Kaisiyuan Wang
iDiT-HOI: Inpainting-based Hand Object Interaction Reenactment via Video Diffusion Transformer
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Digital human video generation is gaining traction in fields like education and e-commerce, driven by advancements in head-body animation and lip-syncing technologies. However, realistic Hand-Object Interaction (HOI) - the complex dynamics between human hands and objects - continues to pose challenges. Generating natural and believable HOI reenactments is difficult due to issues such as occlusion between hands and objects, variations in object shapes and orientations, and the necessity for precise physical interactions, and importantly, the ability to generalize to unseen humans and objects. This paper presents a novel framework iDiT-HOI that enables in-the-wild HOI reenactment generation. Specifically, we propose a unified inpainting-based token process method, called Inp-TPU, with a two-stage video diffusion transformer (DiT) model. The first stage generates a key frame by inserting the designated object into the hand region, providing a reference for subsequent frames. The second stage ensures temporal coherence and fluidity in hand-object interactions. The key contribution of our method is to reuse the pretrained model's context perception capabilities without introducing additional parameters, enabling strong generalization to unseen objects and scenarios, and our proposed paradigm naturally supports long video generation. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing methods, particularly in challenging real-world scenes, offering enhanced realism and more seamless hand-object interactions.
AudCast: Audio-Driven Human Video Generation by Cascaded Diffusion Transformers
Mar 25, 2025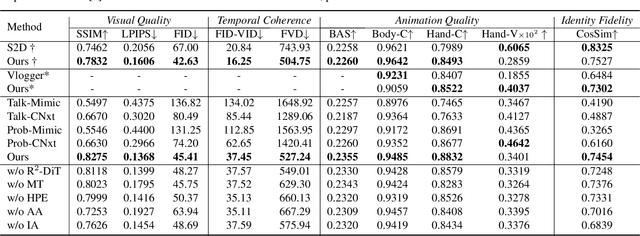
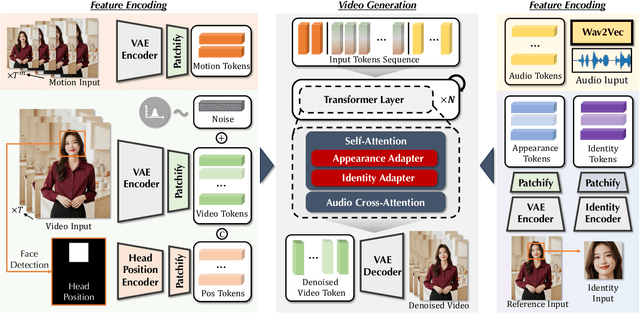
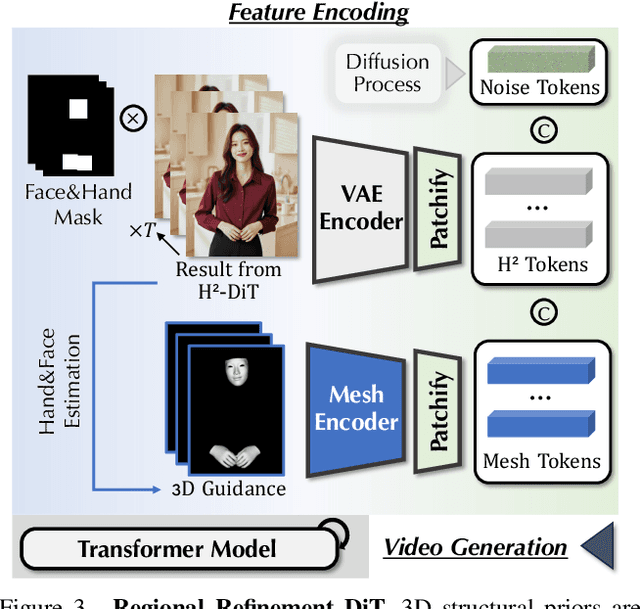

Abstract:Despite the recent progress of audio-driven video generation, existing methods mostly focus on driving facial movements, leading to non-coherent head and body dynamics. Moving forward, it is desirable yet challenging to generate holistic human videos with both accurate lip-sync and delicate co-speech gestures w.r.t. given audio. In this work, we propose AudCast, a generalized audio-driven human video generation framework adopting a cascade Diffusion-Transformers (DiTs) paradigm, which synthesizes holistic human videos based on a reference image and a given audio. 1) Firstly, an audio-conditioned Holistic Human DiT architecture is proposed to directly drive the movements of any human body with vivid gesture dynamics. 2) Then to enhance hand and face details that are well-knownly difficult to handle, a Regional Refinement DiT leverages regional 3D fitting as the bridge to reform the signals, producing the final results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework generates high-fidelity audio-driven holistic human videos with temporal coherence and fine facial and hand details. Resources can be found at https://guanjz20.github.io/projects/AudCast.
Cosh-DiT: Co-Speech Gesture Video Synthesis via Hybrid Audio-Visual Diffusion Transformers
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Co-speech gesture video synthesis is a challenging task that requires both probabilistic modeling of human gestures and the synthesis of realistic images that align with the rhythmic nuances of speech. To address these challenges, we propose Cosh-DiT, a Co-speech gesture video system with hybrid Diffusion Transformers that perform audio-to-motion and motion-to-video synthesis using discrete and continuous diffusion modeling, respectively. First, we introduce an audio Diffusion Transformer (Cosh-DiT-A) to synthesize expressive gesture dynamics synchronized with speech rhythms. To capture upper body, facial, and hand movement priors, we employ vector-quantized variational autoencoders (VQ-VAEs) to jointly learn their dependencies within a discrete latent space. Then, for realistic video synthesis conditioned on the generated speech-driven motion, we design a visual Diffusion Transformer (Cosh-DiT-V) that effectively integrates spatial and temporal contexts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework consistently generates lifelike videos with expressive facial expressions and natural, smooth gestures that align seamlessly with speech.
TALK-Act: Enhance Textural-Awareness for 2D Speaking Avatar Reenactment with Diffusion Model
Oct 14, 2024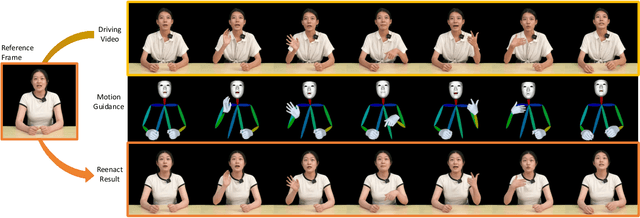
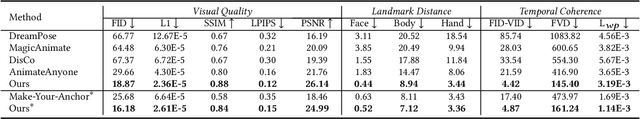
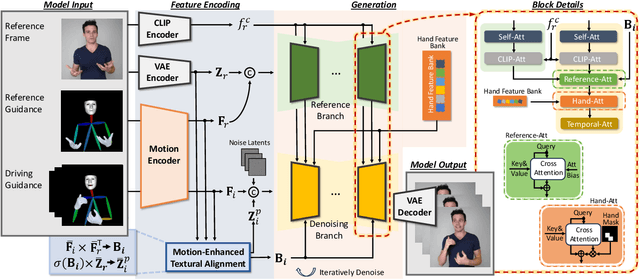
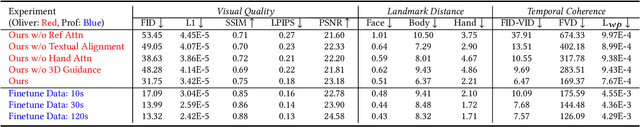
Abstract:Recently, 2D speaking avatars have increasingly participated in everyday scenarios due to the fast development of facial animation techniques. However, most existing works neglect the explicit control of human bodies. In this paper, we propose to drive not only the faces but also the torso and gesture movements of a speaking figure. Inspired by recent advances in diffusion models, we propose the Motion-Enhanced Textural-Aware ModeLing for SpeaKing Avatar Reenactment (TALK-Act) framework, which enables high-fidelity avatar reenactment from only short footage of monocular video. Our key idea is to enhance the textural awareness with explicit motion guidance in diffusion modeling. Specifically, we carefully construct 2D and 3D structural information as intermediate guidance. While recent diffusion models adopt a side network for control information injection, they fail to synthesize temporally stable results even with person-specific fine-tuning. We propose a Motion-Enhanced Textural Alignment module to enhance the bond between driving and target signals. Moreover, we build a Memory-based Hand-Recovering module to help with the difficulties in hand-shape preserving. After pre-training, our model can achieve high-fidelity 2D avatar reenactment with only 30 seconds of person-specific data. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed framework. Resources can be found at https://guanjz20.github.io/projects/TALK-Act.
ReSyncer: Rewiring Style-based Generator for Unified Audio-Visually Synced Facial Performer
Aug 06, 2024



Abstract:Lip-syncing videos with given audio is the foundation for various applications including the creation of virtual presenters or performers. While recent studies explore high-fidelity lip-sync with different techniques, their task-orientated models either require long-term videos for clip-specific training or retain visible artifacts. In this paper, we propose a unified and effective framework ReSyncer, that synchronizes generalized audio-visual facial information. The key design is revisiting and rewiring the Style-based generator to efficiently adopt 3D facial dynamics predicted by a principled style-injected Transformer. By simply re-configuring the information insertion mechanisms within the noise and style space, our framework fuses motion and appearance with unified training. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ReSyncer not only produces high-fidelity lip-synced videos according to audio, but also supports multiple appealing properties that are suitable for creating virtual presenters and performers, including fast personalized fine-tuning, video-driven lip-syncing, the transfer of speaking styles, and even face swapping. Resources can be found at https://guanjz20.github.io/projects/ReSyncer.
AVI-Talking: Learning Audio-Visual Instructions for Expressive 3D Talking Face Generation
Feb 25, 2024Abstract:While considerable progress has been made in achieving accurate lip synchronization for 3D speech-driven talking face generation, the task of incorporating expressive facial detail synthesis aligned with the speaker's speaking status remains challenging. Our goal is to directly leverage the inherent style information conveyed by human speech for generating an expressive talking face that aligns with the speaking status. In this paper, we propose AVI-Talking, an Audio-Visual Instruction system for expressive Talking face generation. This system harnesses the robust contextual reasoning and hallucination capability offered by Large Language Models (LLMs) to instruct the realistic synthesis of 3D talking faces. Instead of directly learning facial movements from human speech, our two-stage strategy involves the LLMs first comprehending audio information and generating instructions implying expressive facial details seamlessly corresponding to the speech. Subsequently, a diffusion-based generative network executes these instructions. This two-stage process, coupled with the incorporation of LLMs, enhances model interpretability and provides users with flexibility to comprehend instructions and specify desired operations or modifications. Extensive experiments showcase the effectiveness of our approach in producing vivid talking faces with expressive facial movements and consistent emotional status.
ObjectSDF++: Improved Object-Compositional Neural Implicit Surfaces
Aug 17, 2023Abstract:In recent years, neural implicit surface reconstruction has emerged as a popular paradigm for multi-view 3D reconstruction. Unlike traditional multi-view stereo approaches, the neural implicit surface-based methods leverage neural networks to represent 3D scenes as signed distance functions (SDFs). However, they tend to disregard the reconstruction of individual objects within the scene, which limits their performance and practical applications. To address this issue, previous work ObjectSDF introduced a nice framework of object-composition neural implicit surfaces, which utilizes 2D instance masks to supervise individual object SDFs. In this paper, we propose a new framework called ObjectSDF++ to overcome the limitations of ObjectSDF. First, in contrast to ObjectSDF whose performance is primarily restricted by its converted semantic field, the core component of our model is an occlusion-aware object opacity rendering formulation that directly volume-renders object opacity to be supervised with instance masks. Second, we design a novel regularization term for object distinction, which can effectively mitigate the issue that ObjectSDF may result in unexpected reconstruction in invisible regions due to the lack of constraint to prevent collisions. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that our novel framework not only produces superior object reconstruction results but also significantly improves the quality of scene reconstruction. Code and more resources can be found in \url{https://qianyiwu.github.io/objectsdf++}
StyleSync: High-Fidelity Generalized and Personalized Lip Sync in Style-based Generator
May 09, 2023



Abstract:Despite recent advances in syncing lip movements with any audio waves, current methods still struggle to balance generation quality and the model's generalization ability. Previous studies either require long-term data for training or produce a similar movement pattern on all subjects with low quality. In this paper, we propose StyleSync, an effective framework that enables high-fidelity lip synchronization. We identify that a style-based generator would sufficiently enable such a charming property on both one-shot and few-shot scenarios. Specifically, we design a mask-guided spatial information encoding module that preserves the details of the given face. The mouth shapes are accurately modified by audio through modulated convolutions. Moreover, our design also enables personalized lip-sync by introducing style space and generator refinement on only limited frames. Thus the identity and talking style of a target person could be accurately preserved. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in producing high-fidelity results on a variety of scenes. Resources can be found at https://hangz-nju-cuhk.github.io/projects/StyleSync.
Make Your Brief Stroke Real and Stereoscopic: 3D-Aware Simplified Sketch to Portrait Generation
Feb 14, 2023



Abstract:Creating the photo-realistic version of people sketched portraits is useful to various entertainment purposes. Existing studies only generate portraits in the 2D plane with fixed views, making the results less vivid. In this paper, we present Stereoscopic Simplified Sketch-to-Portrait (SSSP), which explores the possibility of creating Stereoscopic 3D-aware portraits from simple contour sketches by involving 3D generative models. Our key insight is to design sketch-aware constraints that can fully exploit the prior knowledge of a tri-plane-based 3D-aware generative model. Specifically, our designed region-aware volume rendering strategy and global consistency constraint further enhance detail correspondences during sketch encoding. Moreover, in order to facilitate the usage of layman users, we propose a Contour-to-Sketch module with vector quantized representations, so that easily drawn contours can directly guide the generation of 3D portraits. Extensive comparisons show that our method generates high-quality results that match the sketch. Our usability study verifies that our system is greatly preferred by user.
Masked Lip-Sync Prediction by Audio-Visual Contextual Exploitation in Transformers
Dec 09, 2022



Abstract:Previous studies have explored generating accurately lip-synced talking faces for arbitrary targets given audio conditions. However, most of them deform or generate the whole facial area, leading to non-realistic results. In this work, we delve into the formulation of altering only the mouth shapes of the target person. This requires masking a large percentage of the original image and seamlessly inpainting it with the aid of audio and reference frames. To this end, we propose the Audio-Visual Context-Aware Transformer (AV-CAT) framework, which produces accurate lip-sync with photo-realistic quality by predicting the masked mouth shapes. Our key insight is to exploit desired contextual information provided in audio and visual modalities thoroughly with delicately designed Transformers. Specifically, we propose a convolution-Transformer hybrid backbone and design an attention-based fusion strategy for filling the masked parts. It uniformly attends to the textural information on the unmasked regions and the reference frame. Then the semantic audio information is involved in enhancing the self-attention computation. Additionally, a refinement network with audio injection improves both image and lip-sync quality. Extensive experiments validate that our model can generate high-fidelity lip-synced results for arbitrary subjects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge