Xiaoming Chen
Institute of Marine Biology and Pharmacology, Ocean College, Zhejiang University
SketchPlay: Intuitive Creation of Physically Realistic VR Content with Gesture-Driven Sketching
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Creating physically realistic content in VR often requires complex modeling tools or predefined 3D models, textures, and animations, which present significant barriers for non-expert users. In this paper, we propose SketchPlay, a novel VR interaction framework that transforms humans' air-drawn sketches and gestures into dynamic, physically realistic scenes, making content creation intuitive and playful like drawing. Specifically, sketches capture the structure and spatial arrangement of objects and scenes, while gestures convey physical cues such as velocity, direction, and force that define movement and behavior. By combining these complementary forms of input, SketchPlay captures both the structure and dynamics of user-created content, enabling the generation of a wide range of complex physical phenomena, such as rigid body motion, elastic deformation, and cloth dynamics. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared to traditional text-driven methods, SketchPlay offers significant advantages in expressiveness, and user experience. By providing an intuitive and engaging creation process, SketchPlay lowers the entry barrier for non-expert users and shows strong potential for applications in education, art, and immersive storytelling.
Integrated Communication and Remote Sensing in LEO Satellite Systems: Protocol, Architecture and Prototype
Aug 14, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we explore the integration of communication and synthetic aperture radar (SAR)-based remote sensing in low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite systems to provide real-time SAR imaging and information transmission. Considering the high-mobility characteristics of satellite channels and limited processing capabilities of satellite payloads, we propose an integrated communication and remote sensing architecture based on an orthogonal delay-Doppler division multiplexing (ODDM) signal waveform. Both communication and SAR imaging functionalities are achieved with an integrated transceiver onboard the LEO satellite, utilizing the same waveform and radio frequency (RF) front-end. Based on such an architecture, we propose a transmission protocol compatible with the 5G NR standard using downlink pilots for joint channel estimation and SAR imaging. Furthermore, we design a unified signal processing framework for the integrated satellite receiver to simultaneously achieve high-performance channel sensing, low-complexity channel equalization and interference-free SAR imaging. Finally, the performance of the proposed integrated system is demonstrated through comprehensive analysis and extensive simulations in the sub-6 GHz band. Moreover, a software-defined radio (SDR) prototype is presented to validate its effectiveness for real-time SAR imaging and information transmission in satellite direct-connect user equipment (UE) scenarios within the millimeter-wave (mmWave) band.
Rethinking Multi-User Communication in Semantic Domain: Enhanced OMDMA by Shuffle-Based Orthogonalization and Diffusion Denoising
Jul 28, 2025



Abstract:Inter-user interference remains a critical bottleneck in wireless communication systems, particularly in the emerging paradigm of semantic communication (SemCom). Compared to traditional systems, inter-user interference in SemCom severely degrades key semantic information, often causing worse performance than Gaussian noise under the same power level. To address this challenge, inspired by the recently proposed concept of Orthogonal Model Division Multiple Access (OMDMA) that leverages semantic orthogonality rooted in the personalized joint source and channel (JSCC) models to distinguish users, we propose a novel, scalable framework that eliminates the need for user-specific JSCC models as did in original OMDMA. Our key innovation lies in shuffle-based orthogonalization, where randomly permuting the positions of JSCC feature vectors transforms inter-user interference into Gaussian-like noise. By assigning each user a unique shuffling pattern, the interference is treated as channel noise, enabling effective mitigation using diffusion models (DMs). This approach not only simplifies system design by requiring a single universal JSCC model but also enhances privacy, as shuffling patterns act as implicit private keys. Additionally, we extend the framework to scenarios involving semantically correlated data. By grouping users based on semantic similarity, a cooperative beamforming strategy is introduced to exploit redundancy in correlated data, further improving system performance. Extensive simulations demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art multi-user SemCom frameworks, achieving superior semantic fidelity, robustness to interference, and scalability-all without requiring additional training overhead.
Robust Deep Learning-Based Physical Layer Communications: Strategies and Approaches
May 02, 2025Abstract:Deep learning (DL) has emerged as a transformative technology with immense potential to reshape the sixth-generation (6G) wireless communication network. By utilizing advanced algorithms for feature extraction and pattern recognition, DL provides unprecedented capabilities in optimizing the network efficiency and performance, particularly in physical layer communications. Although DL technologies present the great potential, they also face significant challenges related to the robustness, which are expected to intensify in the complex and demanding 6G environment. Specifically, current DL models typically exhibit substantial performance degradation in dynamic environments with time-varying channels, interference of noise and different scenarios, which affect their effectiveness in diverse real-world applications. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of strategies and approaches for robust DL-based methods in physical layer communications. First we introduce the key challenges that current DL models face. Then we delve into a detailed examination of DL approaches specifically tailored to enhance robustness in 6G, which are classified into data-driven and model-driven strategies. Finally, we verify the effectiveness of these methods by case studies and outline future research directions.
Wireless Large AI Model: Shaping the AI-Native Future of 6G and Beyond
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:The emergence of sixth-generation and beyond communication systems is expected to fundamentally transform digital experiences through introducing unparalleled levels of intelligence, efficiency, and connectivity. A promising technology poised to enable this revolutionary vision is the wireless large AI model (WLAM), characterized by its exceptional capabilities in data processing, inference, and decision-making. In light of these remarkable capabilities, this paper provides a comprehensive survey of WLAM, elucidating its fundamental principles, diverse applications, critical challenges, and future research opportunities. We begin by introducing the background of WLAM and analyzing the key synergies with wireless networks, emphasizing the mutual benefits. Subsequently, we explore the foundational characteristics of WLAM, delving into their unique relevance in wireless environments. Then, the role of WLAM in optimizing wireless communication systems across various use cases and the reciprocal benefits are systematically investigated. Furthermore, we discuss the integration of WLAM with emerging technologies, highlighting their potential to enable transformative capabilities and breakthroughs in wireless communication. Finally, we thoroughly examine the high-level challenges hindering the practical implementation of WLAM and discuss pivotal future research directions.
AccidentSim: Generating Physically Realistic Vehicle Collision Videos from Real-World Accident Reports
Mar 26, 2025
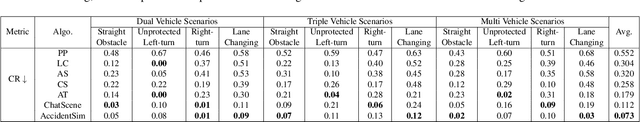
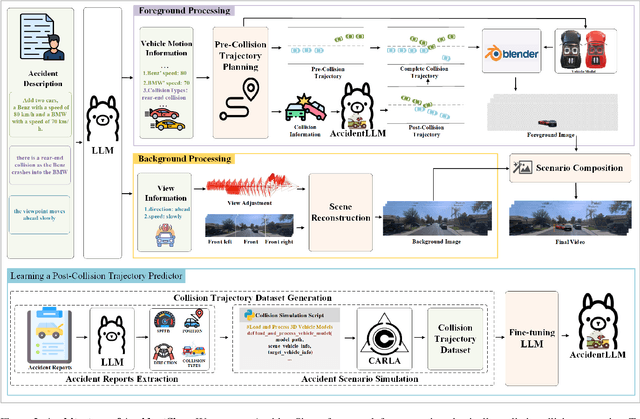
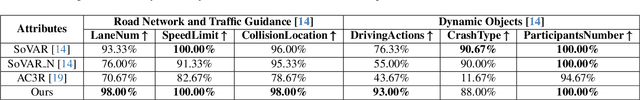
Abstract:Collecting real-world vehicle accident videos for autonomous driving research is challenging due to their rarity and complexity. While existing driving video generation methods may produce visually realistic videos, they often fail to deliver physically realistic simulations because they lack the capability to generate accurate post-collision trajectories. In this paper, we introduce AccidentSim, a novel framework that generates physically realistic vehicle collision videos by extracting and utilizing the physical clues and contextual information available in real-world vehicle accident reports. Specifically, AccidentSim leverages a reliable physical simulator to replicate post-collision vehicle trajectories from the physical and contextual information in the accident reports and to build a vehicle collision trajectory dataset. This dataset is then used to fine-tune a language model, enabling it to respond to user prompts and predict physically consistent post-collision trajectories across various driving scenarios based on user descriptions. Finally, we employ Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) to render high-quality backgrounds, merging them with the foreground vehicles that exhibit physically realistic trajectories to generate vehicle collision videos. Experimental results demonstrate that the videos produced by AccidentSim excel in both visual and physical authenticity.
EvAnimate: Event-conditioned Image-to-Video Generation for Human Animation
Mar 24, 2025



Abstract:Conditional human animation transforms a static reference image into a dynamic sequence by applying motion cues such as poses. These motion cues are typically derived from video data but are susceptible to limitations including low temporal resolution, motion blur, overexposure, and inaccuracies under low-light conditions. In contrast, event cameras provide data streams with exceptionally high temporal resolution, a wide dynamic range, and inherent resistance to motion blur and exposure issues. In this work, we propose EvAnimate, a framework that leverages event streams as motion cues to animate static human images. Our approach employs a specialized event representation that transforms asynchronous event streams into 3-channel slices with controllable slicing rates and appropriate slice density, ensuring compatibility with diffusion models. Subsequently, a dual-branch architecture generates high-quality videos by harnessing the inherent motion dynamics of the event streams, thereby enhancing both video quality and temporal consistency. Specialized data augmentation strategies further enhance cross-person generalization. Finally, we establish a new benchmarking, including simulated event data for training and validation, and a real-world event dataset capturing human actions under normal and extreme scenarios. The experiment results demonstrate that EvAnimate achieves high temporal fidelity and robust performance in scenarios where traditional video-derived cues fall short.
LLM-EvRep: Learning an LLM-Compatible Event Representation Using a Self-Supervised Framework
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in event-based recognition have demonstrated significant promise, yet most existing approaches rely on extensive training, limiting their adaptability for efficient processing of event-driven visual content. Meanwhile, large language models (LLMs) have exhibited remarkable zero-shot capabilities across diverse domains, but their application to event-based visual recognition remains largely unexplored. To bridge this gap, we propose \textbf{LLM-EvGen}, an event representation generator that produces LLM-compatible event representations \textbf{LLM-EvRep}, thereby enhancing the performance of LLMs on event recognition tasks. The generator is trained using a self-supervised framework, aligning the generated representations with semantic consistency and structural fidelity. Comprehensive experiments were conducted on three datasets: N-ImageNet, N-Caltech101, and N-MNIST. The results demonstrate that our method, \textbf{LLM-EvRep}, outperforms the event-to-video method, E2VID, by 15.93\%, 0.82\%, and 50.21\%, respectively, in recognition tasks when evaluated using GPT-4o.
Terahertz Integrated Sensing and Communication-Empowered UAVs in 6G: A Transceiver Design Perspective
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Due to their high maneuverability, flexible deployment, and low cost, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are expected to play a pivotal role in not only communication, but also sensing. Especially by exploiting the ultra-wide bandwidth of terahertz (THz) bands, integrated sensing and communication (ISAC)-empowered UAV has been a promising technology of 6G space-air-ground integrated networks. In this article, we systematically investigate the key techniques and essential obstacles for THz-ISAC-empowered UAV from a transceiver design perspective, with the highlight of its major challenges and key technologies. Specifically, we discuss the THz-ISAC-UAV wireless propagation environment, based on which several channel characteristics for communication and sensing are revealed. We point out the transceiver payload design peculiarities for THz-ISAC-UAV from the perspective of antenna design, radio frequency front-end, and baseband signal processing. To deal with the specificities faced by the payload, we shed light on three key technologies, i.e., hybrid beamforming for ultra-massive MIMO-ISAC, power-efficient THz-ISAC waveform design, as well as communication and sensing channel state information acquisition, and extensively elaborate their concepts and key issues. More importantly, future research directions and associated open problems are presented, which may unleash the full potential of THz-ISAC-UAV for 6G wireless networks.
NVS-SQA: Exploring Self-Supervised Quality Representation Learning for Neurally Synthesized Scenes without References
Jan 11, 2025



Abstract:Neural View Synthesis (NVS), such as NeRF and 3D Gaussian Splatting, effectively creates photorealistic scenes from sparse viewpoints, typically evaluated by quality assessment methods like PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS. However, these full-reference methods, which compare synthesized views to reference views, may not fully capture the perceptual quality of neurally synthesized scenes (NSS), particularly due to the limited availability of dense reference views. Furthermore, the challenges in acquiring human perceptual labels hinder the creation of extensive labeled datasets, risking model overfitting and reduced generalizability. To address these issues, we propose NVS-SQA, a NSS quality assessment method to learn no-reference quality representations through self-supervision without reliance on human labels. Traditional self-supervised learning predominantly relies on the "same instance, similar representation" assumption and extensive datasets. However, given that these conditions do not apply in NSS quality assessment, we employ heuristic cues and quality scores as learning objectives, along with a specialized contrastive pair preparation process to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of learning. The results show that NVS-SQA outperforms 17 no-reference methods by a large margin (i.e., on average 109.5% in SRCC, 98.6% in PLCC, and 91.5% in KRCC over the second best) and even exceeds 16 full-reference methods across all evaluation metrics (i.e., 22.9% in SRCC, 19.1% in PLCC, and 18.6% in KRCC over the second best).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge