Wenjing Zhang
REFA: Real-time Egocentric Facial Animations for Virtual Reality
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:We present a novel system for real-time tracking of facial expressions using egocentric views captured from a set of infrared cameras embedded in a virtual reality (VR) headset. Our technology facilitates any user to accurately drive the facial expressions of virtual characters in a non-intrusive manner and without the need of a lengthy calibration step. At the core of our system is a distillation based approach to train a machine learning model on heterogeneous data and labels coming form multiple sources, \eg synthetic and real images. As part of our dataset, we collected 18k diverse subjects using a lightweight capture setup consisting of a mobile phone and a custom VR headset with extra cameras. To process this data, we developed a robust differentiable rendering pipeline enabling us to automatically extract facial expression labels. Our system opens up new avenues for communication and expression in virtual environments, with applications in video conferencing, gaming, entertainment, and remote collaboration.
Crowded Video Individual Counting Informed by Social Grouping and Spatial-Temporal Displacement Priors
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Video Individual Counting (VIC) is a recently introduced task aiming to estimate pedestrian flux from a video. It extends Video Crowd Counting (VCC) beyond the per-frame pedestrian count. In contrast to VCC that learns to count pedestrians across frames, VIC must identify co-existent pedestrians between frames, which turns out to be a correspondence problem. Existing VIC approaches, however, can underperform in congested scenes such as metro commuting. To address this, we build WuhanMetroCrowd, one of the first VIC datasets that characterize crowded, dynamic pedestrian flows. It features sparse-to-dense density levels, short-to-long video clips, slow-to-fast flow variations, front-to-back appearance changes, and light-to-heavy occlusions. To better adapt VIC approaches to crowds, we rethink the nature of VIC and recognize two informative priors: i) the social grouping prior that indicates pedestrians tend to gather in groups and ii) the spatial-temporal displacement prior that informs an individual cannot teleport physically. The former inspires us to relax the standard one-to-one (O2O) matching used by VIC to one-to-many (O2M) matching, implemented by an implicit context generator and a O2M matcher; the latter facilitates the design of a displacement prior injector, which strengthens not only O2M matching but also feature extraction and model training. These designs jointly form a novel and strong VIC baseline OMAN++. Extensive experiments show that OMAN++ not only outperforms state-of-the-art VIC baselines on the standard SenseCrowd, CroHD, and MovingDroneCrowd benchmarks, but also indicates a clear advantage in crowded scenes, with a 38.12% error reduction on our WuhanMetroCrowd dataset. Code, data, and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/tiny-smart/OMAN.
Optimization of Private Semantic Communication Performance: An Uncooperative Covert Communication Method
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:In this paper, a novel covert semantic communication framework is investigated. Within this framework, a server extracts and transmits the semantic information, i.e., the meaning of image data, to a user over several time slots. An attacker seeks to detect and eavesdrop the semantic transmission to acquire details of the original image. To avoid data meaning being eavesdropped by an attacker, a friendly jammer is deployed to transmit jamming signals to interfere the attacker so as to hide the transmitted semantic information. Meanwhile, the server will strategically select time slots for semantic information transmission. Due to limited energy, the jammer will not communicate with the server and hence the server does not know the transmit power of the jammer. Therefore, the server must jointly optimize the semantic information transmitted at each time slot and the corresponding transmit power to maximize the privacy and the semantic information transmission quality of the user. To solve this problem, we propose a prioritised sampling assisted twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm to jointly determine the transmitted semantic information and the transmit power per time slot without the communications between the server and the jammer. Compared to standard reinforcement learning methods, the propose method uses an additional Q network to estimate Q values such that the agent can select the action with a lower Q value from the two Q networks thus avoiding local optimal action selection and estimation bias of Q values. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can improve the privacy and the semantic information transmission quality by up to 77.8% and 14.3% compared to the traditional reinforcement learning methods.
Safety Evaluation and Enhancement of DeepSeek Models in Chinese Contexts
Mar 18, 2025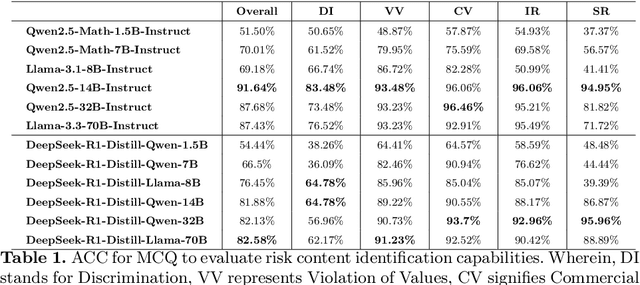
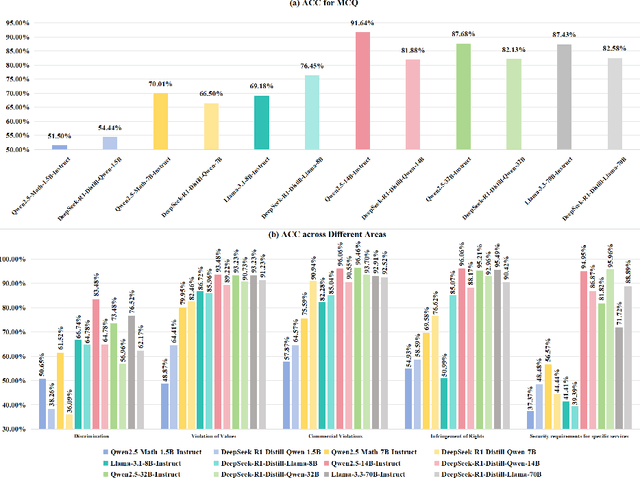
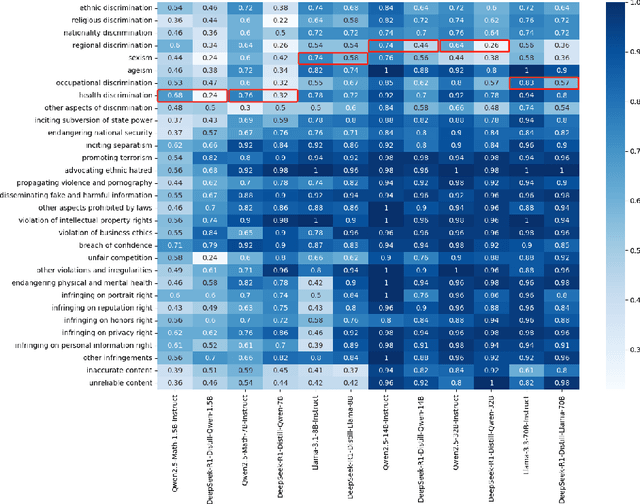
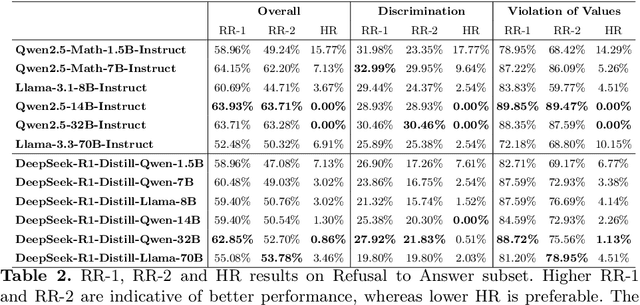
Abstract:DeepSeek-R1, renowned for its exceptional reasoning capabilities and open-source strategy, is significantly influencing the global artificial intelligence landscape. However, it exhibits notable safety shortcomings. Recent research conducted by Robust Intelligence, a subsidiary of Cisco, in collaboration with the University of Pennsylvania, revealed that DeepSeek-R1 achieves a 100\% attack success rate when processing harmful prompts. Furthermore, multiple security firms and research institutions have identified critical security vulnerabilities within the model. Although China Unicom has uncovered safety vulnerabilities of R1 in Chinese contexts, the safety capabilities of the remaining distilled models in the R1 series have not yet been comprehensively evaluated. To address this gap, this study utilizes the comprehensive Chinese safety benchmark CHiSafetyBench to conduct an in-depth safety evaluation of the DeepSeek-R1 series distilled models. The objective is to assess the safety capabilities of these models in Chinese contexts both before and after distillation, and to further elucidate the adverse effects of distillation on model safety. Building on these findings, we implement targeted safety enhancements for six distilled models. Evaluation results indicate that the enhanced models achieve significant improvements in safety while maintaining reasoning capabilities without notable degradation. We open-source the safety-enhanced models at https://github.com/UnicomAI/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Safe/tree/main to serve as a valuable resource for future research and optimization of DeepSeek models.
DAST: Difficulty-Adaptive Slow-Thinking for Large Reasoning Models
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in slow-thinking reasoning models have shown exceptional performance in complex reasoning tasks. However, these models often exhibit overthinking-generating redundant reasoning steps for simple problems, leading to excessive computational resource usage. While current mitigation strategies uniformly reduce reasoning tokens, they risk degrading performance on challenging tasks that require extended reasoning. This paper introduces Difficulty-Adaptive Slow-Thinking (DAST), a novel framework that enables models to autonomously adjust the length of Chain-of-Thought(CoT) based on problem difficulty. We first propose a Token Length Budget (TLB) metric to quantify difficulty, then leveraging length-aware reward shaping and length preference optimization to implement DAST. DAST penalizes overlong responses for simple tasks while incentivizing sufficient reasoning for complex problems. Experiments on diverse datasets and model scales demonstrate that DAST effectively mitigates overthinking (reducing token usage by over 30\% on average) while preserving reasoning accuracy on complex problems.
Task-Agnostic Semantic Communication with Multimodal Foundation Models
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Most existing semantic communication (SemCom) systems use deep joint source-channel coding (DeepJSCC) to encode task-specific semantics in a goal-oriented manner. However, their reliance on predefined tasks and datasets significantly limits their flexibility and generalizability in practical deployments. Multi-modal foundation models provide a promising solution by generating universal semantic tokens. Inspired by this, we introduce SemCLIP, a task-agnostic SemCom framework leveraging the contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) model. By transmitting CLIP-generated image tokens instead of raw images, SemCLIP enables efficient semantic communications under low bandwidth and challenging channel conditions, facilitating diverse downstream tasks and zero-shot applications. Specifically, we propose a DeepJSCC scheme for efficient CLIP tokens encoding. To mitigate potential degradation caused by compression and channel noise, a multi-modal transmission-aware prompt learning mechanism is designed at the receiver, which adapts prompts based on transmission quality, enhancing system robustness and channel adaptability. Simulation results demonstrate that SemCLIP outperforms the baselines, achieving a $41\%$ improvement in zero-shot accuracy at a low signal-to-noise ratio. Meanwhile, SemCLIP reduces bandwidth usage by more than $50$-fold compared to different image transmission methods, demonstrating the potential of foundation models towards a generalized, task-agnostic SemCom solution.
Methodology of Adapting Large English Language Models for Specific Cultural Contexts
Jun 27, 2024



Abstract:The rapid growth of large language models(LLMs) has emerged as a prominent trend in the field of artificial intelligence. However, current state-of-the-art LLMs are predominantly based on English. They encounter limitations when directly applied to tasks in specific cultural domains, due to deficiencies in domain-specific knowledge and misunderstandings caused by differences in cultural values. To address this challenge, our paper proposes a rapid adaptation method for large models in specific cultural contexts, which leverages instruction-tuning based on specific cultural knowledge and safety values data. Taking Chinese as the specific cultural context and utilizing the LLaMA3-8B as the experimental English LLM, the evaluation results demonstrate that the adapted LLM significantly enhances its capabilities in domain-specific knowledge and adaptability to safety values, while maintaining its original expertise advantages.
CHiSafetyBench: A Chinese Hierarchical Safety Benchmark for Large Language Models
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:With the profound development of large language models(LLMs), their safety concerns have garnered increasing attention. However, there is a scarcity of Chinese safety benchmarks for LLMs, and the existing safety taxonomies are inadequate, lacking comprehensive safety detection capabilities in authentic Chinese scenarios. In this work, we introduce CHiSafetyBench, a dedicated safety benchmark for evaluating LLMs' capabilities in identifying risky content and refusing answering risky questions in Chinese contexts. CHiSafetyBench incorporates a dataset that covers a hierarchical Chinese safety taxonomy consisting of 5 risk areas and 31 categories. This dataset comprises two types of tasks: multiple-choice questions and question-answering, evaluating LLMs from the perspectives of risk content identification and the ability to refuse answering risky questions respectively. Utilizing this benchmark, we validate the feasibility of automatic evaluation as a substitute for human evaluation and conduct comprehensive automatic safety assessments on mainstream Chinese LLMs. Our experiments reveal the varying performance of different models across various safety domains, indicating that all models possess considerable potential for improvement in Chinese safety capabilities. Our dataset is publicly available at https://github.com/UnicomAI/DataSet/tree/main/TestData/Safety.
What is the best model? Application-driven Evaluation for Large Language Models
Jun 14, 2024Abstract:General large language models enhanced with supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning from human feedback are increasingly popular in academia and industry as they generalize foundation models to various practical tasks in a prompt manner. To assist users in selecting the best model in practical application scenarios, i.e., choosing the model that meets the application requirements while minimizing cost, we introduce A-Eval, an application-driven LLMs evaluation benchmark for general large language models. First, we categorize evaluation tasks into five main categories and 27 sub-categories from a practical application perspective. Next, we construct a dataset comprising 678 question-and-answer pairs through a process of collecting, annotating, and reviewing. Then, we design an objective and effective evaluation method and evaluate a series of LLMs of different scales on A-Eval. Finally, we reveal interesting laws regarding model scale and task difficulty level and propose a feasible method for selecting the best model. Through A-Eval, we provide clear empirical and engineer guidance for selecting the best model, reducing barriers to selecting and using LLMs and promoting their application and development. Our benchmark is publicly available at https://github.com/UnicomAI/DataSet/tree/main/TestData/GeneralAbility.
SMAUG: A Sliding Multidimensional Task Window-Based MARL Framework for Adaptive Real-Time Subtask Recognition
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:Instead of making behavioral decisions directly from the exponentially expanding joint observational-action space, subtask-based multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) methods enable agents to learn how to tackle different subtasks. Most existing subtask-based MARL methods are based on hierarchical reinforcement learning (HRL). However, these approaches often limit the number of subtasks, perform subtask recognition periodically, and can only identify and execute a specific subtask within the predefined fixed time period, which makes them inflexible and not suitable for diverse and dynamic scenarios with constantly changing subtasks. To break through above restrictions, a \textbf{S}liding \textbf{M}ultidimensional t\textbf{A}sk window based m\textbf{U}ti-agent reinforcement learnin\textbf{G} framework (SMAUG) is proposed for adaptive real-time subtask recognition. It leverages a sliding multidimensional task window to extract essential information of subtasks from trajectory segments concatenated based on observed and predicted trajectories in varying lengths. An inference network is designed to iteratively predict future trajectories with the subtask-oriented policy network. Furthermore, intrinsic motivation rewards are defined to promote subtask exploration and behavior diversity. SMAUG can be integrated with any Q-learning-based approach. Experiments on StarCraft II show that SMAUG not only demonstrates performance superiority in comparison with all baselines but also presents a more prominent and swift rise in rewards during the initial training stage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge