Chen Zhao
SAGE: Benchmarking and Improving Retrieval for Deep Research Agents
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Deep research agents have emerged as powerful systems for addressing complex queries. Meanwhile, LLM-based retrievers have demonstrated strong capability in following instructions or reasoning. This raises a critical question: can LLM-based retrievers effectively contribute to deep research agent workflows? To investigate this, we introduce SAGE, a benchmark for scientific literature retrieval comprising 1,200 queries across four scientific domains, with a 200,000 paper retrieval corpus.We evaluate six deep research agents and find that all systems struggle with reasoning-intensive retrieval. Using DR Tulu as backbone, we further compare BM25 and LLM-based retrievers (i.e., ReasonIR and gte-Qwen2-7B-instruct) as alternative search tools. Surprisingly, BM25 significantly outperforms LLM-based retrievers by approximately 30%, as existing agents generate keyword-oriented sub-queries. To improve performance, we propose a corpus-level test-time scaling framework that uses LLMs to augment documents with metadata and keywords, making retrieval easier for off-the-shelf retrievers. This yields 8% and 2% gains on short-form and open-ended questions, respectively.
Factuality on Demand: Controlling the Factuality-Informativeness Trade-off in Text Generation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) encode knowledge with varying degrees of confidence. When responding to queries, models face an inherent trade-off: they can generate responses that are less informative but highly factual, or more informative but potentially less accurate. Different applications demand different balances between informativeness and factuality. We introduce Factuality-Controlled Generation (FCG), a framework that enables users to specify factuality constraints alongside their queries. We propose to evaluate FCG performance on two dimensions: adherence to factuality constraints and response informativeness. We propose to train models on the FCG task using synthetic data, and show that our synthetic training significantly improves models' ability to both respect factuality requirements and maintain informativeness in their outputs.
Beyond Single-shot Writing: Deep Research Agents are Unreliable at Multi-turn Report Revision
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Existing benchmarks for Deep Research Agents (DRAs) treat report generation as a single-shot writing task, which fundamentally diverges from how human researchers iteratively draft and revise reports via self-reflection or peer feedback. Whether DRAs can reliably revise reports with user feedback remains unexplored. We introduce Mr Dre, an evaluation suite that establishes multi-turn report revision as a new evaluation axis for DRAs. Mr Dre consists of (1) a unified long-form report evaluation protocol spanning comprehensiveness, factuality, and presentation, and (2) a human-verified feedback simulation pipeline for multi-turn revision. Our analysis of five diverse DRAs reveals a critical limitation: while agents can address most user feedback, they also regress on 16-27% of previously covered content and citation quality. Over multiple revision turns, even the best-performing agents leave significant headroom, as they continue to disrupt content outside the feedback's scope and fail to preserve earlier edits. We further show that these issues are not easily resolvable through inference-time fixes such as prompt engineering and a dedicated sub-agent for report revision.
YOLO-IOD: Towards Real Time Incremental Object Detection
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Current methods for incremental object detection (IOD) primarily rely on Faster R-CNN or DETR series detectors; however, these approaches do not accommodate the real-time YOLO detection frameworks. In this paper, we first identify three primary types of knowledge conflicts that contribute to catastrophic forgetting in YOLO-based incremental detectors: foreground-background confusion, parameter interference, and misaligned knowledge distillation. Subsequently, we introduce YOLO-IOD, a real-time Incremental Object Detection (IOD) framework that is constructed upon the pretrained YOLO-World model, facilitating incremental learning via a stage-wise parameter-efficient fine-tuning process. Specifically, YOLO-IOD encompasses three principal components: 1) Conflict-Aware Pseudo-Label Refinement (CPR), which mitigates the foreground-background confusion by leveraging the confidence levels of pseudo labels and identifying potential objects relevant to future tasks. 2) Importancebased Kernel Selection (IKS), which identifies and updates the pivotal convolution kernels pertinent to the current task during the current learning stage. 3) Cross-Stage Asymmetric Knowledge Distillation (CAKD), which addresses the misaligned knowledge distillation conflict by transmitting the features of the student target detector through the detection heads of both the previous and current teacher detectors, thereby facilitating asymmetric distillation between existing and newly introduced categories. We further introduce LoCo COCO, a more realistic benchmark that eliminates data leakage across stages. Experiments on both conventional and LoCo COCO benchmarks show that YOLO-IOD achieves superior performance with minimal forgetting.
Anatomy Guided Coronary Artery Segmentation from CCTA Using Spatial Frequency Joint Modeling
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Accurate coronary artery segmentation from coronary computed tomography angiography is essential for quantitative coronary analysis and clinical decision support. Nevertheless, reliable segmentation remains challenging because of small vessel calibers, complex branching, blurred boundaries, and myocardial interference. We propose a coronary artery segmentation framework that integrates myocardial anatomical priors, structure aware feature encoding, and three dimensional wavelet inverse wavelet transformations. Myocardial priors and residual attention based feature enhancement are incorporated during encoding to strengthen coronary structure representation. Wavelet inverse wavelet based downsampling and upsampling enable joint spatial frequency modeling and preserve multi scale structural consistency, while a multi scale feature fusion module integrates semantic and geometric information in the decoding stage. The model is trained and evaluated on the public ImageCAS dataset using a 3D overlapping patch based strategy with a 7:1:2 split for training, validation, and testing. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves a Dice coefficient of 0.8082, Sensitivity of 0.7946, Precision of 0.8471, and an HD95 of 9.77 mm, outperforming several mainstream segmentation models. Ablation studies further confirm the complementary contributions of individual components. The proposed method enables more stable and consistent coronary artery segmentation under complex geometric conditions, providing reliable segmentation results for subsequent coronary structure analysis tasks.
$β$-CLIP: Text-Conditioned Contrastive Learning for Multi-Granular Vision-Language Alignment
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:CLIP achieves strong zero-shot image-text retrieval by aligning global vision and text representations, yet it falls behind on fine-grained tasks even when fine-tuned on long, detailed captions. In this work, we propose $β$-CLIP, a multi-granular text-conditioned contrastive learning framework designed to achieve hierarchical alignment between multiple textual granularities-from full captions to sentences and phrases-and their corresponding visual regions. For each level of granularity, $β$-CLIP utilizes cross-attention to dynamically pool image patches, producing contextualized visual embeddings. To address the semantic overlap inherent in this hierarchy, we introduce the $β$-Contextualized Contrastive Alignment Loss ($β$-CAL). This objective parameterizes the trade-off between strict query-specific matching and relaxed intra-image contextualization, supporting both soft Cross-Entropy and hard Binary Cross-Entropy formulations. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that $β$-CLIP significantly improves dense alignment: achieving 91.8% T2I 92.3% I2T at R@1 on Urban1K and 30.9% on FG-OVD (Hard), setting state-of-the-art among methods trained without hard negatives. $β$-CLIP establishes a robust, adaptive baseline for dense vision-language correspondence. The code and models are released at https://github.com/fzohra/B-CLIP.
Blood Pressure Prediction for Coronary Artery Disease Diagnosis using Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography
Dec 11, 2025



Abstract:Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) based simulation of coronary blood flow provides valuable hemodynamic markers, such as pressure gradients, for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD). However, CFD is computationally expensive, time-consuming, and difficult to integrate into large-scale clinical workflows. These limitations restrict the availability of labeled hemodynamic data for training AI models and hinder broad adoption of non-invasive, physiology based CAD assessment. To address these challenges, we develop an end to end pipeline that automates coronary geometry extraction from coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), streamlines simulation data generation, and enables efficient learning of coronary blood pressure distributions. The pipeline reduces the manual burden associated with traditional CFD workflows while producing consistent training data. We further introduce a diffusion-based regression model designed to predict coronary blood pressure directly from CCTA derived features, bypassing the need for slow CFD computation during inference. Evaluated on a dataset of simulated coronary hemodynamics, the proposed model achieves state of the art performance, with an R2 of 64.42%, a root mean squared error of 0.0974, and a normalized RMSE of 0.154, outperforming several baseline approaches. This work provides a scalable and accessible framework for rapid, non-invasive blood pressure prediction to support CAD diagnosis.
SkillGen: Learning Domain Skills for In-Context Sequential Decision Making
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly applied to sequential decision-making through in-context learning (ICL), yet their effectiveness is highly sensitive to prompt quality. Effective prompts should meet three principles: focus on decision-critical information, provide step-level granularity, and minimize reliance on expert annotations through label efficiency. However, existing ICL methods often fail to satisfy all three criteria simultaneously. Motivated by these challenges, we introduce SkillGen, a skill-based ICL framework for structured sequential reasoning. It constructs an action-centric, domain-level graph from sampled trajectories, identifies high-utility actions via temporal-difference credit assignment, and retrieves step-wise skills to generate fine-grained, context-aware prompts. We further present a theoretical analysis showing that focusing on high-utility segments supports task identifiability and informs more effective ICL prompt design. Experiments on ALFWorld, BabyAI, and ScienceWorld, using both open-source and proprietary LLMs, show that SkillGen achieves consistent gains, improving progress rate by 5.9%-16.5% on average across models.
Out-of-Distribution Detection with Positive and Negative Prompt Supervision Using Large Language Models
Nov 14, 2025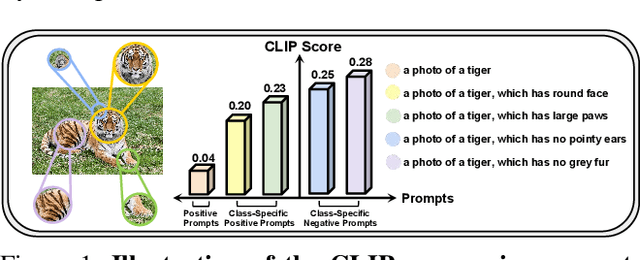
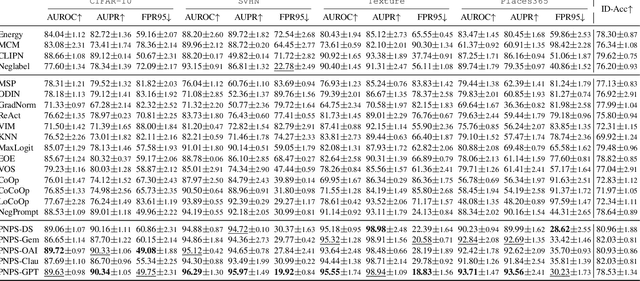
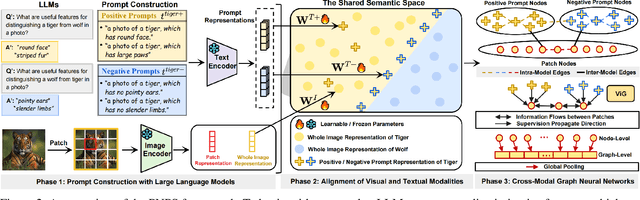
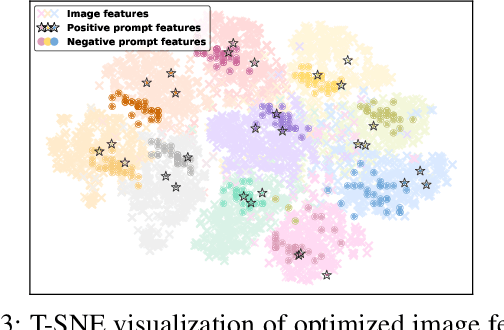
Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection is committed to delineating the classification boundaries between in-distribution (ID) and OOD images. Recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable OOD detection performance by integrating both visual and textual modalities. In this context, negative prompts are introduced to emphasize the dissimilarity between image features and prompt content. However, these prompts often include a broad range of non-ID features, which may result in suboptimal outcomes due to the capture of overlapping or misleading information. To address this issue, we propose Positive and Negative Prompt Supervision, which encourages negative prompts to capture inter-class features and transfers this semantic knowledge to the visual modality to enhance OOD detection performance. Our method begins with class-specific positive and negative prompts initialized by large language models (LLMs). These prompts are subsequently optimized, with positive prompts focusing on features within each class, while negative prompts highlight features around category boundaries. Additionally, a graph-based architecture is employed to aggregate semantic-aware supervision from the optimized prompt representations and propagate it to the visual branch, thereby enhancing the performance of the energy-based OOD detector. Extensive experiments on two benchmarks, CIFAR-100 and ImageNet-1K, across eight OOD datasets and five different LLMs, demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines.
Exploring the Feasibility of End-to-End Large Language Model as a Compiler
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:In recent years, end-to-end Large Language Model (LLM) technology has shown substantial advantages across various domains. As critical system software and infrastructure, compilers are responsible for transforming source code into target code. While LLMs have been leveraged to assist in compiler development and maintenance, their potential as an end-to-end compiler remains largely unexplored. This paper explores the feasibility of LLM as a Compiler (LaaC) and its future directions. We designed the CompilerEval dataset and framework specifically to evaluate the capabilities of mainstream LLMs in source code comprehension and assembly code generation. In the evaluation, we analyzed various errors, explored multiple methods to improve LLM-generated code, and evaluated cross-platform compilation capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that LLMs exhibit basic capabilities as compilers but currently achieve low compilation success rates. By optimizing prompts, scaling up the model, and incorporating reasoning methods, the quality of assembly code generated by LLMs can be significantly enhanced. Based on these findings, we maintain an optimistic outlook for LaaC and propose practical architectural designs and future research directions. We believe that with targeted training, knowledge-rich prompts, and specialized infrastructure, LaaC has the potential to generate high-quality assembly code and drive a paradigm shift in the field of compilation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge