks: LaSOT, LaSOText, TrackingNet, GOT-10k, TNL2K, and UAV123.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge