Chunlin Tian
RAP: Runtime-Adaptive Pruning for LLM Inference
May 26, 2025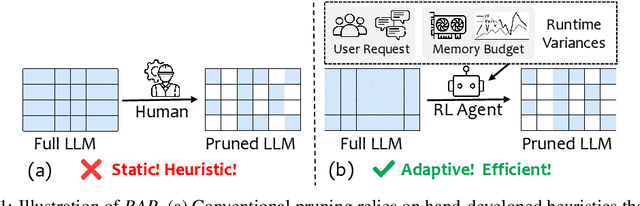

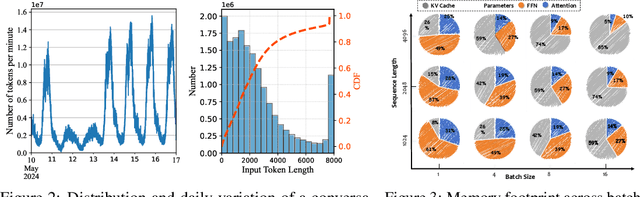

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at language understanding and generation, but their enormous computational and memory requirements hinder deployment. Compression offers a potential solution to mitigate these constraints. However, most existing methods rely on fixed heuristics and thus fail to adapt to runtime memory variations or heterogeneous KV-cache demands arising from diverse user requests. To address these limitations, we propose RAP, an elastic pruning framework driven by reinforcement learning (RL) that dynamically adjusts compression strategies in a runtime-aware manner. Specifically, RAP dynamically tracks the evolving ratio between model parameters and KV-cache across practical execution. Recognizing that FFNs house most parameters, whereas parameter -light attention layers dominate KV-cache formation, the RL agent retains only those components that maximize utility within the current memory budget, conditioned on instantaneous workload and device state. Extensive experiments results demonstrate that RAP outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, marking the first time to jointly consider model weights and KV-cache on the fly.
A Survey on Federated Fine-tuning of Large Language Models
Mar 15, 2025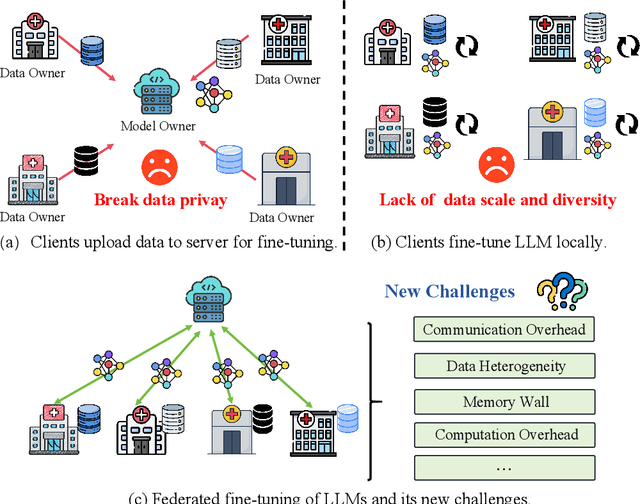
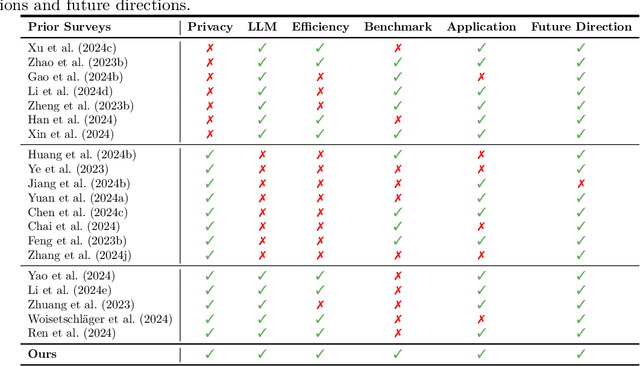
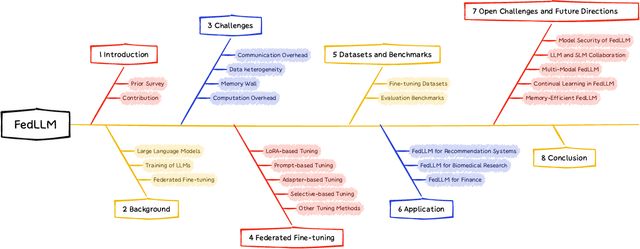
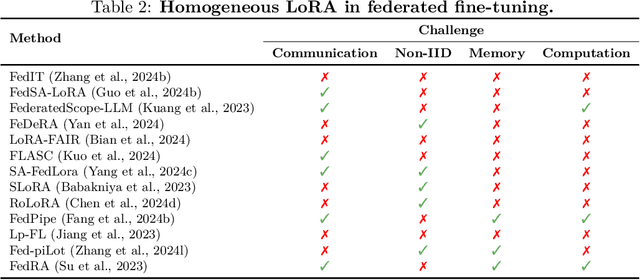
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success across a wide range of tasks, with fine-tuning playing a pivotal role in adapting them to specific downstream applications. Federated Learning (FL) offers a promising approach that enables collaborative model adaptation while ensuring data privacy, i.e., FedLLM. In this survey, we provide a systematic and thorough review of the integration of LLMs with FL. Specifically, we first trace the historical evolution of both LLMs and FL, while summarizing relevant prior surveys. We then present an in-depth analysis of the fundamental challenges encountered in deploying FedLLM. Following this, we conduct an extensive study of existing parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods and explore their applicability in FL. Furthermore, we introduce a comprehensive evaluation benchmark to rigorously assess FedLLM performance and discuss its diverse real-world applications across multiple domains. Finally, we identify critical open challenges and outline promising research directions to drive future advancements in FedLLM. We maintain an active \href{https://github.com/Clin0212/Awesome-Federated-LLM-Learning}{GitHub repository} tracking cutting-edge advancements. This survey serves as a foundational resource for researchers and practitioners, offering insights into the evolving landscape of federated fine-tuning for LLMs while guiding future innovations in privacy-preserving AI.
AsymLoRA: Harmonizing Data Conflicts and Commonalities in MLLMs
Feb 27, 2025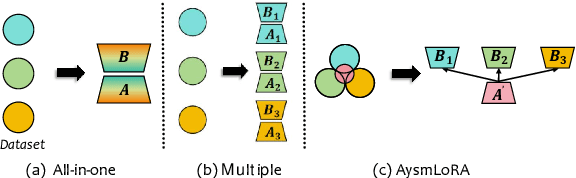



Abstract:Effective instruction fine-tuning on diverse image-text datasets is crucial for developing a versatile Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM), where dataset composition dictates the model's adaptability across multimodal tasks. However, complex datasets often contain inherent conflicts -- stemming from modality-specific optimization objectives -- and latent commonalities that enable cross-task transfer, which most existing approaches handle separately. To bridge this gap, we introduce AsymLoRA, a parameter-efficient tuning framework that unifies knowledge modularization and cross-modal coordination via asymmetric LoRA: task-specific low-rank projections (matrix B) that preserve distinct adaptation pathways for conflicting objectives, and a shared projection (matrix A) that consolidates cross-modal commonalities. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that AsymLoRA consistently surpasses both vanilla LoRA, which captures only commonalities, and LoRA-MoE, which focuses solely on conflicts, achieving superior model performance and system efficiency across diverse benchmarks.\href{Code}{https://github.com/Clin0212/HydraLoRA/blob/main/MLLM-HydraLoRA/README.md}.
Heterogeneity-Aware Coordination for Federated Learning via Stitching Pre-trained blocks
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) coordinates multiple devices to collaboratively train a shared model while preserving data privacy. However, large memory footprint and high energy consumption during the training process excludes the low-end devices from contributing to the global model with their own data, which severely deteriorates the model performance in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose FedStitch, a hierarchical coordination framework for heterogeneous federated learning with pre-trained blocks. Unlike the traditional approaches that train the global model from scratch, for a new task, FedStitch composes the global model via stitching pre-trained blocks. Specifically, each participating client selects the most suitable block based on their local data from the candidate pool composed of blocks from pre-trained models. The server then aggregates the optimal block for stitching. This process iterates until a new stitched network is generated. Except for the new training paradigm, FedStitch consists of the following three core components: 1) an RL-weighted aggregator, 2) a search space optimizer deployed on the server side, and 3) a local energy optimizer deployed on each participating client. The RL-weighted aggregator helps to select the right block in the non-IID scenario, while the search space optimizer continuously reduces the size of the candidate block pool during stitching. Meanwhile, the local energy optimizer is designed to minimize energy consumption of each client while guaranteeing the overall training progress. The results demonstrate that compared to existing approaches, FedStitch improves the model accuracy up to 20.93%. At the same time, it achieves up to 8.12% speedup, reduces the memory footprint up to 79.5%, and achieves 89.41% energy saving at most during the learning procedure.
When, Where, and What? A Novel Benchmark for Accident Anticipation and Localization with Large Language Models
Jul 26, 2024



Abstract:As autonomous driving systems increasingly become part of daily transportation, the ability to accurately anticipate and mitigate potential traffic accidents is paramount. Traditional accident anticipation models primarily utilizing dashcam videos are adept at predicting when an accident may occur but fall short in localizing the incident and identifying involved entities. Addressing this gap, this study introduces a novel framework that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance predictive capabilities across multiple dimensions--what, when, and where accidents might occur. We develop an innovative chain-based attention mechanism that dynamically adjusts to prioritize high-risk elements within complex driving scenes. This mechanism is complemented by a three-stage model that processes outputs from smaller models into detailed multimodal inputs for LLMs, thus enabling a more nuanced understanding of traffic dynamics. Empirical validation on the DAD, CCD, and A3D datasets demonstrates superior performance in Average Precision (AP) and Mean Time-To-Accident (mTTA), establishing new benchmarks for accident prediction technology. Our approach not only advances the technological framework for autonomous driving safety but also enhances human-AI interaction, making predictive insights generated by autonomous systems more intuitive and actionable.
CRASH: Crash Recognition and Anticipation System Harnessing with Context-Aware and Temporal Focus Attentions
Jul 25, 2024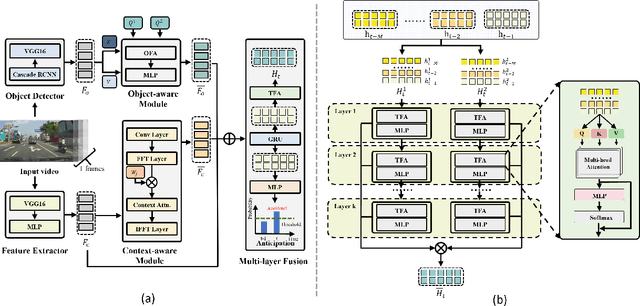



Abstract:Accurately and promptly predicting accidents among surrounding traffic agents from camera footage is crucial for the safety of autonomous vehicles (AVs). This task presents substantial challenges stemming from the unpredictable nature of traffic accidents, their long-tail distribution, the intricacies of traffic scene dynamics, and the inherently constrained field of vision of onboard cameras. To address these challenges, this study introduces a novel accident anticipation framework for AVs, termed CRASH. It seamlessly integrates five components: object detector, feature extractor, object-aware module, context-aware module, and multi-layer fusion. Specifically, we develop the object-aware module to prioritize high-risk objects in complex and ambiguous environments by calculating the spatial-temporal relationships between traffic agents. In parallel, the context-aware is also devised to extend global visual information from the temporal to the frequency domain using the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) and capture fine-grained visual features of potential objects and broader context cues within traffic scenes. To capture a wider range of visual cues, we further propose a multi-layer fusion that dynamically computes the temporal dependencies between different scenes and iteratively updates the correlations between different visual features for accurate and timely accident prediction. Evaluated on real-world datasets--Dashcam Accident Dataset (DAD), Car Crash Dataset (CCD), and AnAn Accident Detection (A3D) datasets--our model surpasses existing top baselines in critical evaluation metrics like Average Precision (AP) and mean Time-To-Accident (mTTA). Importantly, its robustness and adaptability are particularly evident in challenging driving scenarios with missing or limited training data, demonstrating significant potential for application in real-world autonomous driving systems.
Less is More: Efficient Brain-Inspired Learning for Autonomous Driving Trajectory Prediction
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:Accurately and safely predicting the trajectories of surrounding vehicles is essential for fully realizing autonomous driving (AD). This paper presents the Human-Like Trajectory Prediction model (HLTP++), which emulates human cognitive processes to improve trajectory prediction in AD. HLTP++ incorporates a novel teacher-student knowledge distillation framework. The "teacher" model equipped with an adaptive visual sector, mimics the dynamic allocation of attention human drivers exhibit based on factors like spatial orientation, proximity, and driving speed. On the other hand, the "student" model focuses on real-time interaction and human decision-making, drawing parallels to the human memory storage mechanism. Furthermore, we improve the model's efficiency by introducing a new Fourier Adaptive Spike Neural Network (FA-SNN), allowing for faster and more precise predictions with fewer parameters. Evaluated using the NGSIM, HighD, and MoCAD benchmarks, HLTP++ demonstrates superior performance compared to existing models, which reduces the predicted trajectory error with over 11% on the NGSIM dataset and 25% on the HighD datasets. Moreover, HLTP++ demonstrates strong adaptability in challenging environments with incomplete input data. This marks a significant stride in the journey towards fully AD systems.
FedGCS: A Generative Framework for Efficient Client Selection in Federated Learning via Gradient-based Optimization
May 10, 2024



Abstract:Federated Learning faces significant challenges in statistical and system heterogeneity, along with high energy consumption, necessitating efficient client selection strategies. Traditional approaches, including heuristic and learning-based methods, fall short of addressing these complexities holistically. In response, we propose FedGCS, a novel generative client selection framework that innovatively recasts the client selection process as a generative task. Drawing inspiration from the methodologies used in large language models, FedGCS efficiently encodes abundant decision-making knowledge within a continuous representation space, enabling efficient gradient-based optimization to search for optimal client selection that will be finally output via generation. The framework comprises four steps: (1) automatic collection of diverse "selection-score" pair data using classical client selection methods; (2) training an encoder-evaluator-decoder framework on this data to construct a continuous representation space; (3) employing gradient-based optimization in this space for optimal client selection; (4) generating the final optimal client selection via using beam search for the well-trained decoder. FedGCS outperforms traditional methods by being more comprehensive, generalizable, and efficient, simultaneously optimizing for model performance, latency, and energy consumption. The effectiveness of FedGCS is proven through extensive experimental analyses.
Ranking-based Client Selection with Imitation Learning for Efficient Federated Learning
May 07, 2024



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables multiple devices to collaboratively train a shared model while ensuring data privacy. The selection of participating devices in each training round critically affects both the model performance and training efficiency, especially given the vast heterogeneity in training capabilities and data distribution across devices. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel device selection solution called FedRank, which is an end-to-end, ranking-based approach that is pre-trained by imitation learning against state-of-the-art analytical approaches. It not only considers data and system heterogeneity at runtime but also adaptively and efficiently chooses the most suitable clients for model training. Specifically, FedRank views client selection in FL as a ranking problem and employs a pairwise training strategy for the smart selection process. Additionally, an imitation learning-based approach is designed to counteract the cold-start issues often seen in state-of-the-art learning-based approaches. Experimental results reveal that \model~ boosts model accuracy by 5.2\% to 56.9\%, accelerates the training convergence up to $2.01 \times$ and saves the energy consumption up to $40.1\%$.
HydraLoRA: An Asymmetric LoRA Architecture for Efficient Fine-Tuning
Apr 30, 2024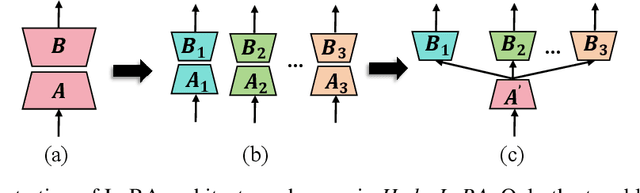

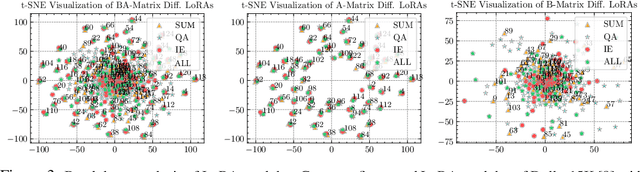

Abstract:Adapting Large Language Models (LLMs) to new tasks through fine-tuning has been made more efficient by the introduction of Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) techniques, such as LoRA. However, these methods often underperform compared to full fine-tuning, particularly in scenarios involving complex datasets. This issue becomes even more pronounced in complex domains, highlighting the need for improved PEFT approaches that can achieve better performance. Through a series of experiments, we have uncovered two critical insights that shed light on the training and parameter inefficiency of LoRA. Building on these insights, we have developed HydraLoRA, a LoRA framework with an asymmetric structure that eliminates the need for domain expertise. Our experiments demonstrate that HydraLoRA outperforms other PEFT approaches, even those that rely on domain knowledge during the training and inference phases. \href{https://github.com/Clin0212/HydraLoRA}{Code}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge