Junbo Chen
VisionTrim: Unified Vision Token Compression for Training-Free MLLM Acceleration
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) suffer from high computational costs due to excessive visual tokens, particularly in high-resolution and video-based scenarios. Existing token reduction methods typically focus on isolated pipeline components and often neglect textual alignment, leading to performance degradation. In this paper, we propose VisionTrim, a unified framework for training-free MLLM acceleration, integrating two effective plug-and-play modules: 1) the Dominant Vision Token Selection (DVTS) module, which preserves essential visual tokens via a global-local view, and 2) the Text-Guided Vision Complement (TGVC) module, which facilitates context-aware token merging guided by textual cues. Extensive experiments across diverse image and video multimodal benchmarks demonstrate the performance superiority of our VisionTrim, advancing practical MLLM deployment in real-world applications. The code is available at: https://github.com/hanxunyu/VisionTrim.
LADY: Linear Attention for Autonomous Driving Efficiency without Transformers
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:End-to-end paradigms have demonstrated great potential for autonomous driving. Additionally, most existing methods are built upon Transformer architectures. However, transformers incur a quadratic attention cost, limiting their ability to model long spatial and temporal sequences-particularly on resource-constrained edge platforms. As autonomous driving inherently demands efficient temporal modeling, this challenge severely limits their deployment and real-time performance. Recently, linear attention mechanisms have gained increasing attention due to their superior spatiotemporal complexity. However, existing linear attention architectures are limited to self-attention, lacking support for cross-modal and cross-temporal interactions-both crucial for autonomous driving. In this work, we propose LADY, the first fully linear attention-based generative model for end-to-end autonomous driving. LADY enables fusion of long-range temporal context at inference with constant computational and memory costs, regardless of the history length of camera and LiDAR features. Additionally, we introduce a lightweight linear cross-attention mechanism that enables effective cross-modal information exchange. Experiments on the NAVSIM and Bench2Drive benchmarks demonstrate that LADY achieves state-of-the-art performance with constant-time and memory complexity, offering improved planning performance and significantly reduced computational cost. Additionally, the model has been deployed and validated on edge devices, demonstrating its practicality in resource-limited scenarios.
MambaMap: Online Vectorized HD Map Construction using State Space Model
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:High-definition (HD) maps are essential for autonomous driving, as they provide precise road information for downstream tasks. Recent advances highlight the potential of temporal modeling in addressing challenges like occlusions and extended perception range. However, existing methods either fail to fully exploit temporal information or incur substantial computational overhead in handling extended sequences. To tackle these challenges, we propose MambaMap, a novel framework that efficiently fuses long-range temporal features in the state space to construct online vectorized HD maps. Specifically, MambaMap incorporates a memory bank to store and utilize information from historical frames, dynamically updating BEV features and instance queries to improve robustness against noise and occlusions. Moreover, we introduce a gating mechanism in the state space, selectively integrating dependencies of map elements in high computational efficiency. In addition, we design innovative multi-directional and spatial-temporal scanning strategies to enhance feature extraction at both BEV and instance levels. These strategies significantly boost the prediction accuracy of our approach while ensuring robust temporal consistency. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes and Argoverse2 datasets demonstrate that our proposed MambaMap approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods across various splits and perception ranges. Source code will be available at https://github.com/ZiziAmy/MambaMap.
RoPETR: Improving Temporal Camera-Only 3D Detection by Integrating Enhanced Rotary Position Embedding
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:This technical report introduces a targeted improvement to the StreamPETR framework, specifically aimed at enhancing velocity estimation, a critical factor influencing the overall NuScenes Detection Score. While StreamPETR exhibits strong 3D bounding box detection performance as reflected by its high mean Average Precision our analysis identified velocity estimation as a substantial bottleneck when evaluated on the NuScenes dataset. To overcome this limitation, we propose a customized positional embedding strategy tailored to enhance temporal modeling capabilities. Experimental evaluations conducted on the NuScenes test set demonstrate that our improved approach achieves a state-of-the-art NDS of 70.86% using the ViT-L backbone, setting a new benchmark for camera-only 3D object detection.
Uncertainty-Instructed Structure Injection for Generalizable HD Map Construction
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Reliable high-definition (HD) map construction is crucial for the driving safety of autonomous vehicles. Although recent studies demonstrate improved performance, their generalization capability across unfamiliar driving scenes remains unexplored. To tackle this issue, we propose UIGenMap, an uncertainty-instructed structure injection approach for generalizable HD map vectorization, which concerns the uncertainty resampling in statistical distribution and employs explicit instance features to reduce excessive reliance on training data. Specifically, we introduce the perspective-view (PV) detection branch to obtain explicit structural features, in which the uncertainty-aware decoder is designed to dynamically sample probability distributions considering the difference in scenes. With probabilistic embedding and selection, UI2DPrompt is proposed to construct PV-learnable prompts. These PV prompts are integrated into the map decoder by designed hybrid injection to compensate for neglected instance structures. To ensure real-time inference, a lightweight Mimic Query Distillation is designed to learn from PV prompts, which can serve as an efficient alternative to the flow of PV branches. Extensive experiments on challenging geographically disjoint (geo-based) data splits demonstrate that our UIGenMap achieves superior performance, with +5.7 mAP improvement on the nuScenes dataset. Source code will be available at https://github.com/xiaolul2/UIGenMap.
ReliOcc: Towards Reliable Semantic Occupancy Prediction via Uncertainty Learning
Sep 26, 2024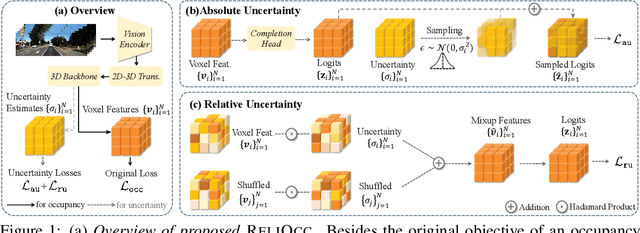
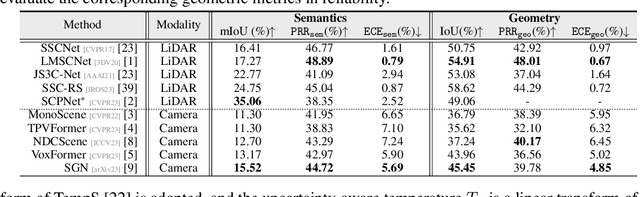
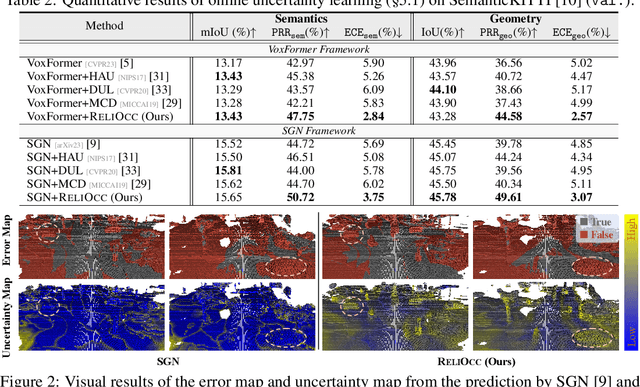
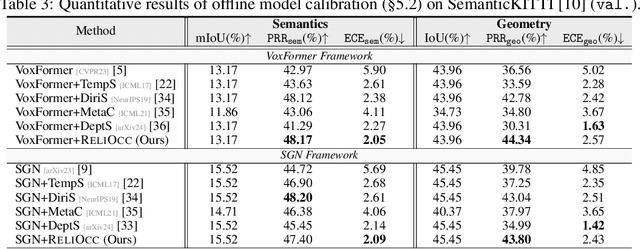
Abstract:Vision-centric semantic occupancy prediction plays a crucial role in autonomous driving, which requires accurate and reliable predictions from low-cost sensors. Although having notably narrowed the accuracy gap with LiDAR, there is still few research effort to explore the reliability in predicting semantic occupancy from camera. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of existing semantic occupancy prediction models from a reliability perspective for the first time. Despite the gradual alignment of camera-based models with LiDAR in term of accuracy, a significant reliability gap persists. To addresses this concern, we propose ReliOcc, a method designed to enhance the reliability of camera-based occupancy networks. ReliOcc provides a plug-and-play scheme for existing models, which integrates hybrid uncertainty from individual voxels with sampling-based noise and relative voxels through mix-up learning. Besides, an uncertainty-aware calibration strategy is devised to further enhance model reliability in offline mode. Extensive experiments under various settings demonstrate that ReliOcc significantly enhances model reliability while maintaining the accuracy of both geometric and semantic predictions. Importantly, our proposed approach exhibits robustness to sensor failures and out of domain noises during inference.
MV-DETR: Multi-modality indoor object detection by Multi-View DEtecton TRansformers
Aug 13, 2024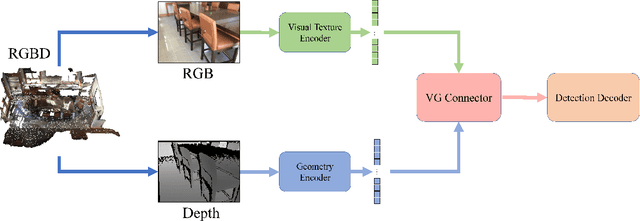
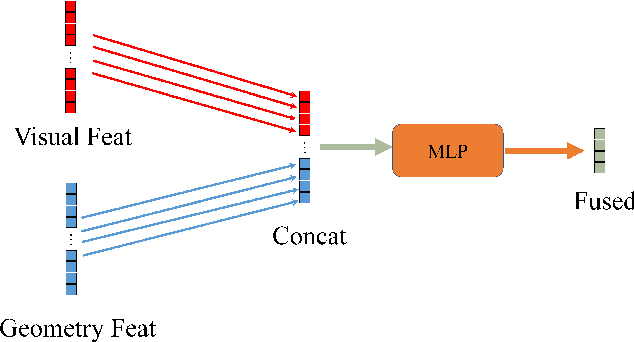
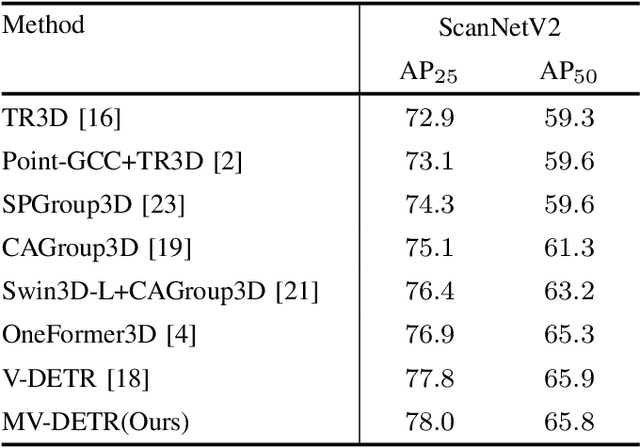
Abstract:We introduce a novel MV-DETR pipeline which is effective while efficient transformer based detection method. Given input RGBD data, we notice that there are super strong pretraining weights for RGB data while less effective works for depth related data. First and foremost , we argue that geometry and texture cues are both of vital importance while could be encoded separately. Secondly, we find that visual texture feature is relatively hard to extract compared with geometry feature in 3d space. Unfortunately, single RGBD dataset with thousands of data is not enough for training an discriminating filter for visual texture feature extraction. Last but certainly not the least, we designed a lightweight VG module consists of a visual textual encoder, a geometry encoder and a VG connector. Compared with previous state of the art works like V-DETR, gains from pretrained visual encoder could be seen. Extensive experiments on ScanNetV2 dataset shows the effectiveness of our method. It is worth mentioned that our method achieve 78\% AP which create new state of the art on ScanNetv2 benchmark.
Label-efficient Semantic Scene Completion with Scribble Annotations
May 24, 2024



Abstract:Semantic scene completion aims to infer the 3D geometric structures with semantic classes from camera or LiDAR, which provide essential occupancy information in autonomous driving. Prior endeavors concentrate on constructing the network or benchmark in a fully supervised manner. While the dense occupancy grids need point-wise semantic annotations, which incur expensive and tedious labeling costs. In this paper, we build a new label-efficient benchmark, named ScribbleSC, where the sparse scribble-based semantic labels are combined with dense geometric labels for semantic scene completion. In particular, we propose a simple yet effective approach called Scribble2Scene, which bridges the gap between the sparse scribble annotations and fully-supervision. Our method consists of geometric-aware auto-labelers construction and online model training with an offline-to-online distillation module to enhance the performance. Experiments on SemanticKITTI demonstrate that Scribble2Scene achieves competitive performance against the fully-supervised counterparts, showing 99% performance of the fully-supervised models with only 13.5% voxels labeled. Both annotations of ScribbleSC and our full implementation are available at https://github.com/songw-zju/Scribble2Scene.
HVOFusion: Incremental Mesh Reconstruction Using Hybrid Voxel Octree
Apr 27, 2024



Abstract:Incremental scene reconstruction is essential to the navigation in robotics. Most of the conventional methods typically make use of either TSDF (truncated signed distance functions) volume or neural networks to implicitly represent the surface. Due to the voxel representation or involving with time-consuming sampling, they have difficulty in balancing speed, memory storage, and surface quality. In this paper, we propose a novel hybrid voxel-octree approach to effectively fuse octree with voxel structures so that we can take advantage of both implicit surface and explicit triangular mesh representation. Such sparse structure preserves triangular faces in the leaf nodes and produces partial meshes sequentially for incremental reconstruction. This storage scheme allows us to naturally optimize the mesh in explicit 3D space to achieve higher surface quality. We iteratively deform the mesh towards the target and recovers vertex colors by optimizing a shading model. Experimental results on several datasets show that our proposed approach is capable of quickly and accurately reconstructing a scene with realistic colors.
Not All Voxels Are Equal: Hardness-Aware Semantic Scene Completion with Self-Distillation
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:Semantic scene completion, also known as semantic occupancy prediction, can provide dense geometric and semantic information for autonomous vehicles, which attracts the increasing attention of both academia and industry. Unfortunately, existing methods usually formulate this task as a voxel-wise classification problem and treat each voxel equally in 3D space during training. As the hard voxels have not been paid enough attention, the performance in some challenging regions is limited. The 3D dense space typically contains a large number of empty voxels, which are easy to learn but require amounts of computation due to handling all the voxels uniformly for the existing models. Furthermore, the voxels in the boundary region are more challenging to differentiate than those in the interior. In this paper, we propose HASSC approach to train the semantic scene completion model with hardness-aware design. The global hardness from the network optimization process is defined for dynamical hard voxel selection. Then, the local hardness with geometric anisotropy is adopted for voxel-wise refinement. Besides, self-distillation strategy is introduced to make training process stable and consistent. Extensive experiments show that our HASSC scheme can effectively promote the accuracy of the baseline model without incurring the extra inference cost. Source code is available at: https://github.com/songw-zju/HASSC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge