Wenbo Tang
Bridge then Begin Anew: Generating Target-relevant Intermediate Model for Source-free Visual Emotion Adaptation
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Visual emotion recognition (VER), which aims at understanding humans' emotional reactions toward different visual stimuli, has attracted increasing attention. Given the subjective and ambiguous characteristics of emotion, annotating a reliable large-scale dataset is hard. For reducing reliance on data labeling, domain adaptation offers an alternative solution by adapting models trained on labeled source data to unlabeled target data. Conventional domain adaptation methods require access to source data. However, due to privacy concerns, source emotional data may be inaccessible. To address this issue, we propose an unexplored task: source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) for VER, which does not have access to source data during the adaptation process. To achieve this, we propose a novel framework termed Bridge then Begin Anew (BBA), which consists of two steps: domain-bridged model generation (DMG) and target-related model adaptation (TMA). First, the DMG bridges cross-domain gaps by generating an intermediate model, avoiding direct alignment between two VER datasets with significant differences. Then, the TMA begins training the target model anew to fit the target structure, avoiding the influence of source-specific knowledge. Extensive experiments are conducted on six SFDA settings for VER. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of BBA, which achieves remarkable performance gains compared with state-of-the-art SFDA methods and outperforms representative unsupervised domain adaptation approaches.
Multi-source Domain Adaptation for Panoramic Semantic Segmentation
Aug 29, 2024



Abstract:Panoramic semantic segmentation has received widespread attention recently due to its comprehensive 360\degree field of view. However, labeling such images demands greater resources compared to pinhole images. As a result, many unsupervised domain adaptation methods for panoramic semantic segmentation have emerged, utilizing real pinhole images or low-cost synthetic panoramic images. But, the segmentation model lacks understanding of the panoramic structure when only utilizing real pinhole images, and it lacks perception of real-world scenes when only adopting synthetic panoramic images. Therefore, in this paper, we propose a new task of multi-source domain adaptation for panoramic semantic segmentation, aiming to utilize both real pinhole and synthetic panoramic images in the source domains, enabling the segmentation model to perform well on unlabeled real panoramic images in the target domain. Further, we propose Deformation Transform Aligner for Panoramic Semantic Segmentation (DTA4PASS), which converts all pinhole images in the source domains into panoramic-like images, and then aligns the converted source domains with the target domain. Specifically, DTA4PASS consists of two main components: Unpaired Semantic Morphing (USM) and Distortion Gating Alignment (DGA). Firstly, in USM, the Semantic Dual-view Discriminator (SDD) assists in training the diffeomorphic deformation network, enabling the effective transformation of pinhole images without paired panoramic views. Secondly, DGA assigns pinhole-like and panoramic-like features to each image by gating, and aligns these two features through uncertainty estimation. DTA4PASS outperforms the previous state-of-the-art methods by 1.92% and 2.19% on the outdoor and indoor multi-source domain adaptation scenarios, respectively. The source code will be released.
LLMI3D: Empowering LLM with 3D Perception from a Single 2D Image
Aug 14, 2024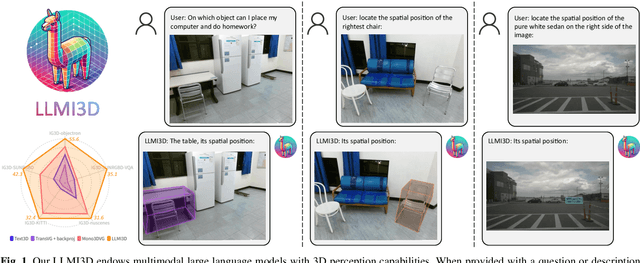
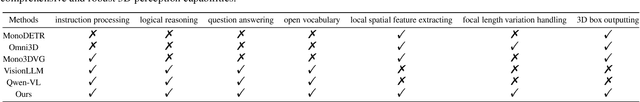
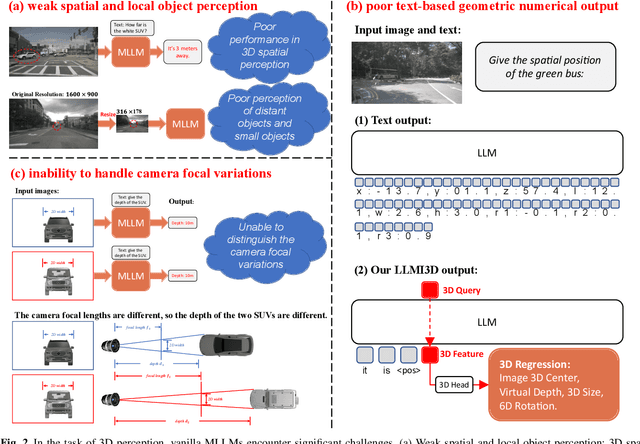

Abstract:Recent advancements in autonomous driving, augmented reality, robotics, and embodied intelligence have necessitated 3D perception algorithms. However, current 3D perception methods, particularly small models, struggle with processing logical reasoning, question-answering, and handling open scenario categories. On the other hand, generative multimodal large language models (MLLMs) excel in general capacity but underperform in 3D tasks, due to weak spatial and local object perception, poor text-based geometric numerical output, and inability to handle camera focal variations. To address these challenges, we propose the following solutions: Spatial-Enhanced Local Feature Mining for better spatial feature extraction, 3D Query Token-Derived Info Decoding for precise geometric regression, and Geometry Projection-Based 3D Reasoning for handling camera focal length variations. We employ parameter-efficient fine-tuning for a pre-trained MLLM and develop LLMI3D, a powerful 3D perception MLLM. Additionally, we have constructed the IG3D dataset, which provides fine-grained descriptions and question-answer annotations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our LLMI3D achieves state-of-the-art performance, significantly outperforming existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge