Hongxun Yao
SfMamba: Efficient Source-Free Domain Adaptation via Selective Scan Modeling
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) tackles the critical challenge of adapting source-pretrained models to unlabeled target domains without access to source data, overcoming data privacy and storage limitations in real-world applications. However, existing SFDA approaches struggle with the trade-off between perception field and computational efficiency in domain-invariant feature learning. Recently, Mamba has offered a promising solution through its selective scan mechanism, which enables long-range dependency modeling with linear complexity. However, the Visual Mamba (i.e., VMamba) remains limited in capturing channel-wise frequency characteristics critical for domain alignment and maintaining spatial robustness under significant domain shifts. To address these, we propose a framework called SfMamba to fully explore the stable dependency in source-free model transfer. SfMamba introduces Channel-wise Visual State-Space block that enables channel-sequence scanning for domain-invariant feature extraction. In addition, SfMamba involves a Semantic-Consistent Shuffle strategy that disrupts background patch sequences in 2D selective scan while preserving prediction consistency to mitigate error accumulation. Comprehensive evaluations across multiple benchmarks show that SfMamba achieves consistently stronger performance than existing methods while maintaining favorable parameter efficiency, offering a practical solution for SFDA. Our code is available at https://github.com/chenxi52/SfMamba.
Limb-Aware Virtual Try-On Network with Progressive Clothing Warping
Mar 18, 2025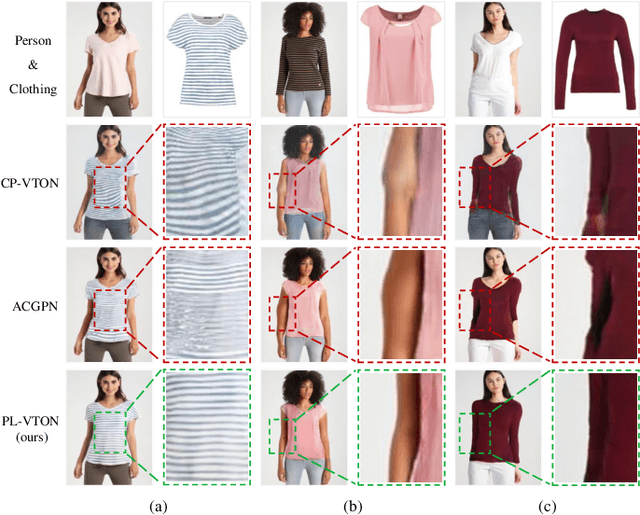
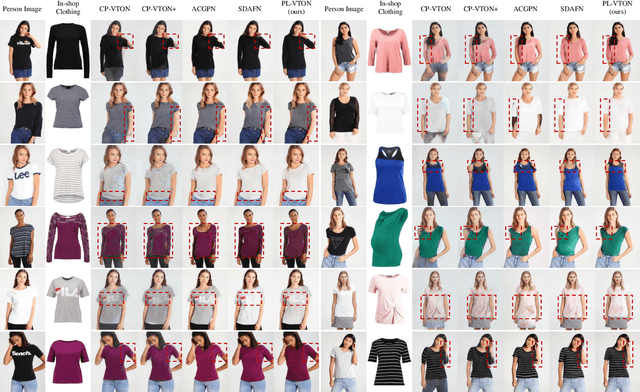


Abstract:Image-based virtual try-on aims to transfer an in-shop clothing image to a person image. Most existing methods adopt a single global deformation to perform clothing warping directly, which lacks fine-grained modeling of in-shop clothing and leads to distorted clothing appearance. In addition, existing methods usually fail to generate limb details well because they are limited by the used clothing-agnostic person representation without referring to the limb textures of the person image. To address these problems, we propose Limb-aware Virtual Try-on Network named PL-VTON, which performs fine-grained clothing warping progressively and generates high-quality try-on results with realistic limb details. Specifically, we present Progressive Clothing Warping (PCW) that explicitly models the location and size of in-shop clothing and utilizes a two-stage alignment strategy to progressively align the in-shop clothing with the human body. Moreover, a novel gravity-aware loss that considers the fit of the person wearing clothing is adopted to better handle the clothing edges. Then, we design Person Parsing Estimator (PPE) with a non-limb target parsing map to semantically divide the person into various regions, which provides structural constraints on the human body and therefore alleviates texture bleeding between clothing and body regions. Finally, we introduce Limb-aware Texture Fusion (LTF) that focuses on generating realistic details in limb regions, where a coarse try-on result is first generated by fusing the warped clothing image with the person image, then limb textures are further fused with the coarse result under limb-aware guidance to refine limb details. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our PL-VTON outperforms the state-of-the-art methods both qualitatively and quantitatively.
* Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (TMM). The code is available at https://github.com/aipixel/PL-VTONv2
PEBench: A Fictitious Dataset to Benchmark Machine Unlearning for Multimodal Large Language Models
Mar 16, 2025



Abstract:In recent years, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable advancements in tasks such as visual question answering, visual understanding, and reasoning. However, this impressive progress relies on vast amounts of data collected from the internet, raising significant concerns about privacy and security. To address these issues, machine unlearning (MU) has emerged as a promising solution, enabling the removal of specific knowledge from an already trained model without requiring retraining from scratch. Although MU for MLLMs has gained attention, current evaluations of its efficacy remain incomplete, and the underlying problem is often poorly defined, which hinders the development of strategies for creating more secure and trustworthy systems. To bridge this gap, we introduce a benchmark, named PEBench, which includes a dataset of personal entities and corresponding general event scenes, designed to comprehensively assess the performance of MU for MLLMs. Through PEBench, we aim to provide a standardized and robust framework to advance research in secure and privacy-preserving multimodal models. We benchmarked 6 MU methods, revealing their strengths and limitations, and shedding light on key challenges and opportunities for MU in MLLMs.
MPBench: A Comprehensive Multimodal Reasoning Benchmark for Process Errors Identification
Mar 16, 2025



Abstract:Reasoning is an essential capacity for large language models (LLMs) to address complex tasks, where the identification of process errors is vital for improving this ability. Recently, process-level reward models (PRMs) were proposed to provide step-wise rewards that facilitate reinforcement learning and data production during training and guide LLMs toward correct steps during inference, thereby improving reasoning accuracy. However, existing benchmarks of PRMs are text-based and focus on error detection, neglecting other scenarios like reasoning search. To address this gap, we introduce MPBench, a comprehensive, multi-task, multimodal benchmark designed to systematically assess the effectiveness of PRMs in diverse scenarios. MPBench employs three evaluation paradigms, each targeting a specific role of PRMs in the reasoning process: (1) Step Correctness, which assesses the correctness of each intermediate reasoning step; (2) Answer Aggregation, which aggregates multiple solutions and selects the best one; and (3) Reasoning Process Search, which guides the search for optimal reasoning steps during inference. Through these paradigms, MPBench makes comprehensive evaluations and provides insights into the development of multimodal PRMs.
Bridge then Begin Anew: Generating Target-relevant Intermediate Model for Source-free Visual Emotion Adaptation
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Visual emotion recognition (VER), which aims at understanding humans' emotional reactions toward different visual stimuli, has attracted increasing attention. Given the subjective and ambiguous characteristics of emotion, annotating a reliable large-scale dataset is hard. For reducing reliance on data labeling, domain adaptation offers an alternative solution by adapting models trained on labeled source data to unlabeled target data. Conventional domain adaptation methods require access to source data. However, due to privacy concerns, source emotional data may be inaccessible. To address this issue, we propose an unexplored task: source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) for VER, which does not have access to source data during the adaptation process. To achieve this, we propose a novel framework termed Bridge then Begin Anew (BBA), which consists of two steps: domain-bridged model generation (DMG) and target-related model adaptation (TMA). First, the DMG bridges cross-domain gaps by generating an intermediate model, avoiding direct alignment between two VER datasets with significant differences. Then, the TMA begins training the target model anew to fit the target structure, avoiding the influence of source-specific knowledge. Extensive experiments are conducted on six SFDA settings for VER. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of BBA, which achieves remarkable performance gains compared with state-of-the-art SFDA methods and outperforms representative unsupervised domain adaptation approaches.
FrozenSeg: Harmonizing Frozen Foundation Models for Open-Vocabulary Segmentation
Sep 05, 2024



Abstract:Open-vocabulary segmentation poses significant challenges, as it requires segmenting and recognizing objects across an open set of categories in unconstrained environments. Building on the success of powerful vision-language (ViL) foundation models, such as CLIP, recent efforts sought to harness their zero-short capabilities to recognize unseen categories. Despite notable performance improvements, these models still encounter the critical issue of generating precise mask proposals for unseen categories and scenarios, resulting in inferior segmentation performance eventually. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel approach, FrozenSeg, designed to integrate spatial knowledge from a localization foundation model (e.g., SAM) and semantic knowledge extracted from a ViL model (e.g., CLIP), in a synergistic framework. Taking the ViL model's visual encoder as the feature backbone, we inject the space-aware feature into the learnable queries and CLIP features within the transformer decoder. In addition, we devise a mask proposal ensemble strategy for further improving the recall rate and mask quality. To fully exploit pre-trained knowledge while minimizing training overhead, we freeze both foundation models, focusing optimization efforts solely on a lightweight transformer decoder for mask proposal generation-the performance bottleneck. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FrozenSeg advances state-of-the-art results across various segmentation benchmarks, trained exclusively on COCO panoptic data, and tested in a zero-shot manner. Code is available at https://github.com/chenxi52/FrozenSeg.
Multi-source Domain Adaptation for Panoramic Semantic Segmentation
Aug 29, 2024



Abstract:Panoramic semantic segmentation has received widespread attention recently due to its comprehensive 360\degree field of view. However, labeling such images demands greater resources compared to pinhole images. As a result, many unsupervised domain adaptation methods for panoramic semantic segmentation have emerged, utilizing real pinhole images or low-cost synthetic panoramic images. But, the segmentation model lacks understanding of the panoramic structure when only utilizing real pinhole images, and it lacks perception of real-world scenes when only adopting synthetic panoramic images. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a new task of multi-source domain adaptation for panoramic semantic segmentation, aiming to utilize both real pinhole and synthetic panoramic images in the source domains, enabling the segmentation model to perform well on unlabeled real panoramic images in the target domain. Further, we propose Deformation Transform Aligner for Panoramic Semantic Segmentation (DTA4PASS), which converts all pinhole images in the source domains into panoramic-like images, and then aligns the converted source domains with the target domain. Specifically, DTA4PASS consists of two main components: Unpaired Semantic Morphing (USM) and Distortion Gating Alignment (DGA). Firstly, in USM, the Semantic Dual-view Discriminator (SDD) assists in training the diffeomorphic deformation network, enabling the effective transformation of pinhole images without paired panoramic views. Secondly, DGA assigns pinhole-like and panoramic-like features to each image by gating, and aligns these two features through uncertainty estimation. DTA4PASS outperforms the previous state-of-the-art methods by 1.92% and 2.19% on the outdoor and indoor multi-source domain adaptation scenarios, respectively. The source code will be released.
Blur-aware Spatio-temporal Sparse Transformer for Video Deblurring
Jun 11, 2024



Abstract:Video deblurring relies on leveraging information from other frames in the video sequence to restore the blurred regions in the current frame. Mainstream approaches employ bidirectional feature propagation, spatio-temporal transformers, or a combination of both to extract information from the video sequence. However, limitations in memory and computational resources constraints the temporal window length of the spatio-temporal transformer, preventing the extraction of longer temporal contextual information from the video sequence. Additionally, bidirectional feature propagation is highly sensitive to inaccurate optical flow in blurry frames, leading to error accumulation during the propagation process. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{BSSTNet}, \textbf{B}lur-aware \textbf{S}patio-temporal \textbf{S}parse \textbf{T}ransformer Network. It introduces the blur map, which converts the originally dense attention into a sparse form, enabling a more extensive utilization of information throughout the entire video sequence. Specifically, BSSTNet (1) uses a longer temporal window in the transformer, leveraging information from more distant frames to restore the blurry pixels in the current frame. (2) introduces bidirectional feature propagation guided by blur maps, which reduces error accumulation caused by the blur frame. The experimental results demonstrate the proposed BSSTNet outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on the GoPro and DVD datasets.
Dataset Growth
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Deep learning benefits from the growing abundance of available data. Meanwhile, efficiently dealing with the growing data scale has become a challenge. Data publicly available are from different sources with various qualities, and it is impractical to do manual cleaning against noise and redundancy given today's data scale. There are existing techniques for cleaning/selecting the collected data. However, these methods are mainly proposed for offline settings that target one of the cleanness and redundancy problems. In practice, data are growing exponentially with both problems. This leads to repeated data curation with sub-optimal efficiency. To tackle this challenge, we propose InfoGrowth, an efficient online algorithm for data cleaning and selection, resulting in a growing dataset that keeps up to date with awareness of cleanliness and diversity. InfoGrowth can improve data quality/efficiency on both single-modal and multi-modal tasks, with an efficient and scalable design. Its framework makes it practical for real-world data engines.
Uncertainty-Aware Pseudo-Label Filtering for Source-Free Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Mar 17, 2024



Abstract:Source-free unsupervised domain adaptation (SFUDA) aims to enable the utilization of a pre-trained source model in an unlabeled target domain without access to source data. Self-training is a way to solve SFUDA, where confident target samples are iteratively selected as pseudo-labeled samples to guide target model learning. However, prior heuristic noisy pseudo-label filtering methods all involve introducing extra models, which are sensitive to model assumptions and may introduce additional errors or mislabeling. In this work, we propose a method called Uncertainty-aware Pseudo-label-filtering Adaptation (UPA) to efficiently address this issue in a coarse-to-fine manner. Specially, we first introduce a sample selection module named Adaptive Pseudo-label Selection (APS), which is responsible for filtering noisy pseudo labels. The APS utilizes a simple sample uncertainty estimation method by aggregating knowledge from neighboring samples and confident samples are selected as clean pseudo-labeled. Additionally, we incorporate Class-Aware Contrastive Learning (CACL) to mitigate the memorization of pseudo-label noise by learning robust pair-wise representation supervised by pseudo labels. Through extensive experiments conducted on three widely used benchmarks, we demonstrate that our proposed method achieves competitive performance on par with state-of-the-art SFUDA methods. Code is available at https://github.com/chenxi52/UPA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge