Shengyi He
AudCast: Audio-Driven Human Video Generation by Cascaded Diffusion Transformers
Mar 25, 2025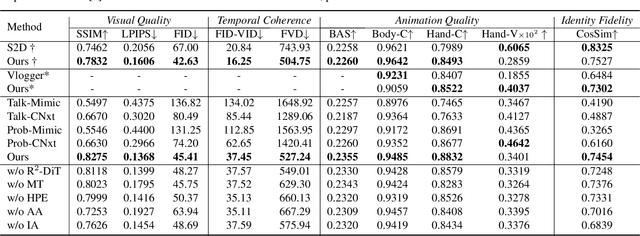
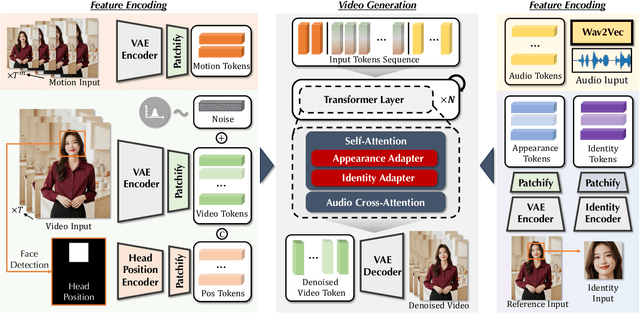
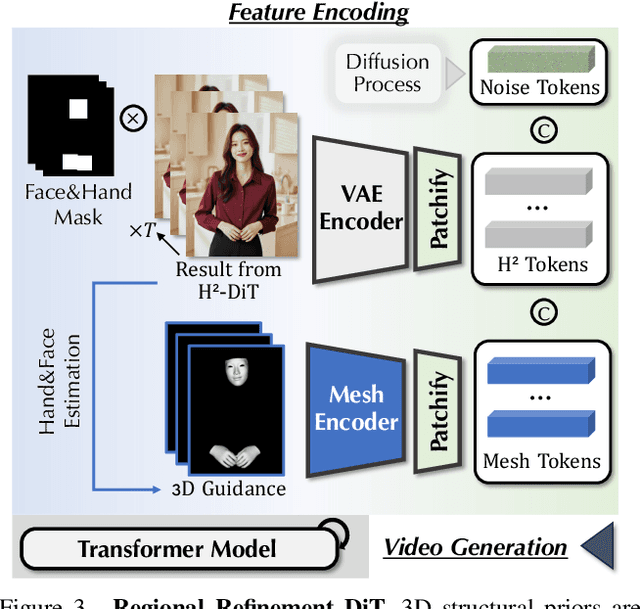

Abstract:Despite the recent progress of audio-driven video generation, existing methods mostly focus on driving facial movements, leading to non-coherent head and body dynamics. Moving forward, it is desirable yet challenging to generate holistic human videos with both accurate lip-sync and delicate co-speech gestures w.r.t. given audio. In this work, we propose AudCast, a generalized audio-driven human video generation framework adopting a cascade Diffusion-Transformers (DiTs) paradigm, which synthesizes holistic human videos based on a reference image and a given audio. 1) Firstly, an audio-conditioned Holistic Human DiT architecture is proposed to directly drive the movements of any human body with vivid gesture dynamics. 2) Then to enhance hand and face details that are well-knownly difficult to handle, a Regional Refinement DiT leverages regional 3D fitting as the bridge to reform the signals, producing the final results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework generates high-fidelity audio-driven holistic human videos with temporal coherence and fine facial and hand details. Resources can be found at https://guanjz20.github.io/projects/AudCast.
TALK-Act: Enhance Textural-Awareness for 2D Speaking Avatar Reenactment with Diffusion Model
Oct 14, 2024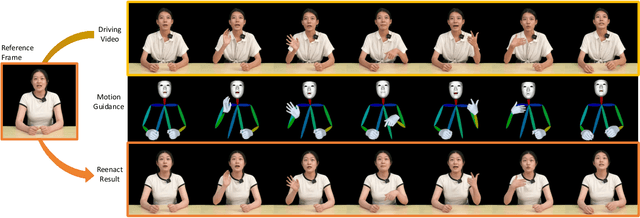
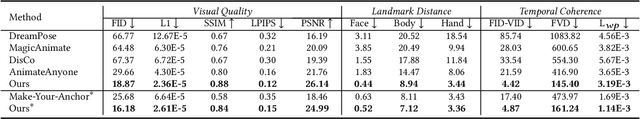
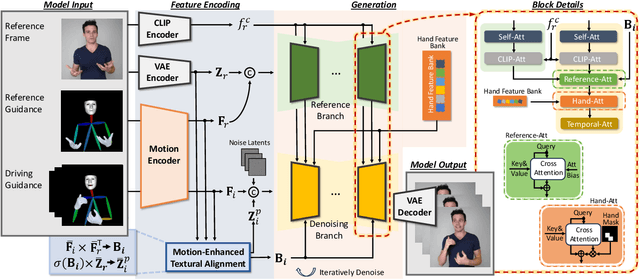
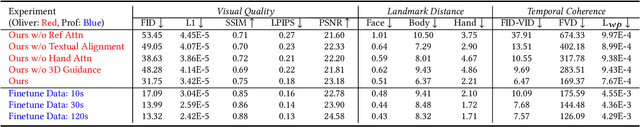
Abstract:Recently, 2D speaking avatars have increasingly participated in everyday scenarios due to the fast development of facial animation techniques. However, most existing works neglect the explicit control of human bodies. In this paper, we propose to drive not only the faces but also the torso and gesture movements of a speaking figure. Inspired by recent advances in diffusion models, we propose the Motion-Enhanced Textural-Aware ModeLing for SpeaKing Avatar Reenactment (TALK-Act) framework, which enables high-fidelity avatar reenactment from only short footage of monocular video. Our key idea is to enhance the textural awareness with explicit motion guidance in diffusion modeling. Specifically, we carefully construct 2D and 3D structural information as intermediate guidance. While recent diffusion models adopt a side network for control information injection, they fail to synthesize temporally stable results even with person-specific fine-tuning. We propose a Motion-Enhanced Textural Alignment module to enhance the bond between driving and target signals. Moreover, we build a Memory-based Hand-Recovering module to help with the difficulties in hand-shape preserving. After pre-training, our model can achieve high-fidelity 2D avatar reenactment with only 30 seconds of person-specific data. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed framework. Resources can be found at https://guanjz20.github.io/projects/TALK-Act.
ReSyncer: Rewiring Style-based Generator for Unified Audio-Visually Synced Facial Performer
Aug 06, 2024



Abstract:Lip-syncing videos with given audio is the foundation for various applications including the creation of virtual presenters or performers. While recent studies explore high-fidelity lip-sync with different techniques, their task-orientated models either require long-term videos for clip-specific training or retain visible artifacts. In this paper, we propose a unified and effective framework ReSyncer, that synchronizes generalized audio-visual facial information. The key design is revisiting and rewiring the Style-based generator to efficiently adopt 3D facial dynamics predicted by a principled style-injected Transformer. By simply re-configuring the information insertion mechanisms within the noise and style space, our framework fuses motion and appearance with unified training. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ReSyncer not only produces high-fidelity lip-synced videos according to audio, but also supports multiple appealing properties that are suitable for creating virtual presenters and performers, including fast personalized fine-tuning, video-driven lip-syncing, the transfer of speaking styles, and even face swapping. Resources can be found at https://guanjz20.github.io/projects/ReSyncer.
Certifiable Deep Importance Sampling for Rare-Event Simulation of Black-Box Systems
Nov 03, 2021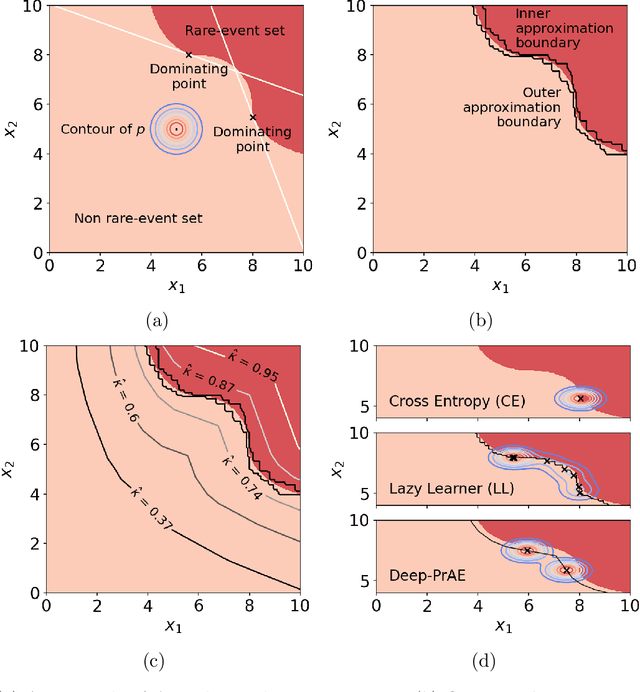
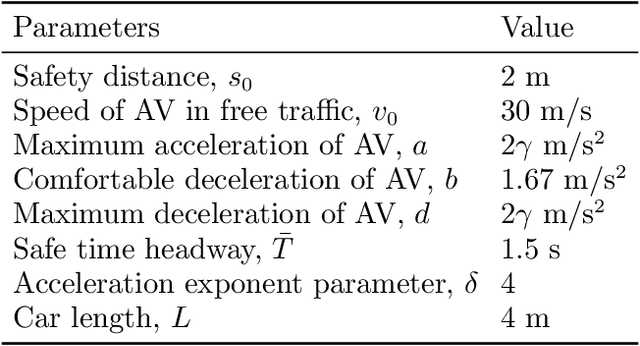
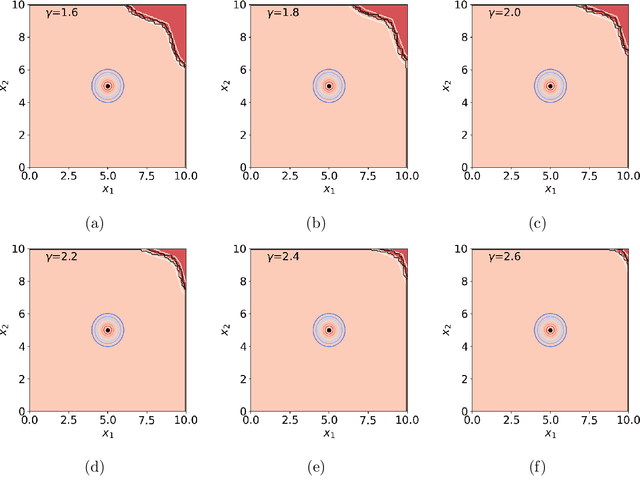
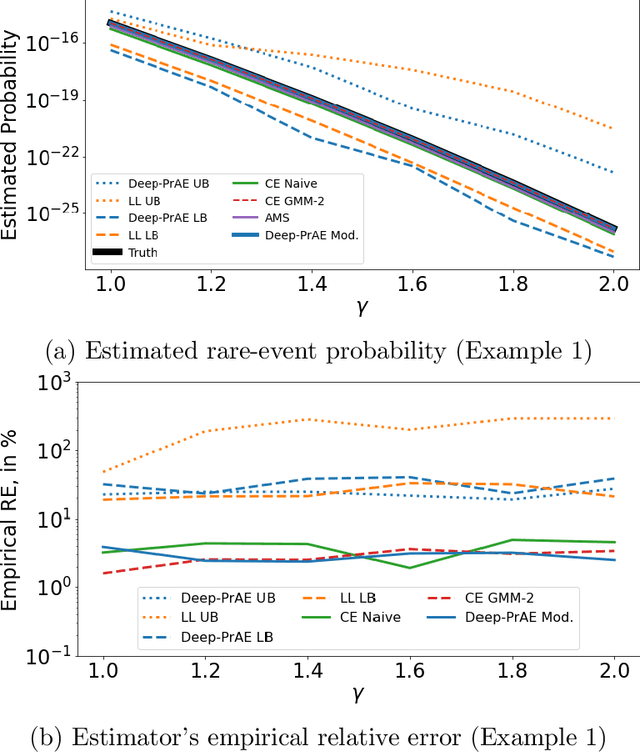
Abstract:Rare-event simulation techniques, such as importance sampling (IS), constitute powerful tools to speed up challenging estimation of rare catastrophic events. These techniques often leverage the knowledge and analysis on underlying system structures to endow desirable efficiency guarantees. However, black-box problems, especially those arising from recent safety-critical applications of AI-driven physical systems, can fundamentally undermine their efficiency guarantees and lead to dangerous under-estimation without diagnostically detected. We propose a framework called Deep Probabilistic Accelerated Evaluation (Deep-PrAE) to design statistically guaranteed IS, by converting black-box samplers that are versatile but could lack guarantees, into one with what we call a relaxed efficiency certificate that allows accurate estimation of bounds on the rare-event probability. We present the theory of Deep-PrAE that combines the dominating point concept with rare-event set learning via deep neural network classifiers, and demonstrate its effectiveness in numerical examples including the safety-testing of intelligent driving algorithms.
Deep Probabilistic Accelerated Evaluation: A Certifiable Rare-Event Simulation Methodology for Black-Box Autonomy
Jul 01, 2020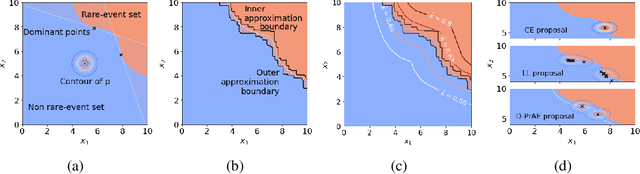



Abstract:Evaluating the reliability of intelligent physical systems against rare catastrophic events poses a huge testing burden for real-world applications. Simulation provides a useful, if not unique, platform to evaluate the extremal risks of these AI-enabled systems before their deployments. Importance Sampling (IS), while proven to be powerful for rare-event simulation, faces challenges in handling these systems due to their black-box nature that fundamentally undermines its efficiency guarantee. To overcome this challenge, we propose a framework called Deep Probabilistic Accelerated Evaluation (D-PrAE) to design IS, which leverages rare-event-set learning and a new notion of efficiency certificate. D-PrAE combines the dominating point method with deep neural network classifiers to achieve superior estimation efficiency. We present theoretical guarantees and demonstrate the empirical effectiveness of D-PrAE via examples on the safety-testing of self-driving algorithms that are beyond the reach of classical variance reduction techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge