Zhan Shi
Position: Agentic Evolution is the Path to Evolving LLMs
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) move from curated training sets into open-ended real-world environments, a fundamental limitation emerges: static training cannot keep pace with continual deployment environment change. Scaling training-time and inference-time compute improves static capability but does not close this train-deploy gap. We argue that addressing this limitation requires a new scaling axis-evolution. Existing deployment-time adaptation methods, whether parametric fine-tuning or heuristic memory accumulation, lack the strategic agency needed to diagnose failures and produce durable improvements. Our position is that agentic evolution represents the inevitable future of LLM adaptation, elevating evolution itself from a fixed pipeline to an autonomous evolver agent. We instantiate this vision in a general framework, A-Evolve, which treats deployment-time improvement as a deliberate, goal-directed optimization process over persistent system state. We further propose the evolution-scaling hypothesis: the capacity for adaptation scales with the compute allocated to evolution, positioning agentic evolution as a scalable path toward sustained, open-ended adaptation in the real world.
Selective LLM-Guided Regularization for Enhancing Recommendation Models
Dec 25, 2025



Abstract:Large language models provide rich semantic priors and strong reasoning capabilities, making them promising auxiliary signals for recommendation. However, prevailing approaches either deploy LLMs as standalone recommender or apply global knowledge distillation, both of which suffer from inherent drawbacks. Standalone LLM recommender are costly, biased, and unreliable across large regions of the user item space, while global distillation forces the downstream model to imitate LLM predictions even when such guidance is inaccurate. Meanwhile, recent studies show that LLMs excel particularly in re-ranking and challenging scenarios, rather than uniformly across all contexts.We introduce Selective LLM Guided Regularization, a model-agnostic and computation efficient framework that activates LLM based pairwise ranking supervision only when a trainable gating mechanism informing by user history length, item popularity, and model uncertainty predicts the LLM to be reliable. All LLM scoring is performed offline, transferring knowledge without increasing inference cost. Experiments across multiple datasets show that this selective strategy consistently improves overall accuracy and yields substantial gains in cold start and long tail regimes, outperforming global distillation baselines.
Privacy-Preserving Synthetic Review Generation with Diverse Writing Styles Using LLMs
Jul 24, 2025Abstract:The increasing use of synthetic data generated by Large Language Models (LLMs) presents both opportunities and challenges in data-driven applications. While synthetic data provides a cost-effective, scalable alternative to real-world data to facilitate model training, its diversity and privacy risks remain underexplored. Focusing on text-based synthetic data, we propose a comprehensive set of metrics to quantitatively assess the diversity (i.e., linguistic expression, sentiment, and user perspective), and privacy (i.e., re-identification risk and stylistic outliers) of synthetic datasets generated by several state-of-the-art LLMs. Experiment results reveal significant limitations in LLMs' capabilities in generating diverse and privacy-preserving synthetic data. Guided by the evaluation results, a prompt-based approach is proposed to enhance the diversity of synthetic reviews while preserving reviewer privacy.
CoT-RAG: Integrating Chain of Thought and Retrieval-Augmented Generation to Enhance Reasoning in Large Language Models
Apr 18, 2025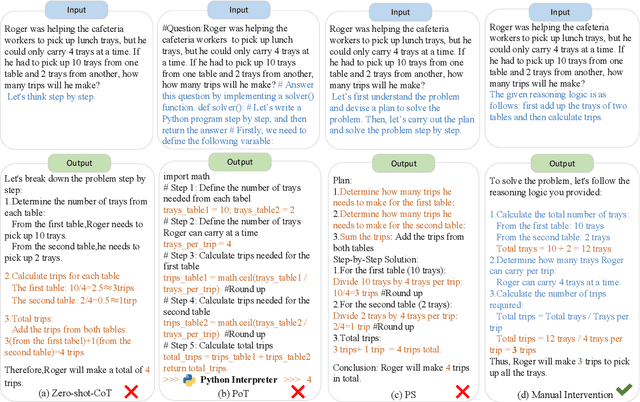
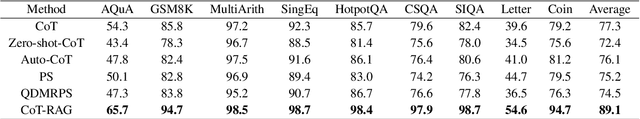
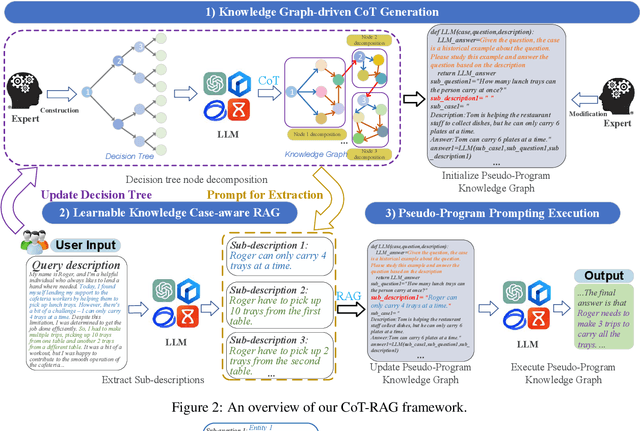
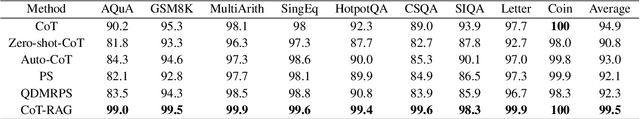
Abstract:While chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning improves the performance of large language models (LLMs) in complex tasks, it still has two main challenges: the low reliability of relying solely on LLMs to generate reasoning chains and the interference of natural language reasoning chains on the inference logic of LLMs. To address these issues, we propose CoT-RAG, a novel reasoning framework with three key designs: (i) Knowledge Graph-driven CoT Generation, featuring knowledge graphs to modulate reasoning chain generation of LLMs, thereby enhancing reasoning credibility; (ii) Learnable Knowledge Case-aware RAG, which incorporates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) into knowledge graphs to retrieve relevant sub-cases and sub-descriptions, providing LLMs with learnable information; (iii) Pseudo-Program Prompting Execution, which encourages LLMs to execute reasoning tasks in pseudo-programs with greater logical rigor. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation on nine public datasets, covering three reasoning problems. Compared with the-state-of-the-art methods, CoT-RAG exhibits a significant accuracy improvement, ranging from 4.0% to 23.0%. Furthermore, testing on four domain-specific datasets, CoT-RAG shows remarkable accuracy and efficient execution, highlighting its strong practical applicability and scalability.
Measuring Large Language Models Capacity to Annotate Journalistic Sourcing
Dec 30, 2024



Abstract:Since the launch of ChatGPT in late 2022, the capacities of Large Language Models and their evaluation have been in constant discussion and evaluation both in academic research and in the industry. Scenarios and benchmarks have been developed in several areas such as law, medicine and math (Bommasani et al., 2023) and there is continuous evaluation of model variants. One area that has not received sufficient scenario development attention is journalism, and in particular journalistic sourcing and ethics. Journalism is a crucial truth-determination function in democracy (Vincent, 2023), and sourcing is a crucial pillar to all original journalistic output. Evaluating the capacities of LLMs to annotate stories for the different signals of sourcing and how reporters justify them is a crucial scenario that warrants a benchmark approach. It offers potential to build automated systems to contrast more transparent and ethically rigorous forms of journalism with everyday fare. In this paper we lay out a scenario to evaluate LLM performance on identifying and annotating sourcing in news stories on a five-category schema inspired from journalism studies (Gans, 2004). We offer the use case, our dataset and metrics and as the first step towards systematic benchmarking. Our accuracy findings indicate LLM-based approaches have more catching to do in identifying all the sourced statements in a story, and equally, in matching the type of sources. An even harder task is spotting source justifications.
UdeerLID+: Integrating LiDAR, Image, and Relative Depth with Semi-Supervised
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:Road segmentation is a critical task for autonomous driving systems, requiring accurate and robust methods to classify road surfaces from various environmental data. Our work introduces an innovative approach that integrates LiDAR point cloud data, visual image, and relative depth maps derived from images. The integration of multiple data sources in road segmentation presents both opportunities and challenges. One of the primary challenges is the scarcity of large-scale, accurately labeled datasets that are necessary for training robust deep learning models. To address this, we have developed the [UdeerLID+] framework under a semi-supervised learning paradigm. Experiments results on KITTI datasets validate the superior performance.
MV-DETR: Multi-modality indoor object detection by Multi-View DEtecton TRansformers
Aug 13, 2024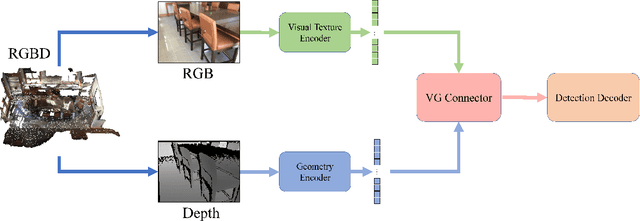
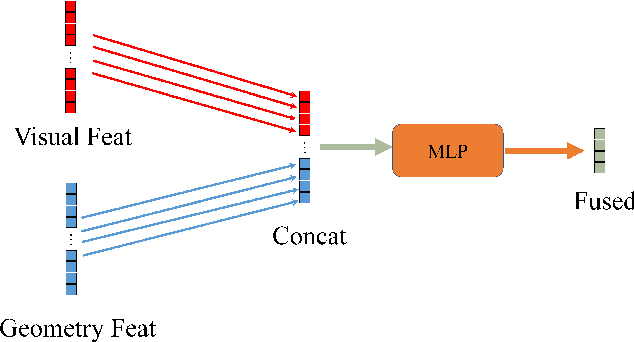
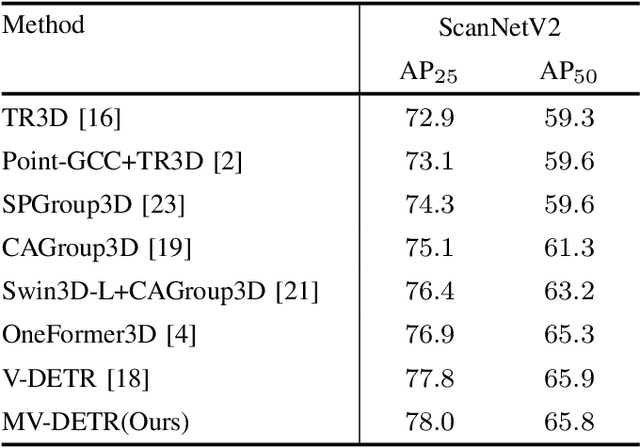
Abstract:We introduce a novel MV-DETR pipeline which is effective while efficient transformer based detection method. Given input RGBD data, we notice that there are super strong pretraining weights for RGB data while less effective works for depth related data. First and foremost , we argue that geometry and texture cues are both of vital importance while could be encoded separately. Secondly, we find that visual texture feature is relatively hard to extract compared with geometry feature in 3d space. Unfortunately, single RGBD dataset with thousands of data is not enough for training an discriminating filter for visual texture feature extraction. Last but certainly not the least, we designed a lightweight VG module consists of a visual textual encoder, a geometry encoder and a VG connector. Compared with previous state of the art works like V-DETR, gains from pretrained visual encoder could be seen. Extensive experiments on ScanNetV2 dataset shows the effectiveness of our method. It is worth mentioned that our method achieve 78\% AP which create new state of the art on ScanNetv2 benchmark.
Multi-Stage Face-Voice Association Learning with Keynote Speaker Diarization
Jul 25, 2024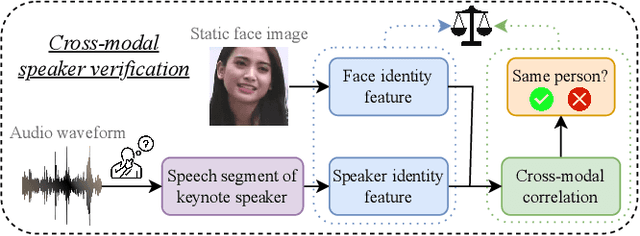
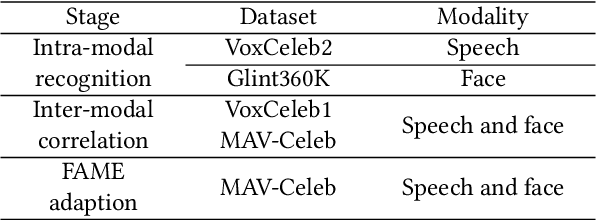
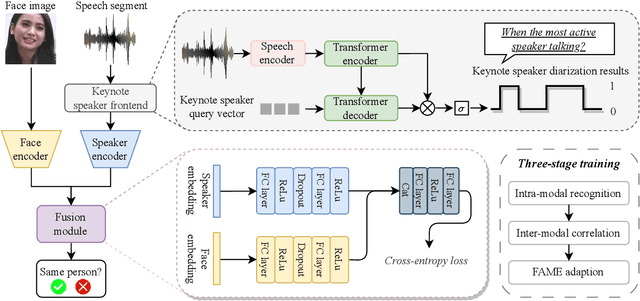

Abstract:The human brain has the capability to associate the unknown person's voice and face by leveraging their general relationship, referred to as ``cross-modal speaker verification''. This task poses significant challenges due to the complex relationship between the modalities. In this paper, we propose a ``Multi-stage Face-voice Association Learning with Keynote Speaker Diarization''~(MFV-KSD) framework. MFV-KSD contains a keynote speaker diarization front-end to effectively address the noisy speech inputs issue. To balance and enhance the intra-modal feature learning and inter-modal correlation understanding, MFV-KSD utilizes a novel three-stage training strategy. Our experimental results demonstrated robust performance, achieving the first rank in the 2024 Face-voice Association in Multilingual Environments (FAME) challenge with an overall Equal Error Rate (EER) of 19.9%. Details can be found in https://github.com/TaoRuijie/MFV-KSD.
MR-BEN: A Comprehensive Meta-Reasoning Benchmark for Large Language Models
Jun 20, 2024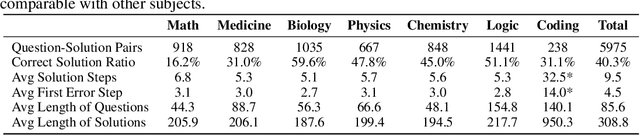
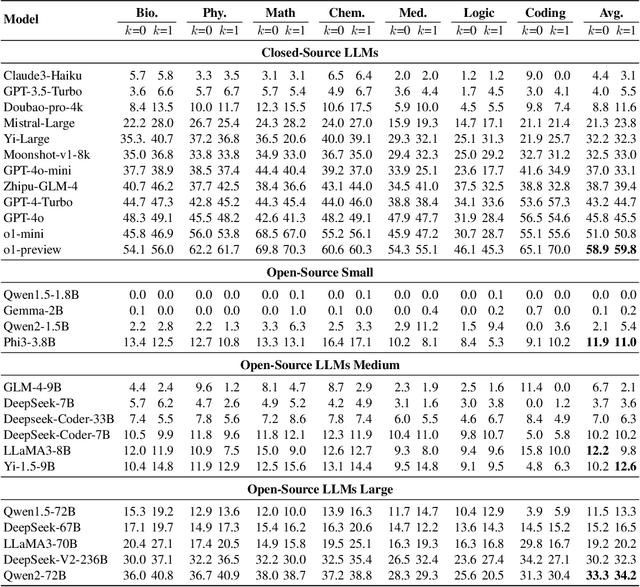
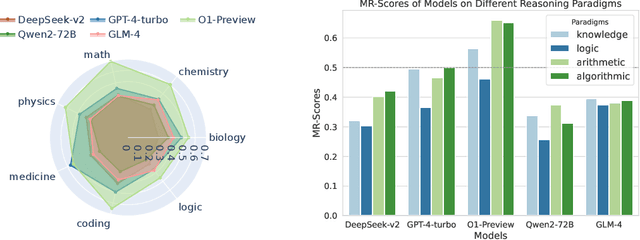
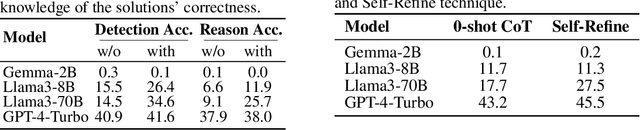
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown increasing capability in problem-solving and decision-making, largely based on the step-by-step chain-of-thought reasoning processes. However, it has been increasingly challenging to evaluate the reasoning capability of LLMs. Concretely, existing outcome-based benchmarks begin to saturate and become less sufficient to monitor the progress. To this end, we present a process-based benchmark MR-BEN that demands a meta reasoning skill, where LMs are asked to locate and analyse potential errors in automatically generated reasoning steps. MR-BEN is a comprehensive benchmark comprising 5,975 questions collected from human experts, covering various subjects such as physics, chemistry, logic, coding, and more. Through our designed metrics for assessing meta-reasoning on this benchmark, we identify interesting limitations and weaknesses of current LLMs (open-source and closed-source models). For example, open-source models are seemingly comparable to GPT-4 on outcome-based benchmarks, but they lag far behind on our benchmark, revealing the underlying reasoning capability gap between them. Our dataset and codes are available on https://randolph-zeng.github.io/Mr-Ben.github.io/.
Ranking-based Client Selection with Imitation Learning for Efficient Federated Learning
May 07, 2024



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables multiple devices to collaboratively train a shared model while ensuring data privacy. The selection of participating devices in each training round critically affects both the model performance and training efficiency, especially given the vast heterogeneity in training capabilities and data distribution across devices. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel device selection solution called FedRank, which is an end-to-end, ranking-based approach that is pre-trained by imitation learning against state-of-the-art analytical approaches. It not only considers data and system heterogeneity at runtime but also adaptively and efficiently chooses the most suitable clients for model training. Specifically, FedRank views client selection in FL as a ranking problem and employs a pairwise training strategy for the smart selection process. Additionally, an imitation learning-based approach is designed to counteract the cold-start issues often seen in state-of-the-art learning-based approaches. Experimental results reveal that \model~ boosts model accuracy by 5.2\% to 56.9\%, accelerates the training convergence up to $2.01 \times$ and saves the energy consumption up to $40.1\%$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge