Selim F. Yilmaz
SING: Semantic Image Communications using Null-Space and INN-Guided Diffusion Models
Mar 16, 2025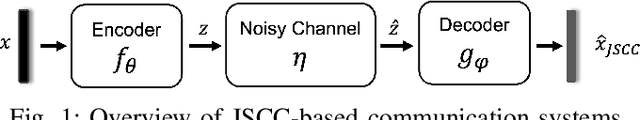
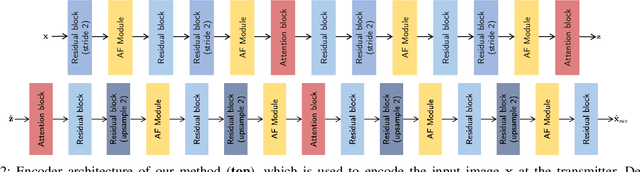
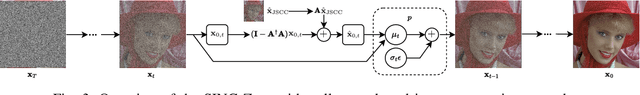
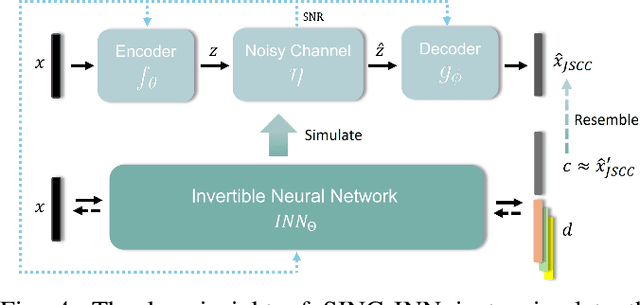
Abstract:Joint source-channel coding systems based on deep neural networks (DeepJSCC) have recently demonstrated remarkable performance in wireless image transmission. Existing methods primarily focus on minimizing distortion between the transmitted image and the reconstructed version at the receiver, often overlooking perceptual quality. This can lead to severe perceptual degradation when transmitting images under extreme conditions, such as low bandwidth compression ratios (BCRs) and low signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs). In this work, we propose SING, a novel two-stage JSCC framework that formulates the recovery of high-quality source images from corrupted reconstructions as an inverse problem. Depending on the availability of information about the DeepJSCC encoder/decoder and the channel at the receiver, SING can either approximate the stochastic degradation as a linear transformation, or leverage invertible neural networks (INNs) for precise modeling. Both approaches enable the seamless integration of diffusion models into the reconstruction process, enhancing perceptual quality. Experimental results demonstrate that SING outperforms DeepJSCC and other approaches, delivering superior perceptual quality even under extremely challenging conditions, including scenarios with significant distribution mismatches between the training and test data.
Federated Learning in Mobile Networks: A Comprehensive Case Study on Traffic Forecasting
Dec 05, 2024



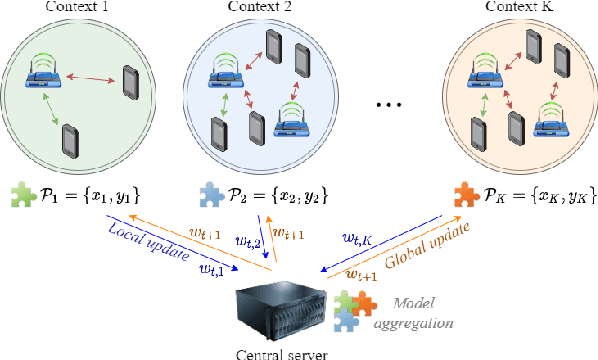
Abstract:The increasing demand for efficient resource allocation in mobile networks has catalyzed the exploration of innovative solutions that could enhance the task of real-time cellular traffic prediction. Under these circumstances, federated learning (FL) stands out as a distributed and privacy-preserving solution to foster collaboration among different sites, thus enabling responsive near-the-edge solutions. In this paper, we comprehensively study the potential benefits of FL in telecommunications through a case study on federated traffic forecasting using real-world data from base stations (BSs) in Barcelona (Spain). Our study encompasses relevant aspects within the federated experience, including model aggregation techniques, outlier management, the impact of individual clients, personalized learning, and the integration of exogenous sources of data. The performed evaluation is based on both prediction accuracy and sustainability, thus showcasing the environmental impact of employed FL algorithms in various settings. The findings from our study highlight FL as a promising and robust solution for mobile traffic prediction, emphasizing its twin merits as a privacy-conscious and environmentally sustainable approach, while also demonstrating its capability to overcome data heterogeneity and ensure high-quality predictions, marking a significant stride towards its integration in mobile traffic management systems.
Private Collaborative Edge Inference via Over-the-Air Computation
Jul 30, 2024

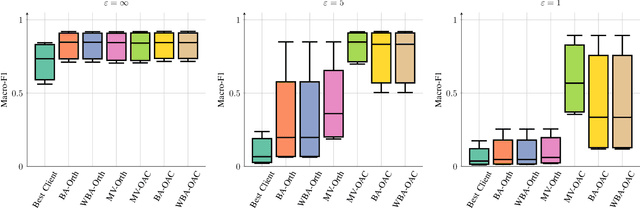

Abstract:We consider collaborative inference at the wireless edge, where each client's model is trained independently on their local datasets. Clients are queried in parallel to make an accurate decision collaboratively. In addition to maximizing the inference accuracy, we also want to ensure the privacy of local models. To this end, we leverage the superposition property of the multiple access channel to implement bandwidth-efficient multi-user inference methods. Specifically, we propose different methods for ensemble and multi-view classification that exploit over-the-air computation. We show that these schemes perform better than their orthogonal counterparts with statistically significant differences while using fewer resources and providing privacy guarantees. We also provide experimental results verifying the benefits of the proposed over-the-air multi-user inference approach and perform an ablation study to demonstrate the effectiveness of our design choices. We share the source code of the framework publicly on Github to facilitate further research and reproducibility.
Distributed Deep Joint Source-Channel Coding with Decoder-Only Side Information
Oct 06, 2023Abstract:We consider low-latency image transmission over a noisy wireless channel when correlated side information is present only at the receiver side (the Wyner-Ziv scenario). In particular, we are interested in developing practical schemes using a data-driven joint source-channel coding (JSCC) approach, which has been previously shown to outperform conventional separation-based approaches in the practical finite blocklength regimes, and to provide graceful degradation with channel quality. We propose a novel neural network architecture that incorporates the decoder-only side information at multiple stages at the receiver side. Our results demonstrate that the proposed method succeeds in integrating the side information, yielding improved performance at all channel noise levels in terms of the various distortion criteria considered here, especially at low channel signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) and small bandwidth ratios (BRs). We also provide the source code of the proposed method to enable further research and reproducibility of the results.
High Perceptual Quality Wireless Image Delivery with Denoising Diffusion Models
Sep 27, 2023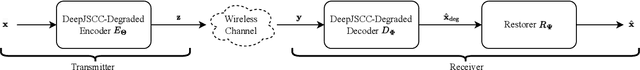
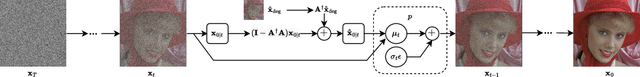
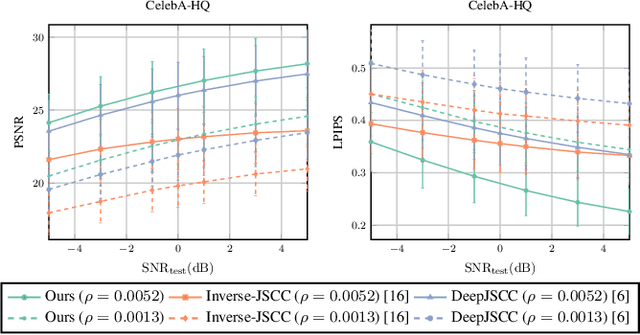
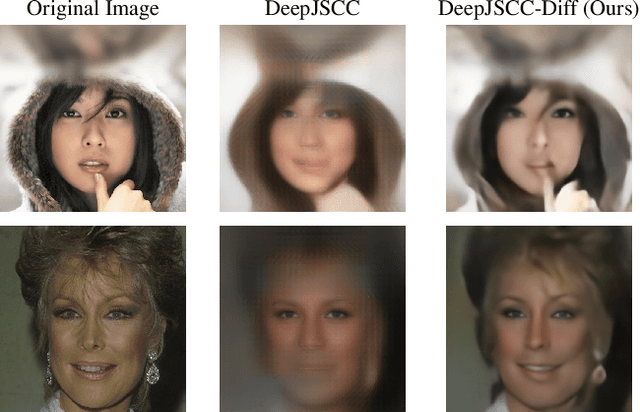
Abstract:We consider the image transmission problem over a noisy wireless channel via deep learning-based joint source-channel coding (DeepJSCC) along with a denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM) at the receiver. Specifically, we are interested in the perception-distortion trade-off in the practical finite block length regime, in which separate source and channel coding can be highly suboptimal. We introduce a novel scheme that utilizes the range-null space decomposition of the target image. We transmit the range-space of the image after encoding and employ DDPM to progressively refine its null space contents. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate significant improvements in distortion and perceptual quality of reconstructed images compared to standard DeepJSCC and the state-of-the-art generative learning-based method. We will publicly share our source code to facilitate further research and reproducibility.
Towards Energy-Aware Federated Traffic Prediction for Cellular Networks
Sep 19, 2023Abstract:Cellular traffic prediction is a crucial activity for optimizing networks in fifth-generation (5G) networks and beyond, as accurate forecasting is essential for intelligent network design, resource allocation and anomaly mitigation. Although machine learning (ML) is a promising approach to effectively predict network traffic, the centralization of massive data in a single data center raises issues regarding confidentiality, privacy and data transfer demands. To address these challenges, federated learning (FL) emerges as an appealing ML training framework which offers high accurate predictions through parallel distributed computations. However, the environmental impact of these methods is often overlooked, which calls into question their sustainability. In this paper, we address the trade-off between accuracy and energy consumption in FL by proposing a novel sustainability indicator that allows assessing the feasibility of ML models. Then, we comprehensively evaluate state-of-the-art deep learning (DL) architectures in a federated scenario using real-world measurements from base station (BS) sites in the area of Barcelona, Spain. Our findings indicate that larger ML models achieve marginally improved performance but have a significant environmental impact in terms of carbon footprint, which make them impractical for real-world applications.
Distributed Deep Joint Source-Channel Coding over a Multiple Access Channel
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:We consider distributed image transmission over a noisy multiple access channel (MAC) using deep joint source-channel coding (DeepJSCC). It is known that Shannon's separation theorem holds when transmitting independent sources over a MAC in the asymptotic infinite block length regime. However, we are interested in the practical finite block length regime, in which case separate source and channel coding is known to be suboptimal. We introduce a novel joint image compression and transmission scheme, where the devices send their compressed image representations in a non-orthogonal manner. While non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) is known to achieve the capacity region, to the best of our knowledge, non-orthogonal joint source channel coding (JSCC) scheme for practical systems has not been studied before. Through extensive experiments, we show significant improvements in terms of the quality of the reconstructed images compared to orthogonal transmission employing current DeepJSCC approaches particularly for low bandwidth ratios. We publicly share source code to facilitate further research and reproducibility.
Federated Spatial Reuse Optimization in Next-Generation Decentralized IEEE 802.11 WLANs
Mar 20, 2022

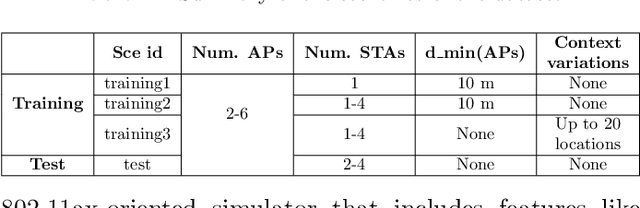
Abstract:As wireless standards evolve, more complex functionalities are introduced to address the increasing requirements in terms of throughput, latency, security, and efficiency. To unleash the potential of such new features, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are currently being exploited for deriving models and protocols from data, rather than by hand-programming. In this paper, we explore the feasibility of applying ML in next-generation wireless local area networks (WLANs). More specifically, we focus on the IEEE 802.11ax spatial reuse (SR) problem and predict its performance through federated learning (FL) models. The set of FL solutions overviewed in this work is part of the 2021 International Telecommunication Union (ITU) AI for 5G Challenge.
Over-the-Air Ensemble Inference with Model Privacy
Feb 07, 2022


Abstract:We consider distributed inference at the wireless edge, where multiple clients with an ensemble of models, each trained independently on a local dataset, are queried in parallel to make an accurate decision on a new sample. In addition to maximizing inference accuracy, we also want to maximize the privacy of local models. We exploit the superposition property of the air to implement bandwidth-efficient ensemble inference methods. We introduce different over-the-air ensemble methods and show that these schemes perform significantly better than their orthogonal counterparts, while using less resources and providing privacy guarantees. We also provide experimental results verifying the benefits of the proposed over-the-air inference approach, whose source code is shared publicly on Github.
PySAD: A Streaming Anomaly Detection Framework in Python
Sep 05, 2020

Abstract:PySAD is an open-source python framework for anomaly detection on streaming data. PySAD serves various state-of-the-art methods for streaming anomaly detection. The framework provides a complete set of tools to design anomaly detection experiments ranging from projectors to probability calibrators. PySAD builds upon popular open-source frameworks such as PyOD and scikit-learn. We enforce software quality by enforcing compliance with PEP8 guidelines, functional testing and using continuous integration. The source code is publicly available on https://github.com/selimfirat/pysad.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge