Rick Siow Mong Goh
Aligning Medical Conversational AI through Online Reinforcement Learning with Information-Theoretic Rewards
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:We present Information Gain Fine-Tuning (IGFT), a novel approach for training medical conversational AI to conduct effective patient interviews and generate comprehensive History of Present Illness (HPI) without requiring pre-collected human conversations. IGFT combines online Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with information-theoretic rewards, enabling models to learn from self-generated conversations with simulated patients. Unlike existing approaches that rely on expensive expert-annotated conversations or static datasets, our online RL framework allows models to discover effective questioning strategies through exploration. Our key innovation is an information gain reward function that tracks which clinical entities such as symptoms, temporal patterns, and medical history, are revealed during conversation. Each question's reward is computed based on its expected information gain combined with GPT-4o-mini quality assessments across dimensions including clinical relevance, patient engagement, and specificity. This hybrid approach ensures models learn to ask targeted, clinically appropriate questions that efficiently gather diagnostic information. We fine-tune two models using LoRA: Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B (a reasoning-optimized model). Training exclusively on Avey data containing concise HPIs, we evaluate generalization to MIMIC data with longer, more elaborate HPIs. DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B (IGFT) achieves F1 scores of 0.408 on Avey (10.9% improvement over base) and 0.289 on MIMIC (12.9% improvement), while Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct (IGFT) reaches 0.384 and 0.336 respectively. Both models outperform OpenAI's model on MIMIC and surpass medical domain-specific baselines like HuatuoGPT and UltraMedical, which were optimized for single-turn medical QA rather than multi-turn conversations.
Optimizing Neural Networks with Learnable Non-Linear Activation Functions via Lookup-Based FPGA Acceleration
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Learned activation functions in models like Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) outperform fixed-activation architectures in terms of accuracy and interpretability; however, their computational complexity poses critical challenges for energy-constrained edge AI deployments. Conventional CPUs/GPUs incur prohibitive latency and power costs when evaluating higher order activations, limiting deployability under ultra-tight energy budgets. We address this via a reconfigurable lookup architecture with edge FPGAs. By coupling fine-grained quantization with adaptive lookup tables, our design minimizes energy-intensive arithmetic operations while preserving activation fidelity. FPGA reconfigurability enables dynamic hardware specialization for learned functions, a key advantage for edge systems that require post-deployment adaptability. Evaluations using KANs - where unique activation functions play a critical role - demonstrate that our FPGA-based design achieves superior computational speed and over $10^4$ times higher energy efficiency compared to edge CPUs and GPUs, while maintaining matching accuracy and minimal footprint overhead. This breakthrough positions our approach as a practical enabler for energy-critical edge AI, where computational intensity and power constraints traditionally preclude the use of adaptive activation networks.
Improving Learning of New Diseases through Knowledge-Enhanced Initialization for Federated Adapter Tuning
Aug 14, 2025

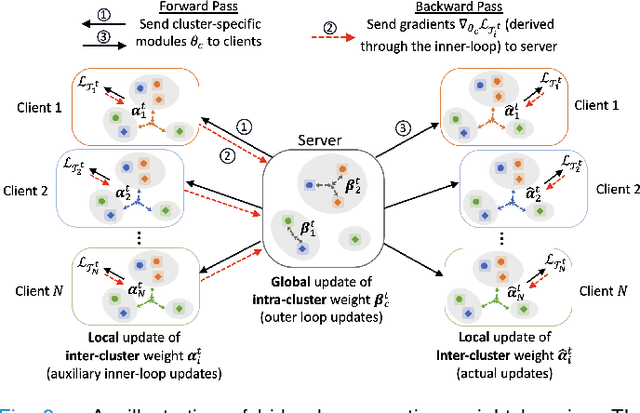
Abstract:In healthcare, federated learning (FL) is a widely adopted framework that enables privacy-preserving collaboration among medical institutions. With large foundation models (FMs) demonstrating impressive capabilities, using FMs in FL through cost-efficient adapter tuning has become a popular approach. Given the rapidly evolving healthcare environment, it is crucial for individual clients to quickly adapt to new tasks or diseases by tuning adapters while drawing upon past experiences. In this work, we introduce Federated Knowledge-Enhanced Initialization (FedKEI), a novel framework that leverages cross-client and cross-task transfer from past knowledge to generate informed initializations for learning new tasks with adapters. FedKEI begins with a global clustering process at the server to generalize knowledge across tasks, followed by the optimization of aggregation weights across clusters (inter-cluster weights) and within each cluster (intra-cluster weights) to personalize knowledge transfer for each new task. To facilitate more effective learning of the inter- and intra-cluster weights, we adopt a bi-level optimization scheme that collaboratively learns the global intra-cluster weights across clients and optimizes the local inter-cluster weights toward each client's task objective. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets of different modalities, including dermatology, chest X-rays, and retinal OCT, demonstrate FedKEI's advantage in adapting to new diseases compared to state-of-the-art methods.
MaskedCLIP: Bridging the Masked and CLIP Space for Semi-Supervised Medical Vision-Language Pre-training
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Foundation models have recently gained tremendous popularity in medical image analysis. State-of-the-art methods leverage either paired image-text data via vision-language pre-training or unpaired image data via self-supervised pre-training to learn foundation models with generalizable image features to boost downstream task performance. However, learning foundation models exclusively on either paired or unpaired image data limits their ability to learn richer and more comprehensive image features. In this paper, we investigate a novel task termed semi-supervised vision-language pre-training, aiming to fully harness the potential of both paired and unpaired image data for foundation model learning. To this end, we propose MaskedCLIP, a synergistic masked image modeling and contrastive language-image pre-training framework for semi-supervised vision-language pre-training. The key challenge in combining paired and unpaired image data for learning a foundation model lies in the incompatible feature spaces derived from these two types of data. To address this issue, we propose to connect the masked feature space with the CLIP feature space with a bridge transformer. In this way, the more semantic specific CLIP features can benefit from the more general masked features for semantic feature extraction. We further propose a masked knowledge distillation loss to distill semantic knowledge of original image features in CLIP feature space back to the predicted masked image features in masked feature space. With this mutually interactive design, our framework effectively leverages both paired and unpaired image data to learn more generalizable image features for downstream tasks. Extensive experiments on retinal image analysis demonstrate the effectiveness and data efficiency of our method.
AdvMIM: Adversarial Masked Image Modeling for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:Vision Transformer has recently gained tremendous popularity in medical image segmentation task due to its superior capability in capturing long-range dependencies. However, transformer requires a large amount of labeled data to be effective, which hinders its applicability in annotation scarce semi-supervised learning scenario where only limited labeled data is available. State-of-the-art semi-supervised learning methods propose combinatorial CNN-Transformer learning to cross teach a transformer with a convolutional neural network, which achieves promising results. However, it remains a challenging task to effectively train the transformer with limited labeled data. In this paper, we propose an adversarial masked image modeling method to fully unleash the potential of transformer for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. The key challenge in semi-supervised learning with transformer lies in the lack of sufficient supervision signal. To this end, we propose to construct an auxiliary masked domain from original domain with masked image modeling and train the transformer to predict the entire segmentation mask with masked inputs to increase supervision signal. We leverage the original labels from labeled data and pseudo-labels from unlabeled data to learn the masked domain. To further benefit the original domain from masked domain, we provide a theoretical analysis of our method from a multi-domain learning perspective and devise a novel adversarial training loss to reduce the domain gap between the original and masked domain, which boosts semi-supervised learning performance. We also extend adversarial masked image modeling to CNN network. Extensive experiments on three public medical image segmentation datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, where our method outperforms existing methods significantly. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/zlheui/AdvMIM.
Text to Image for Multi-Label Image Recognition with Joint Prompt-Adapter Learning
Jun 12, 2025



Abstract:Benefited from image-text contrastive learning, pre-trained vision-language models, e.g., CLIP, allow to direct leverage texts as images (TaI) for parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT). While CLIP is capable of making image features to be similar to the corresponding text features, the modality gap remains a nontrivial issue and limits image recognition performance of TaI. Using multi-label image recognition (MLR) as an example, we present a novel method, called T2I-PAL to tackle the modality gap issue when using only text captions for PEFT. The core design of T2I-PAL is to leverage pre-trained text-to-image generation models to generate photo-realistic and diverse images from text captions, thereby reducing the modality gap. To further enhance MLR, T2I-PAL incorporates a class-wise heatmap and learnable prototypes. This aggregates local similarities, making the representation of local visual features more robust and informative for multi-label recognition. For better PEFT, we further combine both prompt tuning and adapter learning to enhance classification performance. T2I-PAL offers significant advantages: it eliminates the need for fully semantically annotated training images, thereby reducing the manual annotation workload, and it preserves the intrinsic mode of the CLIP model, allowing for seamless integration with any existing CLIP framework. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks, including MS-COCO, VOC2007, and NUS-WIDE, show that our T2I-PAL can boost recognition performance by 3.47% in average above the top-ranked state-of-the-art methods.
Is Quantum Optimization Ready? An Effort Towards Neural Network Compression using Adiabatic Quantum Computing
May 22, 2025



Abstract:Quantum optimization is the most mature quantum computing technology to date, providing a promising approach towards efficiently solving complex combinatorial problems. Methods such as adiabatic quantum computing (AQC) have been employed in recent years on important optimization problems across various domains. In deep learning, deep neural networks (DNN) have reached immense sizes to support new predictive capabilities. Optimization of large-scale models is critical for sustainable deployment, but becomes increasingly challenging with ever-growing model sizes and complexity. While quantum optimization is suitable for solving complex problems, its application to DNN optimization is not straightforward, requiring thorough reformulation for compatibility with commercially available quantum devices. In this work, we explore the potential of adopting AQC for fine-grained pruning-quantization of convolutional neural networks. We rework established heuristics to formulate model compression as a quadratic unconstrained binary optimization (QUBO) problem, and assess the solution space offered by commercial quantum annealing devices. Through our exploratory efforts of reformulation, we demonstrate that AQC can achieve effective compression of practical DNN models. Experiments demonstrate that adiabatic quantum computing (AQC) not only outperforms classical algorithms like genetic algorithms and reinforcement learning in terms of time efficiency but also excels at identifying global optima.
An integrated language-vision foundation model for conversational diagnostics and triaging in primary eye care
May 13, 2025Abstract:Current deep learning models are mostly task specific and lack a user-friendly interface to operate. We present Meta-EyeFM, a multi-function foundation model that integrates a large language model (LLM) with vision foundation models (VFMs) for ocular disease assessment. Meta-EyeFM leverages a routing mechanism to enable accurate task-specific analysis based on text queries. Using Low Rank Adaptation, we fine-tuned our VFMs to detect ocular and systemic diseases, differentiate ocular disease severity, and identify common ocular signs. The model achieved 100% accuracy in routing fundus images to appropriate VFMs, which achieved $\ge$ 82.2% accuracy in disease detection, $\ge$ 89% in severity differentiation, $\ge$ 76% in sign identification. Meta-EyeFM was 11% to 43% more accurate than Gemini-1.5-flash and ChatGPT-4o LMMs in detecting various eye diseases and comparable to an ophthalmologist. This system offers enhanced usability and diagnostic performance, making it a valuable decision support tool for primary eye care or an online LLM for fundus evaluation.
Partially Supervised Unpaired Multi-Modal Learning for Label-Efficient Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Unpaired Multi-Modal Learning (UMML) which leverages unpaired multi-modal data to boost model performance on each individual modality has attracted a lot of research interests in medical image analysis. However, existing UMML methods require multi-modal datasets to be fully labeled, which incurs tremendous annotation cost. In this paper, we investigate the use of partially labeled data for label-efficient unpaired multi-modal learning, which can reduce the annotation cost by up to one half. We term the new learning paradigm as Partially Supervised Unpaired Multi-Modal Learning (PSUMML) and propose a novel Decomposed partial class adaptation with snapshot Ensembled Self-Training (DEST) framework for it. Specifically, our framework consists of a compact segmentation network with modality specific normalization layers for learning with partially labeled unpaired multi-modal data. The key challenge in PSUMML lies in the complex partial class distribution discrepancy due to partial class annotation, which hinders effective knowledge transfer across modalities. We theoretically analyze this phenomenon with a decomposition theorem and propose a decomposed partial class adaptation technique to precisely align the partially labeled classes across modalities to reduce the distribution discrepancy. We further propose a snapshot ensembled self-training technique to leverage the valuable snapshot models during training to assign pseudo-labels to partially labeled pixels for self-training to boost model performance. We perform extensive experiments under different scenarios of PSUMML for two medical image segmentation tasks, namely cardiac substructure segmentation and abdominal multi-organ segmentation. Our framework outperforms existing methods significantly.
AiRacleX: Automated Detection of Price Oracle Manipulations via LLM-Driven Knowledge Mining and Prompt Generation
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Decentralized finance applications depend on accurate price oracles to ensure secure transactions, yet these oracles are highly vulnerable to manipulation, enabling attackers to exploit smart contract vulnerabilities for unfair asset valuation and financial gain. Detecting such manipulations traditionally relies on the manual effort of experienced experts, presenting significant challenges. In this paper, we propose a novel LLM-driven framework that automates the detection of price oracle manipulations by leveraging the complementary strengths of different LLM models. Our approach begins with domain-specific knowledge extraction, where an LLM model synthesizes precise insights about price oracle vulnerabilities from top-tier academic papers, eliminating the need for profound expertise from developers or auditors. This knowledge forms the foundation for a second LLM model to generate structured, context-aware chain of thought prompts, which guide a third LLM model in accurately identifying manipulation patterns in smart contracts. We validate the framework effectiveness through experiments on 60 known vulnerabilities from 46 real-world DeFi attacks or projects spanning 2021 to 2023. The best performing combination of LLMs (Haiku-Haiku-4o-mini) identified by AiRacleX demonstrate a 2.58-times improvement in recall (0.667 vs 0.259) compared to the state-of-the-art tool GPTScan, while maintaining comparable precision. Furthermore, our framework demonstrates the feasibility of replacing commercial models with open-source alternatives, enhancing privacy and security for developers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge