Jesse Dodge
Signal and Noise: A Framework for Reducing Uncertainty in Language Model Evaluation
Aug 18, 2025Abstract:Developing large language models is expensive and involves making decisions with small experiments, typically by evaluating on large, multi-task evaluation suites. In this work, we analyze specific properties which make a benchmark more reliable for such decisions, and interventions to design higher-quality evaluation benchmarks. We introduce two key metrics that show differences in current benchmarks: signal, a benchmark's ability to separate better models from worse models, and noise, a benchmark's sensitivity to random variability between training steps. We demonstrate that benchmarks with a better signal-to-noise ratio are more reliable when making decisions at small scale, and those with less noise have lower scaling law prediction error. These results suggest that improving signal or noise will lead to more useful benchmarks, so we introduce three interventions designed to directly affect signal or noise. For example, we propose that switching to a metric that has better signal and noise (e.g., perplexity rather than accuracy) leads to better reliability and improved scaling law error. We also find that filtering noisy subtasks, to improve an aggregate signal-to-noise ratio, leads to more reliable multi-task evaluations. We also find that averaging the output of a model's intermediate checkpoints to reduce noise leads to consistent improvements. We conclude by recommending that those creating new benchmarks, or selecting which existing benchmarks to use, aim for high signal and low noise. We use 30 benchmarks for these experiments, and 375 open-weight language models from 60M to 32B parameters, resulting in a new, publicly available dataset of 900K evaluation benchmark results, totaling 200M instances.
SciArena: An Open Evaluation Platform for Foundation Models in Scientific Literature Tasks
Jul 01, 2025
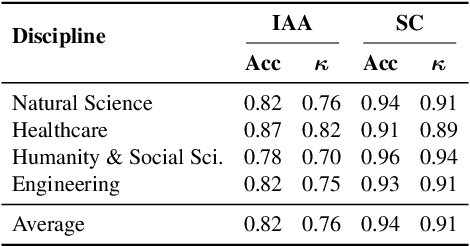

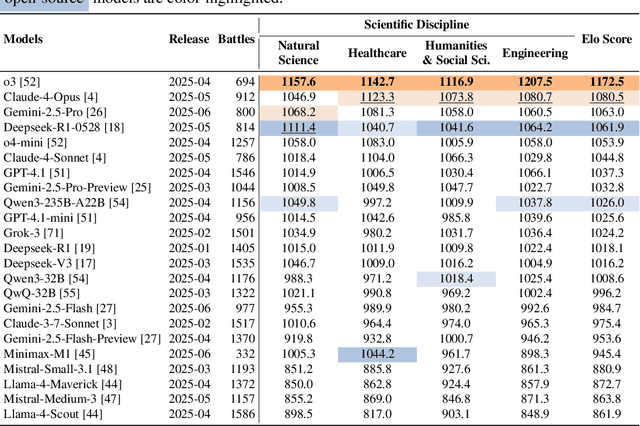
Abstract:We present SciArena, an open and collaborative platform for evaluating foundation models on scientific literature tasks. Unlike traditional benchmarks for scientific literature understanding and synthesis, SciArena engages the research community directly, following the Chatbot Arena evaluation approach of community voting on model comparisons. By leveraging collective intelligence, SciArena offers a community-driven evaluation of model performance on open-ended scientific tasks that demand literature-grounded, long-form responses. The platform currently supports 23 open-source and proprietary foundation models and has collected over 13,000 votes from trusted researchers across diverse scientific domains. We analyze the data collected so far and confirm that the submitted questions are diverse, aligned with real-world literature needs, and that participating researchers demonstrate strong self-consistency and inter-annotator agreement in their evaluations. We discuss the results and insights based on the model ranking leaderboard. To further promote research in building model-based automated evaluation systems for literature tasks, we release SciArena-Eval, a meta-evaluation benchmark based on our collected preference data. The benchmark measures the accuracy of models in judging answer quality by comparing their pairwise assessments with human votes. Our experiments highlight the benchmark's challenges and emphasize the need for more reliable automated evaluation methods.
DataDecide: How to Predict Best Pretraining Data with Small Experiments
Apr 15, 2025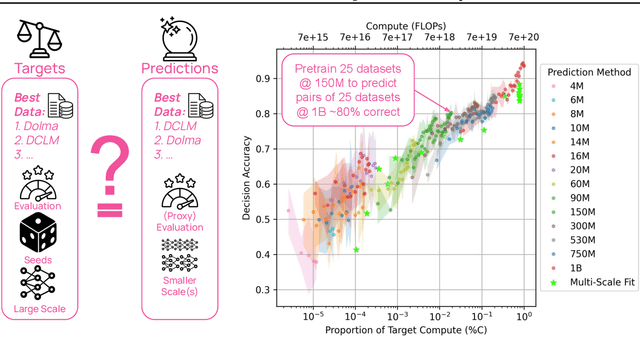
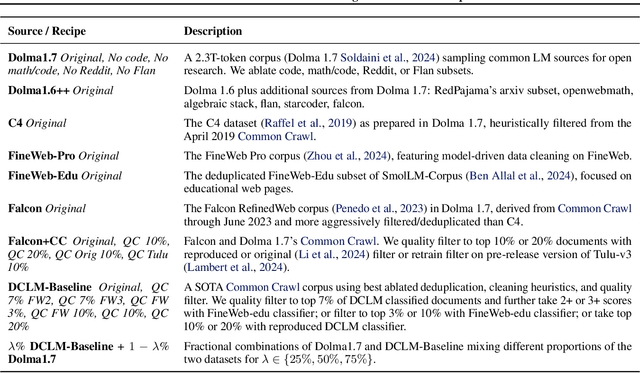
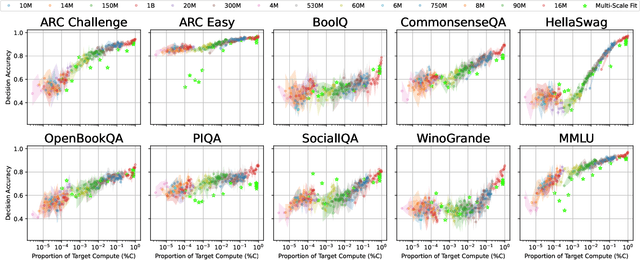
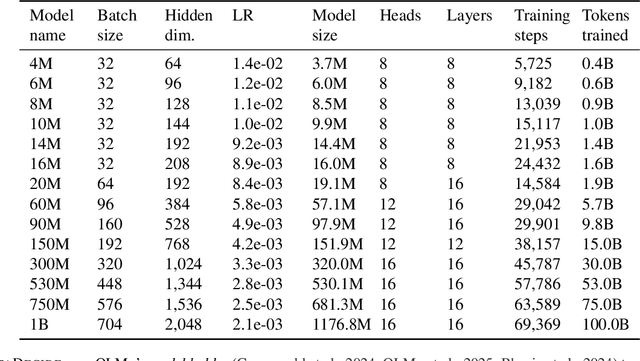
Abstract:Because large language models are expensive to pretrain on different datasets, using smaller-scale experiments to decide on data is crucial for reducing costs. Which benchmarks and methods of making decisions from observed performance at small scale most accurately predict the datasets that yield the best large models? To empower open exploration of this question, we release models, data, and evaluations in DataDecide -- the most extensive open suite of models over differences in data and scale. We conduct controlled pretraining experiments across 25 corpora with differing sources, deduplication, and filtering up to 100B tokens, model sizes up to 1B parameters, and 3 random seeds. We find that the ranking of models at a single, small size (e.g., 150M parameters) is a strong baseline for predicting best models at our larger target scale (1B) (~80% of com parisons correct). No scaling law methods among 8 baselines exceed the compute-decision frontier of single-scale predictions, but DataDecide can measure improvement in future scaling laws. We also identify that using continuous likelihood metrics as proxies in small experiments makes benchmarks including MMLU, ARC, HellaSwag, MBPP, and HumanEval >80% predictable at the target 1B scale with just 0.01% of the compute.
OLMoTrace: Tracing Language Model Outputs Back to Trillions of Training Tokens
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:We present OLMoTrace, the first system that traces the outputs of language models back to their full, multi-trillion-token training data in real time. OLMoTrace finds and shows verbatim matches between segments of language model output and documents in the training text corpora. Powered by an extended version of infini-gram (Liu et al., 2024), our system returns tracing results within a few seconds. OLMoTrace can help users understand the behavior of language models through the lens of their training data. We showcase how it can be used to explore fact checking, hallucination, and the creativity of language models. OLMoTrace is publicly available and fully open-source.
Establishing Task Scaling Laws via Compute-Efficient Model Ladders
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:We develop task scaling laws and model ladders to predict the individual task performance of pretrained language models (LMs) in the overtrained setting. Standard power laws for language modeling loss cannot accurately model task performance. Therefore, we leverage a two-step prediction approach: first use model and data size to predict a task-specific loss, and then use this task loss to predict task performance. We train a set of small-scale "ladder" models, collect data points to fit the parameterized functions of the two prediction steps, and make predictions for two target models: a 7B model trained to 4T tokens and a 13B model trained to 5T tokens. Training the ladder models only costs 1% of the compute used for the target models. On four multiple-choice tasks written in ranked classification format, we can predict the accuracy of both target models within 2 points of absolute error. We have higher prediction error on four other tasks (average absolute error 6.9) and find that these are often tasks with higher variance in task metrics. We also find that using less compute to train fewer ladder models tends to deteriorate predictions. Finally, we empirically show that our design choices and the two-step approach lead to superior performance in establishing scaling laws.
Scalable Data Ablation Approximations for Language Models through Modular Training and Merging
Oct 21, 2024


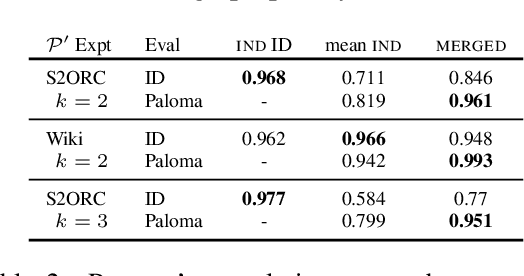
Abstract:Training data compositions for Large Language Models (LLMs) can significantly affect their downstream performance. However, a thorough data ablation study exploring large sets of candidate data mixtures is typically prohibitively expensive since the full effect is seen only after training the models; this can lead practitioners to settle for sub-optimal data mixtures. We propose an efficient method for approximating data ablations which trains individual models on subsets of a training corpus and reuses them across evaluations of combinations of subsets. In continued pre-training experiments, we find that, given an arbitrary evaluation set, the perplexity score of a single model trained on a candidate set of data is strongly correlated with perplexity scores of parameter averages of models trained on distinct partitions of that data. From this finding, we posit that researchers and practitioners can conduct inexpensive simulations of data ablations by maintaining a pool of models that were each trained on partitions of a large training corpus, and assessing candidate data mixtures by evaluating parameter averages of combinations of these models. This approach allows for substantial improvements in amortized training efficiency -- scaling only linearly with respect to new data -- by enabling reuse of previous training computation, opening new avenues for improving model performance through rigorous, incremental data assessment and mixing.
Merge to Learn: Efficiently Adding Skills to Language Models with Model Merging
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:Adapting general-purpose language models to new skills is currently an expensive process that must be repeated as new instruction datasets targeting new skills are created, or can cause the models to forget older skills. In this work, we investigate the effectiveness of adding new skills to preexisting models by training on the new skills in isolation and later merging with the general model (e.g. using task vectors). In experiments focusing on scientific literature understanding, safety, and coding, we find that the parallel-train-then-merge procedure, which is significantly cheaper than retraining the models on updated data mixtures, is often comparably effective. Our experiments also show that parallel training is especially well-suited for enabling safety features in LMs relative to continued finetuning and retraining, as it dramatically improves model compliance with safe prompts while preserving its ability to refuse dangerous or harmful prompts.
OLMES: A Standard for Language Model Evaluations
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Progress in AI is often demonstrated by new models claiming improved performance on tasks measuring model capabilities. Evaluating language models in particular is challenging, as small changes to how a model is evaluated on a task can lead to large changes in measured performance. There is no common standard setup, so different models are evaluated on the same tasks in different ways, leading to claims about which models perform best not being reproducible. We propose OLMES, a completely documented, practical, open standard for reproducible LLM evaluations. In developing this standard, we identify and review the varying factors in evaluation practices adopted by the community - such as details of prompt formatting, choice of in-context examples, probability normalizations, and task formulation. In particular, OLMES supports meaningful comparisons between smaller base models that require the unnatural "cloze" formulation of multiple-choice questions against larger models that can utilize the original formulation. OLMES includes well-considered recommendations guided by results from existing literature as well as new experiments investigating open questions.
OLMo: Accelerating the Science of Language Models
Feb 07, 2024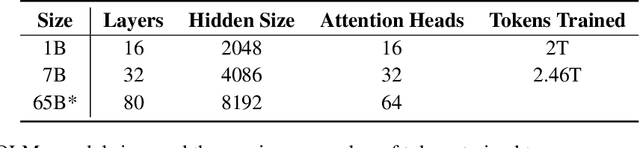
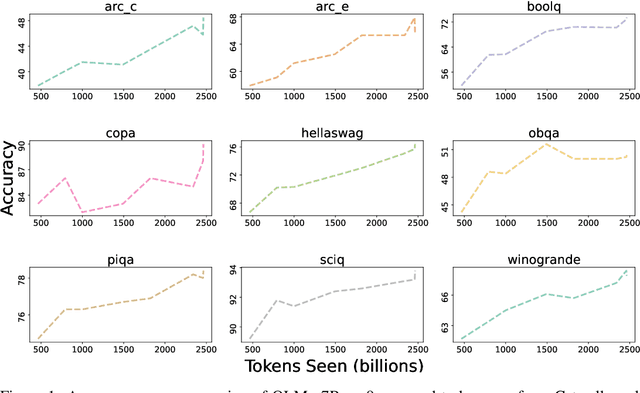
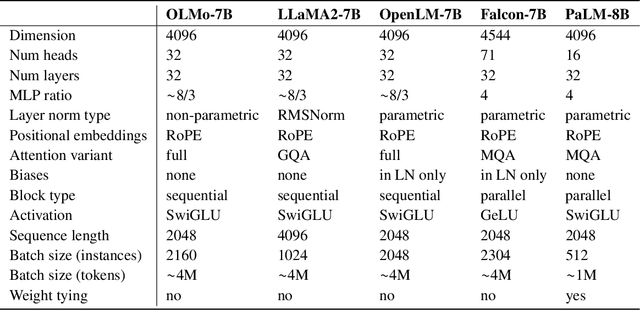
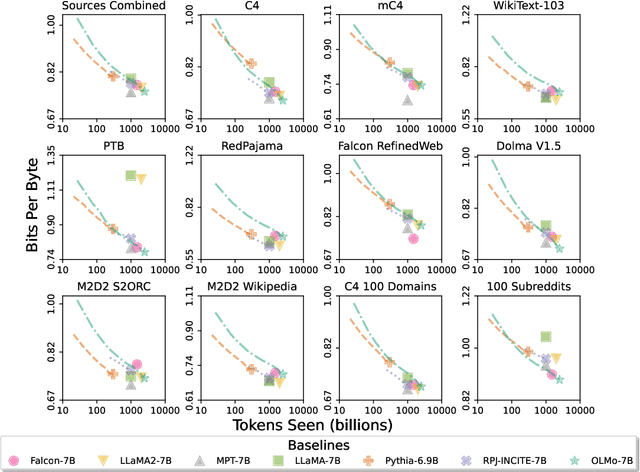
Abstract:Language models (LMs) have become ubiquitous in both NLP research and in commercial product offerings. As their commercial importance has surged, the most powerful models have become closed off, gated behind proprietary interfaces, with important details of their training data, architectures, and development undisclosed. Given the importance of these details in scientifically studying these models, including their biases and potential risks, we believe it is essential for the research community to have access to powerful, truly open LMs. To this end, this technical report details the first release of OLMo, a state-of-the-art, truly Open Language Model and its framework to build and study the science of language modeling. Unlike most prior efforts that have only released model weights and inference code, we release OLMo and the whole framework, including training data and training and evaluation code. We hope this release will empower and strengthen the open research community and inspire a new wave of innovation.
Dolma: an Open Corpus of Three Trillion Tokens for Language Model Pretraining Research
Jan 31, 2024



Abstract:Language models have become a critical technology to tackling a wide range of natural language processing tasks, yet many details about how the best-performing language models were developed are not reported. In particular, information about their pretraining corpora is seldom discussed: commercial language models rarely provide any information about their data; even open models rarely release datasets they are trained on, or an exact recipe to reproduce them. As a result, it is challenging to conduct certain threads of language modeling research, such as understanding how training data impacts model capabilities and shapes their limitations. To facilitate open research on language model pretraining, we release Dolma, a three trillion tokens English corpus, built from a diverse mixture of web content, scientific papers, code, public-domain books, social media, and encyclopedic materials. In addition, we open source our data curation toolkit to enable further experimentation and reproduction of our work. In this report, we document Dolma, including its design principles, details about its construction, and a summary of its contents. We interleave this report with analyses and experimental results from training language models on intermediate states of Dolma to share what we have learned about important data curation practices, including the role of content or quality filters, deduplication, and multi-source mixing. Dolma has been used to train OLMo, a state-of-the-art, open language model and framework designed to build and study the science of language modeling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge