Jianfei Cai
FlashBlock: Attention Caching for Efficient Long-Context Block Diffusion
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Generating long-form content, such as minute-long videos and extended texts, is increasingly important for modern generative models. Block diffusion improves inference efficiency via KV caching and block-wise causal inference and has been widely adopted in diffusion language models and video generation. However, in long-context settings, block diffusion still incurs substantial overhead from repeatedly computing attention over a growing KV cache. We identify an underexplored property of block diffusion: cross-step redundancy of attention within a block. Our analysis shows that attention outputs from tokens outside the current block remain largely stable across diffusion steps, while block-internal attention varies significantly. Based on this observation, we propose FlashBlock, a cached block-external attention mechanism that reuses stable attention output, reducing attention computation and KV cache access without modifying the diffusion process. Moreover, FlashBlock is orthogonal to sparse attention and can be combined as a complementary residual reuse strategy, substantially improving model accuracy under aggressive sparsification. Experiments on diffusion language models and video generation demonstrate up to 1.44$\times$ higher token throughput and up to 1.6$\times$ reduction in attention time, with negligible impact on generation quality. Project page: https://caesarhhh.github.io/FlashBlock/.
Gradient-Aligned Calibration for Post-Training Quantization of Diffusion Models
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Diffusion models have shown remarkable performance in image synthesis by progressively estimating a smooth transition from a Gaussian distribution of noise to a real image. Unfortunately, their practical deployment is limited by slow inference speed, high memory usage, and the computational demands of the noise estimation process. Post-training quantization (PTQ) emerges as a promising solution to accelerate sampling and reduce memory overhead for diffusion models. Existing PTQ methods for diffusion models typically apply uniform weights to calibration samples across timesteps, which is sub-optimal since data at different timesteps may contribute differently to the diffusion process. Additionally, due to varying activation distributions and gradients across timesteps, a uniform quantization approach is sub-optimal. Each timestep requires a different gradient direction for optimal quantization, and treating them equally can lead to conflicting gradients that degrade performance. In this paper, we propose a novel PTQ method that addresses these challenges by assigning appropriate weights to calibration samples. Specifically, our approach learns to assign optimal weights to calibration samples to align the quantized model's gradients across timesteps, facilitating the quantization process. Extensive experiments on CIFAR-10, LSUN-Bedrooms, and ImageNet demonstrate the superiority of our method compared to other PTQ methods for diffusion models.
Omni2Sound: Towards Unified Video-Text-to-Audio Generation
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Training a unified model integrating video-to-audio (V2A), text-to-audio (T2A), and joint video-text-to-audio (VT2A) generation offers significant application flexibility, yet faces two unexplored foundational challenges: (1) the scarcity of high-quality audio captions with tight A-V-T alignment, leading to severe semantic conflict between multimodal conditions, and (2) cross-task and intra-task competition, manifesting as an adverse V2A-T2A performance trade-off and modality bias in the VT2A task. First, to address data scarcity, we introduce SoundAtlas, a large-scale dataset (470k pairs) that significantly outperforms existing benchmarks and even human experts in quality. Powered by a novel agentic pipeline, it integrates Vision-to-Language Compression to mitigate visual bias of MLLMs, a Junior-Senior Agent Handoff for a 5 times cost reduction, and rigorous Post-hoc Filtering to ensure fidelity. Consequently, SoundAtlas delivers semantically rich and temporally detailed captions with tight V-A-T alignment. Second, we propose Omni2Sound, a unified VT2A diffusion model supporting flexible input modalities. To resolve the inherent cross-task and intra-task competition, we design a three-stage multi-task progressive training schedule that converts cross-task competition into joint optimization and mitigates modality bias in the VT2A task, maintaining both audio-visual alignment and off-screen audio generation faithfulness. Finally, we construct VGGSound-Omni, a comprehensive benchmark for unified evaluation, including challenging off-screen tracks. With a standard DiT backbone, Omni2Sound achieves unified SOTA performance across all three tasks within a single model, demonstrating strong generalization across benchmarks with heterogeneous input conditions. The project page is at https://swapforward.github.io/Omni2Sound.
Rethinking Output Alignment For 1-bit Post-Training Quantization of Large Language Models
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) deliver strong performance across a wide range of NLP tasks, but their massive sizes hinder deployment on resource-constrained devices. To reduce their computational and memory burden, various compression techniques have been proposed, including quantization, pruning, and knowledge distillation. Among these, post-training quantization (PTQ) is widely adopted for its efficiency, as it requires no retraining and only a small dataset for calibration, enabling low-cost deployment. Recent advances for post-training quantization have demonstrated that even sub-4-bit methods can maintain most of the original model performance. However, 1-bit quantization that converts floating-point weights to \(\pm\)1, remains particularly challenging, as existing 1-bit PTQ methods often suffer from significant performance degradation compared to the full-precision models. Specifically, most of existing 1-bit PTQ approaches focus on weight alignment, aligning the full-precision model weights with those of the quantized models, rather than directly aligning their outputs. Although the output-matching approach objective is more intuitive and aligns with the quantization goal, naively applying it in 1-bit LLMs often leads to notable performance degradation. In this paper, we investigate why and under what conditions output-matching fails, in the context of 1-bit LLM quantization. Based on our findings, we propose a novel data-aware PTQ approach for 1-bit LLMs that explicitly accounts for activation error accumulation while keeping optimization efficient. Empirical experiments demonstrate that our solution consistently outperforms existing 1-bit PTQ methods with minimal overhead.
OpenView: Empowering MLLMs with Out-of-view VQA
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Recent multimodal large language models (MLLMs) show great potential in natural image understanding. Yet, they perform well, mainly on reasoning in-view contents within the image frame. This paper presents the first study on out-of-view (OOV) understanding, i.e., the ability to reason objects, activities, and scenes beyond the visible frame of a perspective view. Our technical contributions are threefold. First, we design OpenView, a four-stage pipeline to massively generate multi-choice VQA by leveraging panoramic imagery to enable context-rich and spatial-grounded VQA synthesis with free-view framing. Second, we curate OpenView-Dataset, a high-quality synthetic dataset from diverse real-world panoramas to empower MLLMs upon supervised fine-tuning. Third, we build OpenView-Bench, a benchmark that jointly measures choice and rationale accuracy for interpretable and diagnosable evaluation. Experimental results show that despite having a large gap from human performance in OOV VQA answer selection, upon empowered by OpenView, multiple MLLMs can consistently boost their performance, uplifted from 48.6% to 64.1% on average. Code, benchmark, and data will be available at https://github.com/q1xiangchen/OpenView.
ASAP-Textured Gaussians: Enhancing Textured Gaussians with Adaptive Sampling and Anisotropic Parameterization
Dec 16, 2025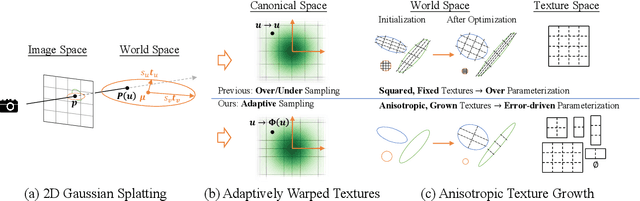
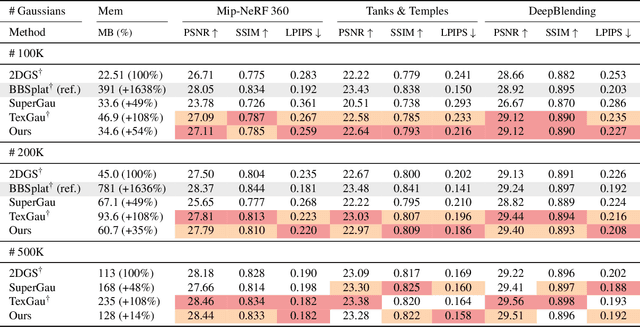
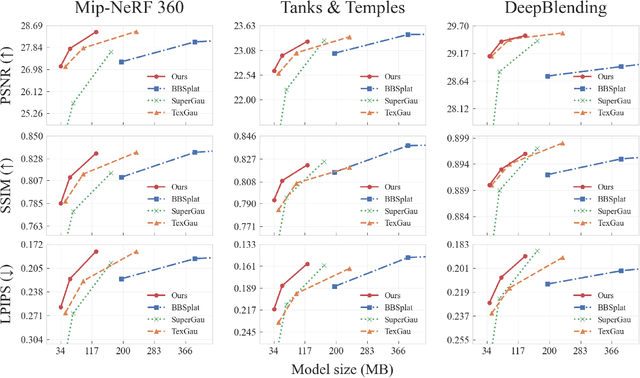
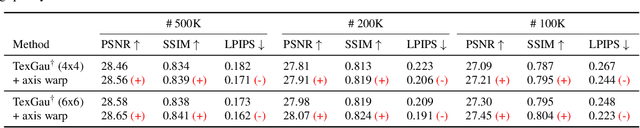
Abstract:Recent advances have equipped 3D Gaussian Splatting with texture parameterizations to capture spatially varying attributes, improving the performance of both appearance modeling and downstream tasks. However, the added texture parameters introduce significant memory efficiency challenges. Rather than proposing new texture formulations, we take a step back to examine the characteristics of existing textured Gaussian methods and identify two key limitations in common: (1) Textures are typically defined in canonical space, leading to inefficient sampling that wastes textures' capacity on low-contribution regions; and (2) texture parameterization is uniformly assigned across all Gaussians, regardless of their visual complexity, resulting in over-parameterization. In this work, we address these issues through two simple yet effective strategies: adaptive sampling based on the Gaussian density distribution and error-driven anisotropic parameterization that allocates texture resources according to rendering error. Our proposed ASAP Textured Gaussians, short for Adaptive Sampling and Anisotropic Parameterization, significantly improve the quality efficiency tradeoff, achieving high-fidelity rendering with far fewer texture parameters.
Relightable and Dynamic Gaussian Avatar Reconstruction from Monocular Video
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Modeling relightable and animatable human avatars from monocular video is a long-standing and challenging task. Recently, Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) methods have been employed to reconstruct the avatars. However, they often produce unsatisfactory photo-realistic results because of insufficient geometrical details related to body motion, such as clothing wrinkles. In this paper, we propose a 3DGS-based human avatar modeling framework, termed as Relightable and Dynamic Gaussian Avatar (RnD-Avatar), that presents accurate pose-variant deformation for high-fidelity geometrical details. To achieve this, we introduce dynamic skinning weights that define the human avatar's articulation based on pose while also learning additional deformations induced by body motion. We also introduce a novel regularization to capture fine geometric details under sparse visual cues. Furthermore, we present a new multi-view dataset with varied lighting conditions to evaluate relight. Our framework enables realistic rendering of novel poses and views while supporting photo-realistic lighting effects under arbitrary lighting conditions. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in novel view synthesis, novel pose rendering, and relighting.
* 8 pages, 9 figures, published in ACM MM 2025
Unified Camera Positional Encoding for Controlled Video Generation
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Transformers have emerged as a universal backbone across 3D perception, video generation, and world models for autonomous driving and embodied AI, where understanding camera geometry is essential for grounding visual observations in three-dimensional space. However, existing camera encoding methods often rely on simplified pinhole assumptions, restricting generalization across the diverse intrinsics and lens distortions in real-world cameras. We introduce Relative Ray Encoding, a geometry-consistent representation that unifies complete camera information, including 6-DoF poses, intrinsics, and lens distortions. To evaluate its capability under diverse controllability demands, we adopt camera-controlled text-to-video generation as a testbed task. Within this setting, we further identify pitch and roll as two components effective for Absolute Orientation Encoding, enabling full control over the initial camera orientation. Together, these designs form UCPE (Unified Camera Positional Encoding), which integrates into a pretrained video Diffusion Transformer through a lightweight spatial attention adapter, adding less than 1% trainable parameters while achieving state-of-the-art camera controllability and visual fidelity. To facilitate systematic training and evaluation, we construct a large video dataset covering a wide range of camera motions and lens types. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of UCPE in camera-controllable video generation and highlight its potential as a general camera representation for Transformers across future multi-view, video, and 3D tasks. Code will be available at https://github.com/chengzhag/UCPE.
Where and What Matters: Sensitivity-Aware Task Vectors for Many-Shot Multimodal In-Context Learning
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have shown promising in-context learning (ICL) capabilities, but scaling to many-shot settings remains difficult due to limited context length and high inference cost. To address these challenges, task-vector-based methods have been explored by inserting compact representations of many-shot in-context demonstrations into model activations. However, existing task-vector-based methods either overlook the importance of where to insert task vectors or struggle to determine suitable values for each location. To this end, we propose a novel Sensitivity-aware Task Vector insertion framework (STV) to figure out where and what to insert. Our key insight is that activation deltas across query-context pairs exhibit consistent structural patterns, providing a reliable cue for insertion. Based on the identified sensitive-aware locations, we construct a pre-clustered activation bank for each location by clustering the activation values, and then apply reinforcement learning to choose the most suitable one to insert. We evaluate STV across a range of multimodal models (e.g., Qwen-VL, Idefics-2) and tasks (e.g., VizWiz, OK-VQA), demonstrating its effectiveness and showing consistent improvements over previous task-vector-based methods with strong generalization.
Sharpness-Aware Data Generation for Zero-shot Quantization
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Zero-shot quantization aims to learn a quantized model from a pre-trained full-precision model with no access to original real training data. The common idea in zero-shot quantization approaches is to generate synthetic data for quantizing the full-precision model. While it is well-known that deep neural networks with low sharpness have better generalization ability, none of the previous zero-shot quantization works considers the sharpness of the quantized model as a criterion for generating training data. This paper introduces a novel methodology that takes into account quantized model sharpness in synthetic data generation to enhance generalization. Specifically, we first demonstrate that sharpness minimization can be attained by maximizing gradient matching between the reconstruction loss gradients computed on synthetic and real validation data, under certain assumptions. We then circumvent the problem of the gradient matching without real validation set by approximating it with the gradient matching between each generated sample and its neighbors. Experimental evaluations on CIFAR-100 and ImageNet datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over the state-of-the-art techniques in low-bit quantization settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge