Deniz Gündüz
Optimal QAM Constellation for Over-the-Air Computation in the Presence of Heavy-Tailed Channel Noise
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:Over-the-air computation (OAC) enables low-latency aggregation over multiple-access channels (MACs) by exploiting the superposition property of the wireless medium to compute functions efficiently in distributed networks. A critical but often overlooked challenge is that electromagnetic interference in practical radio channels frequently exhibits heavy-tailed behavior, causing strong impulsive noise that severely degrades computation performance. This work studies digital OAC with QAM-based signaling under heavy-tailed interference modeled by a Cauchy distribution (lacking a finite second moment). We seek QAM-like constellations that minimize the mean-squared error (MSE) of sum aggregation subject to an average-power constraint. The problem is formulated as a constrained optimization, whose solution yields unique optimality conditions. Numerical results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed design. Notably, the framework extends naturally to nomographic functions, broader constellation families, and alternative noise models.
Leveraging Overfitting for Low-Complexity and Modality-Agnostic Joint Source-Channel Coding
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces Implicit-JSCC, a novel overfitted joint source-channel coding paradigm that directly optimizes channel symbols and a lightweight neural decoder for each source. This instance-specific strategy eliminates the need for training datasets or pre-trained models, enabling a storage-free, modality-agnostic solution. As a low-complexity alternative, Implicit-JSCC achieves efficient image transmission with around 1000x lower decoding complexity, using as few as 607 model parameters and 641 multiplications per pixel. This overfitted design inherently addresses source generalizability and achieves state-of-the-art results in the high SNR regimes, underscoring its promise for future communication systems, especially streaming scenarios where one-time offline encoding supports multiple online decoding.
Learned Digital Codes for Over-the-Air Computation in Federated Edge Learning
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Federated edge learning (FEEL) enables wireless devices to collaboratively train a centralised model without sharing raw data, but repeated uplink transmission of model updates makes communication the dominant bottleneck. Over-the-air (OTA) aggregation alleviates this by exploiting the superposition property of the wireless channel, enabling simultaneous transmission and merging communication with computation. Digital OTA schemes extend this principle by incorporating the robustness of conventional digital communication, but current designs remain limited in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regimes. This work proposes a learned digital OTA framework that improves recovery accuracy, convergence behaviour, and robustness to challenging SNR conditions while maintaining the same uplink overhead as state-of-the-art methods. The design integrates an unsourced random access (URA) codebook with vector quantisation and AMP-DA-Net, an unrolled approximate message passing (AMP)-style decoder trained end-to-end with the digital codebook and parameter server local training statistics. The proposed design extends OTA aggregation beyond averaging to a broad class of symmetric functions, including trimmed means and majority-based rules. Experiments on highly heterogeneous device datasets and varying numbers of active devices show that the proposed design extends reliable digital OTA operation by more than 10 dB into low SNR regimes while matching or improving performance across the full SNR range. The learned decoder remains effective under message corruption and nonlinear aggregation, highlighting the broader potential of end-to-end learned design for digital OTA communication in FEEL.
Fully Asynchronous Unsourced Random Access over Fading Channels
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:We examine unsourced random access in a fully asynchronous setup, where active users transmit their data without restriction on the start time over a fading channel. In the proposed scheme, the transmitted signal consists of a pilot sequence and a polar codeword, with the polar codeword distributed across the data part of the packet in an on-off pattern. The receiver uses a double sliding-window decoder, where the inner window employs iterative decoding with joint timing and pilot detection, channel estimation, single-user decoding, and successive interference cancellation to recover the message bits, while the outer window enhances interference cancellation. The numerical results indicate that the proposed scheme exhibits only a slight performance loss compared to the synchronous benchmark while being more applicable in practice.
Test-time Verification via Optimal Transport: Coverage, ROC, & Sub-optimality
Oct 21, 2025Abstract:While test-time scaling with verification has shown promise in improving the performance of large language models (LLMs), the role of the verifier and its imperfections remain underexplored. The effect of verification manifests through interactions of three quantities: (i) the generator's coverage, (ii) the verifier's region of convergence (ROC), and (iii) the sampling algorithm's sub-optimality. Though recent studies capture subsets of these factors, a unified framework quantifying the geometry of their interplay is missing. We frame verifiable test-time scaling as a transport problem. This characterizes the interaction of coverage, ROC, and sub-optimality, and uncovers that the sub-optimality--coverage curve exhibits three regimes. A transport regime -- where sub-optimality increases with coverage, a policy improvement regime -- where sub-optimality may decrease with coverage, depending on the verifier's ROC, and a saturation regime -- where sub-optimality plateaus, unaffected by coverage. We further propose and analyze two classes of sampling algorithms -- sequential and batched, and examine how their computational complexities shape these trade-offs. Empirical results with Qwen, Llama, and Gemma models corroborate our theoretical findings.
Multi-hop Deep Joint Source-Channel Coding with Deep Hash Distillation for Semantically Aligned Image Retrieval
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:We consider image transmission via deep joint source-channel coding (DeepJSCC) over multi-hop additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) channels by training a DeepJSCC encoder-decoder pair with a pre-trained deep hash distillation (DHD) module to semantically cluster images, facilitating security-oriented applications through enhanced semantic consistency and improving the perceptual reconstruction quality. We train the DeepJSCC module to both reduce mean square error (MSE) and minimize cosine distance between DHD hashes of source and reconstructed images. Significantly improved perceptual quality as a result of semantic alignment is illustrated for different multi-hop settings, for which classical DeepJSCC may suffer from noise accumulation, measured by the learned perceptual image patch similarity (LPIPS) metric.
Goal-Oriented Joint Source-Channel Coding: Distortion-Classification-Power Trade-off
Sep 17, 2025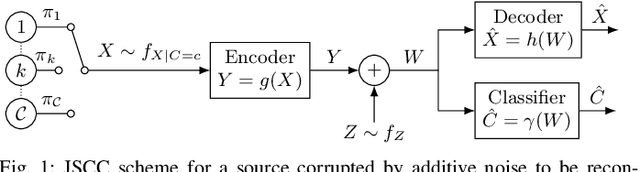
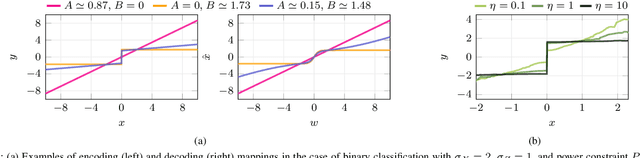
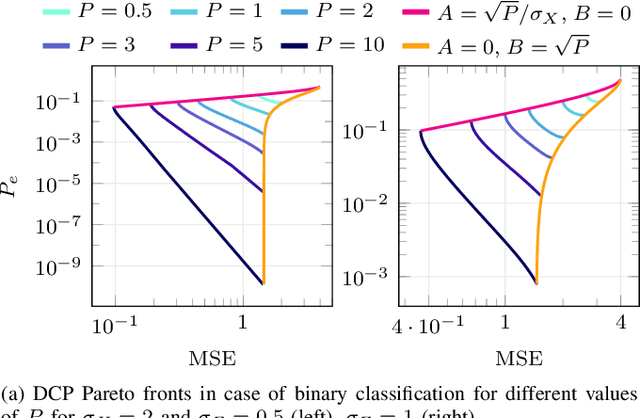
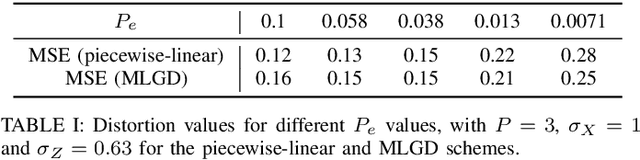
Abstract:Joint source-channel coding is a compelling paradigm when low-latency and low-complexity communication is required. This work proposes a theoretical framework that integrates classification and anomaly detection within the conventional signal reconstruction objective. Assuming a Gaussian scalar source and constraining the encoder to piecewise linear mappings, we derive tractable design rules and explicitly characterize the trade-offs between distortion, classification error, and transmission power.
SharedRep-RLHF: A Shared Representation Approach to RLHF with Diverse Preferences
Sep 03, 2025Abstract:Uniform-reward reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), which trains a single reward model to represent the preferences of all annotators, fails to capture the diversity of opinions across sub-populations, inadvertently favoring dominant groups. The state-of-the-art, MaxMin-RLHF, addresses this by learning group-specific reward models, and by optimizing for the group receiving the minimum reward, thereby promoting fairness. However, we identify that a key limitation of MaxMin-RLHF is its poor performance when the minimum-reward group is a minority. To mitigate this drawback, we introduce a novel framework, termed {\em SharedRep-RLHF}. At its core, SharedRep-RLHF learns and leverages {\em shared traits} in annotations among various groups, in contrast to learning separate reward models across groups. We first show that MaxMin-RLHF is provably suboptimal in learning shared traits, and then quantify the sample complexity of SharedRep-RLHF. Experiments across diverse natural language tasks showcase the effectiveness of SharedRep-RLHF compared to MaxMin-RLHF with a gain of up to 20% in win rate.
LotteryCodec: Searching the Implicit Representation in a Random Network for Low-Complexity Image Compression
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:We introduce and validate the lottery codec hypothesis, which states that untrained subnetworks within randomly initialized networks can serve as synthesis networks for overfitted image compression, achieving rate-distortion (RD) performance comparable to trained networks. This hypothesis leads to a new paradigm for image compression by encoding image statistics into the network substructure. Building on this hypothesis, we propose LotteryCodec, which overfits a binary mask to an individual image, leveraging an over-parameterized and randomly initialized network shared by the encoder and the decoder. To address over-parameterization challenges and streamline subnetwork search, we develop a rewind modulation mechanism that improves the RD performance. LotteryCodec outperforms VTM and sets a new state-of-the-art in single-image compression. LotteryCodec also enables adaptive decoding complexity through adjustable mask ratios, offering flexible compression solutions for diverse device constraints and application requirements.
ToDMA: Large Model-Driven Token-Domain Multiple Access for Semantic Communications
May 16, 2025Abstract:Token communications (TokCom) is an emerging generative semantic communication concept that reduces transmission rates by using context and multimodal large language model (MLLM)-based token processing, with tokens serving as universal semantic units across modalities. In this paper, we propose a semantic multiple access scheme in the token domain, referred to as token domain multiple access (ToDMA), where a large number of devices share a token codebook and a modulation codebook for source and channel coding, respectively. Specifically, each transmitter first tokenizes its source signal and modulate each token to a codeword. At the receiver, compressed sensing is employed first to detect active tokens and the corresponding channel state information (CSI) from the superposed signals. Then, the source token sequences are reconstructed by clustering the token-associated CSI across multiple time slots. In case of token collisions, some active tokens cannot be assigned and some positions in the reconstructed token sequences are empty. We propose to use pre-trained MLLMs to leverage the context, predict masked tokens, and thus mitigate token collisions. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed ToDMA framework for both text and image transmission tasks, achieving significantly lower latency compared to context-unaware orthogonal communication schemes, while also delivering superior distortion and perceptual quality compared to state-of-the-art context-unaware non-orthogonal communication methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge