Tao Luo
Let It Flow: Agentic Crafting on Rock and Roll, Building the ROME Model within an Open Agentic Learning Ecosystem
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Agentic crafting requires LLMs to operate in real-world environments over multiple turns by taking actions, observing outcomes, and iteratively refining artifacts. Despite its importance, the open-source community lacks a principled, end-to-end ecosystem to streamline agent development. We introduce the Agentic Learning Ecosystem (ALE), a foundational infrastructure that optimizes the production pipeline for agent LLMs. ALE consists of three components: ROLL, a post-training framework for weight optimization; ROCK, a sandbox environment manager for trajectory generation; and iFlow CLI, an agent framework for efficient context engineering. We release ROME (ROME is Obviously an Agentic Model), an open-source agent grounded by ALE and trained on over one million trajectories. Our approach includes data composition protocols for synthesizing complex behaviors and a novel policy optimization algorithm, Interaction-based Policy Alignment (IPA), which assigns credit over semantic interaction chunks rather than individual tokens to improve long-horizon training stability. Empirically, we evaluate ROME within a structured setting and introduce Terminal Bench Pro, a benchmark with improved scale and contamination control. ROME demonstrates strong performance across benchmarks like SWE-bench Verified and Terminal Bench, proving the effectiveness of the ALE infrastructure.
From Condensation to Rank Collapse: A Two-Stage Analysis of Transformer Training Dynamics
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Although transformer-based models have shown exceptional empirical performance, the fundamental principles governing their training dynamics are inadequately characterized beyond configuration-specific studies. Inspired by empirical evidence showing improved reasoning capabilities under small initialization scales in language models, we employ the gradient flow analytical framework established in [Zhou et al. NeurIPS 2022] to systematically investigate linearized Transformer training dynamics. Our theoretical analysis dissects the dynamics of attention modules into two distinct stages. In the first stage, asymmetric weight perturbations from random initialization sustain non-degenerate gradient dynamics in parameter matrices, facilitating systematic escape from small initialization regimes. Subsequently, these matrices undergo condensation, progressively aligning toward the target orientation. In the second stage, the previously static key-query matrices actively participate in training, driving the normalized matrices toward asymptotic rank collapse. This two-stage framework generalizes classical directional convergence results.
ASSESS: A Semantic and Structural Evaluation Framework for Statement Similarity
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Statement autoformalization, the automated translation of statements from natural language into formal languages, has seen significant advancements, yet the development of automated evaluation metrics remains limited. Existing metrics for formal statement similarity often fail to balance semantic and structural information. String-based approaches capture syntactic structure but ignore semantic meaning, whereas proof-based methods validate semantic equivalence but disregard structural nuances and, critically, provide no graded similarity score in the event of proof failure. To address these issues, we introduce ASSESS (A Semantic and Structural Evaluation Framework for Statement Similarity), which comprehensively integrates semantic and structural information to provide a continuous similarity score. Our framework first transforms formal statements into Operator Trees to capture their syntactic structure and then computes a similarity score using our novel TransTED (Transformation Tree Edit Distance) Similarity metric, which enhances traditional Tree Edit Distance by incorporating semantic awareness through transformations. For rigorous validation, we present EPLA (Evaluating Provability and Likeness for Autoformalization), a new benchmark of 524 expert-annotated formal statement pairs derived from miniF2F and ProofNet, with labels for both semantic provability and structural likeness. Experiments on EPLA demonstrate that TransTED Similarity outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy and the highest Kappa coefficient. The benchmark, and implementation code will be made public soon.
UniView: Enhancing Novel View Synthesis From A Single Image By Unifying Reference Features
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:The task of synthesizing novel views from a single image is highly ill-posed due to multiple explanations for unobserved areas. Most current methods tend to generate unseen regions from ambiguity priors and interpolation near input views, which often lead to severe distortions. To address this limitation, we propose a novel model dubbed as UniView, which can leverage reference images from a similar object to provide strong prior information during view synthesis. More specifically, we construct a retrieval and augmentation system and employ a multimodal large language model (MLLM) to assist in selecting reference images that meet our requirements. Additionally, a plug-and-play adapter module with multi-level isolation layers is introduced to dynamically generate reference features for the target views. Moreover, in order to preserve the details of an original input image, we design a decoupled triple attention mechanism, which can effectively align and integrate multi-branch features into the synthesis process. Extensive experiments have demonstrated that our UniView significantly improves novel view synthesis performance and outperforms state-of-the-art methods on the challenging datasets.
Adapting Foundation Model for Dental Caries Detection with Dual-View Co-Training
Aug 28, 2025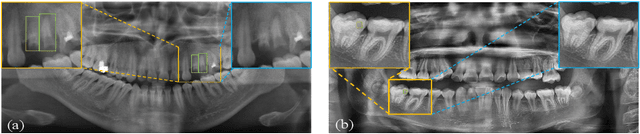
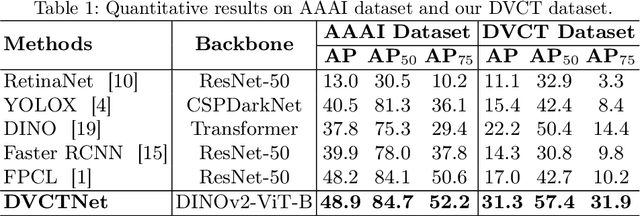
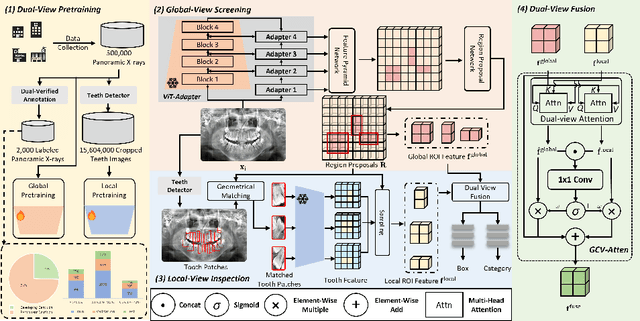
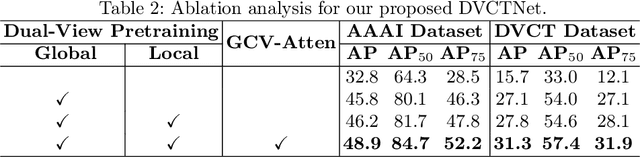
Abstract:Accurate dental caries detection from panoramic X-rays plays a pivotal role in preventing lesion progression. However, current detection methods often yield suboptimal accuracy due to subtle contrast variations and diverse lesion morphology of dental caries. In this work, inspired by the clinical workflow where dentists systematically combine whole-image screening with detailed tooth-level inspection, we present DVCTNet, a novel Dual-View Co-Training network for accurate dental caries detection. Our DVCTNet starts with employing automated tooth detection to establish two complementary views: a global view from panoramic X-ray images and a local view from cropped tooth images. We then pretrain two vision foundation models separately on the two views. The global-view foundation model serves as the detection backbone, generating region proposals and global features, while the local-view model extracts detailed features from corresponding cropped tooth patches matched by the region proposals. To effectively integrate information from both views, we introduce a Gated Cross-View Attention (GCV-Atten) module that dynamically fuses dual-view features, enhancing the detection pipeline by integrating the fused features back into the detection model for final caries detection. To rigorously evaluate our DVCTNet, we test it on a public dataset and further validate its performance on a newly curated, high-precision dental caries detection dataset, annotated using both intra-oral images and panoramic X-rays for double verification. Experimental results demonstrate DVCTNet's superior performance against existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on both datasets, indicating the clinical applicability of our method. Our code and labeled dataset are available at https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/DVCTNet.
Optimizing Neural Networks with Learnable Non-Linear Activation Functions via Lookup-Based FPGA Acceleration
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Learned activation functions in models like Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) outperform fixed-activation architectures in terms of accuracy and interpretability; however, their computational complexity poses critical challenges for energy-constrained edge AI deployments. Conventional CPUs/GPUs incur prohibitive latency and power costs when evaluating higher order activations, limiting deployability under ultra-tight energy budgets. We address this via a reconfigurable lookup architecture with edge FPGAs. By coupling fine-grained quantization with adaptive lookup tables, our design minimizes energy-intensive arithmetic operations while preserving activation fidelity. FPGA reconfigurability enables dynamic hardware specialization for learned functions, a key advantage for edge systems that require post-deployment adaptability. Evaluations using KANs - where unique activation functions play a critical role - demonstrate that our FPGA-based design achieves superior computational speed and over $10^4$ times higher energy efficiency compared to edge CPUs and GPUs, while maintaining matching accuracy and minimal footprint overhead. This breakthrough positions our approach as a practical enabler for energy-critical edge AI, where computational intensity and power constraints traditionally preclude the use of adaptive activation networks.
MMIF-AMIN: Adaptive Loss-Driven Multi-Scale Invertible Dense Network for Multimodal Medical Image Fusion
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Multimodal medical image fusion (MMIF) aims to integrate images from different modalities to produce a comprehensive image that enhances medical diagnosis by accurately depicting organ structures, tissue textures, and metabolic information. Capturing both the unique and complementary information across multiple modalities simultaneously is a key research challenge in MMIF. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a novel image fusion method, MMIF-AMIN, which features a new architecture that can effectively extract these unique and complementary features. Specifically, an Invertible Dense Network (IDN) is employed for lossless feature extraction from individual modalities. To extract complementary information between modalities, a Multi-scale Complementary Feature Extraction Module (MCFEM) is designed, which incorporates a hybrid attention mechanism, convolutional layers of varying sizes, and Transformers. An adaptive loss function is introduced to guide model learning, addressing the limitations of traditional manually-designed loss functions and enhancing the depth of data mining. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MMIF-AMIN outperforms nine state-of-the-art MMIF methods, delivering superior results in both quantitative and qualitative analyses. Ablation experiments confirm the effectiveness of each component of the proposed method. Additionally, extending MMIF-AMIN to other image fusion tasks also achieves promising performance.
Optimization of Private Semantic Communication Performance: An Uncooperative Covert Communication Method
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:In this paper, a novel covert semantic communication framework is investigated. Within this framework, a server extracts and transmits the semantic information, i.e., the meaning of image data, to a user over several time slots. An attacker seeks to detect and eavesdrop the semantic transmission to acquire details of the original image. To avoid data meaning being eavesdropped by an attacker, a friendly jammer is deployed to transmit jamming signals to interfere the attacker so as to hide the transmitted semantic information. Meanwhile, the server will strategically select time slots for semantic information transmission. Due to limited energy, the jammer will not communicate with the server and hence the server does not know the transmit power of the jammer. Therefore, the server must jointly optimize the semantic information transmitted at each time slot and the corresponding transmit power to maximize the privacy and the semantic information transmission quality of the user. To solve this problem, we propose a prioritised sampling assisted twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm to jointly determine the transmitted semantic information and the transmit power per time slot without the communications between the server and the jammer. Compared to standard reinforcement learning methods, the propose method uses an additional Q network to estimate Q values such that the agent can select the action with a lower Q value from the two Q networks thus avoiding local optimal action selection and estimation bias of Q values. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can improve the privacy and the semantic information transmission quality by up to 77.8% and 14.3% compared to the traditional reinforcement learning methods.
RecGPT Technical Report
Jul 30, 2025



Abstract:Recommender systems are among the most impactful applications of artificial intelligence, serving as critical infrastructure connecting users, merchants, and platforms. However, most current industrial systems remain heavily reliant on historical co-occurrence patterns and log-fitting objectives, i.e., optimizing for past user interactions without explicitly modeling user intent. This log-fitting approach often leads to overfitting to narrow historical preferences, failing to capture users' evolving and latent interests. As a result, it reinforces filter bubbles and long-tail phenomena, ultimately harming user experience and threatening the sustainability of the whole recommendation ecosystem. To address these challenges, we rethink the overall design paradigm of recommender systems and propose RecGPT, a next-generation framework that places user intent at the center of the recommendation pipeline. By integrating large language models (LLMs) into key stages of user interest mining, item retrieval, and explanation generation, RecGPT transforms log-fitting recommendation into an intent-centric process. To effectively align general-purpose LLMs to the above domain-specific recommendation tasks at scale, RecGPT incorporates a multi-stage training paradigm, which integrates reasoning-enhanced pre-alignment and self-training evolution, guided by a Human-LLM cooperative judge system. Currently, RecGPT has been fully deployed on the Taobao App. Online experiments demonstrate that RecGPT achieves consistent performance gains across stakeholders: users benefit from increased content diversity and satisfaction, merchants and the platform gain greater exposure and conversions. These comprehensive improvement results across all stakeholders validates that LLM-driven, intent-centric design can foster a more sustainable and mutually beneficial recommendation ecosystem.
Generalized Tree Edit Distance (GTED): A Faithful Evaluation Metric for Statement Autoformalization
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Statement autoformalization, the automated translation of statement from natural language into formal languages, has become a subject of extensive research, yet the development of robust automated evaluation metrics remains limited. Existing evaluation methods often lack semantic understanding, face challenges with high computational costs, and are constrained by the current progress of automated theorem proving. To address these issues, we propose GTED (Generalized Tree Edit Distance), a novel evaluation framework that first standardizes formal statements and converts them into operator trees, then determines the semantic similarity using the eponymous GTED metric. On the miniF2F and ProofNet benchmarks, GTED outperforms all baseline metrics by achieving the highest accuracy and Kappa scores, thus providing the community with a more faithful metric for automated evaluation. The code and experimental results are available at https://github.com/XiaoyangLiu-sjtu/GTED.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge