Guofa Li
LL-GaussianMap: Zero-shot Low-Light Image Enhancement via 2D Gaussian Splatting Guided Gain Maps
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Significant progress has been made in low-light image enhancement with respect to visual quality. However, most existing methods primarily operate in the pixel domain or rely on implicit feature representations. As a result, the intrinsic geometric structural priors of images are often neglected. 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) has emerged as a prominent explicit scene representation technique characterized by superior structural fitting capabilities and high rendering efficiency. Despite these advantages, the utilization of 2DGS in low-level vision tasks remains unexplored. To bridge this gap, LL-GaussianMap is proposed as the first unsupervised framework incorporating 2DGS into low-light image enhancement. Distinct from conventional methodologies, the enhancement task is formulated as a gain map generation process guided by 2DGS primitives. The proposed method comprises two primary stages. First, high-fidelity structural reconstruction is executed utilizing 2DGS. Then, data-driven enhancement dictionary coefficients are rendered via the rasterization mechanism of Gaussian splatting through an innovative unified enhancement module. This design effectively incorporates the structural perception capabilities of 2DGS into gain map generation, thereby preserving edges and suppressing artifacts during enhancement. Additionally, the reliance on paired data is circumvented through unsupervised learning. Experimental results demonstrate that LL-GaussianMap achieves superior enhancement performance with an extremely low storage footprint, highlighting the effectiveness of explicit Gaussian representations for image enhancement.
LL-GaussianImage: Efficient Image Representation for Zero-shot Low-Light Enhancement with 2D Gaussian Splatting
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) is an emerging explicit scene representation method with significant potential for image compression due to high fidelity and high compression ratios. However, existing low-light enhancement algorithms operate predominantly within the pixel domain. Processing 2DGS-compressed images necessitates a cumbersome decompression-enhancement-recompression pipeline, which compromises efficiency and introduces secondary degradation. To address these limitations, we propose LL-GaussianImage, the first zero-shot unsupervised framework designed for low-light enhancement directly within the 2DGS compressed representation domain. Three primary advantages are offered by this framework. First, a semantic-guided Mixture-of-Experts enhancement framework is designed. Dynamic adaptive transformations are applied to the sparse attribute space of 2DGS using rendered images as guidance to enable compression-as-enhancement without full decompression to a pixel grid. Second, a multi-objective collaborative loss function system is established to strictly constrain smoothness and fidelity during enhancement, suppressing artifacts while improving visual quality. Third, a two-stage optimization process is utilized to achieve reconstruction-as-enhancement. The accuracy of the base representation is ensured through single-scale reconstruction and network robustness is enhanced. High-quality enhancement of low-light images is achieved while high compression ratios are maintained. The feasibility and superiority of the paradigm for direct processing within the compressed representation domain are validated through experimental results.
HS-SLAM: A Fast and Hybrid Strategy-Based SLAM Approach for Low-Speed Autonomous Driving
May 27, 2025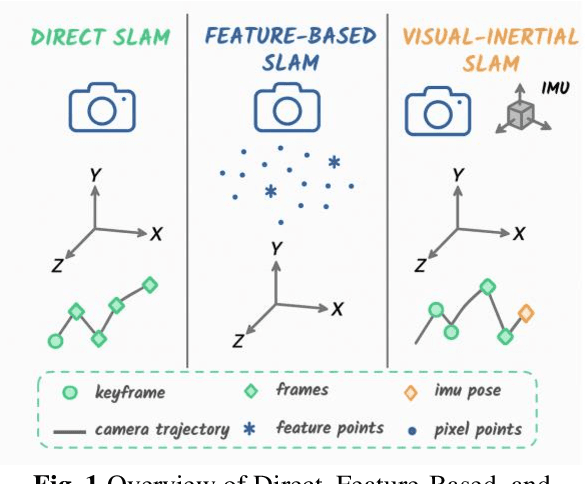

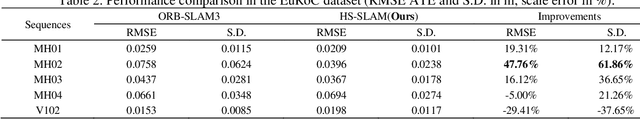
Abstract:Visual-inertial simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is a key module of robotics and low-speed autonomous vehicles, which is usually limited by the high computation burden for practical applications. To this end, an innovative strategy-based hybrid framework HS-SLAM is proposed to integrate the advantages of direct and feature-based methods for fast computation without decreasing the performance. It first estimates the relative positions of consecutive frames using IMU pose estimation within the tracking thread. Then, it refines these estimates through a multi-layer direct method, which progressively corrects the relative pose from coarse to fine, ultimately achieving accurate corner-based feature matching. This approach serves as an alternative to the conventional constant-velocity tracking model. By selectively bypassing descriptor extraction for non-critical frames, HS-SLAM significantly improves the tracking speed. Experimental evaluations on the EuRoC MAV dataset demonstrate that HS-SLAM achieves higher localization accuracies than ORB-SLAM3 while improving the average tracking efficiency by 15%.
Less is More: Efficient Brain-Inspired Learning for Autonomous Driving Trajectory Prediction
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:Accurately and safely predicting the trajectories of surrounding vehicles is essential for fully realizing autonomous driving (AD). This paper presents the Human-Like Trajectory Prediction model (HLTP++), which emulates human cognitive processes to improve trajectory prediction in AD. HLTP++ incorporates a novel teacher-student knowledge distillation framework. The "teacher" model equipped with an adaptive visual sector, mimics the dynamic allocation of attention human drivers exhibit based on factors like spatial orientation, proximity, and driving speed. On the other hand, the "student" model focuses on real-time interaction and human decision-making, drawing parallels to the human memory storage mechanism. Furthermore, we improve the model's efficiency by introducing a new Fourier Adaptive Spike Neural Network (FA-SNN), allowing for faster and more precise predictions with fewer parameters. Evaluated using the NGSIM, HighD, and MoCAD benchmarks, HLTP++ demonstrates superior performance compared to existing models, which reduces the predicted trajectory error with over 11% on the NGSIM dataset and 25% on the HighD datasets. Moreover, HLTP++ demonstrates strong adaptability in challenging environments with incomplete input data. This marks a significant stride in the journey towards fully AD systems.
MFTraj: Map-Free, Behavior-Driven Trajectory Prediction for Autonomous Driving
May 02, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces a trajectory prediction model tailored for autonomous driving, focusing on capturing complex interactions in dynamic traffic scenarios without reliance on high-definition maps. The model, termed MFTraj, harnesses historical trajectory data combined with a novel dynamic geometric graph-based behavior-aware module. At its core, an adaptive structure-aware interactive graph convolutional network captures both positional and behavioral features of road users, preserving spatial-temporal intricacies. Enhanced by a linear attention mechanism, the model achieves computational efficiency and reduced parameter overhead. Evaluations on the Argoverse, NGSIM, HighD, and MoCAD datasets underscore MFTraj's robustness and adaptability, outperforming numerous benchmarks even in data-challenged scenarios without the need for additional information such as HD maps or vectorized maps. Importantly, it maintains competitive performance even in scenarios with substantial missing data, on par with most existing state-of-the-art models. The results and methodology suggest a significant advancement in autonomous driving trajectory prediction, paving the way for safer and more efficient autonomous systems.
A Cognitive-Driven Trajectory Prediction Model for Autonomous Driving in Mixed Autonomy Environment
Apr 26, 2024Abstract:As autonomous driving technology progresses, the need for precise trajectory prediction models becomes paramount. This paper introduces an innovative model that infuses cognitive insights into trajectory prediction, focusing on perceived safety and dynamic decision-making. Distinct from traditional approaches, our model excels in analyzing interactions and behavior patterns in mixed autonomy traffic scenarios. It represents a significant leap forward, achieving marked performance improvements on several key datasets. Specifically, it surpasses existing benchmarks with gains of 16.2% on the Next Generation Simulation (NGSIM), 27.4% on the Highway Drone (HighD), and 19.8% on the Macao Connected Autonomous Driving (MoCAD) dataset. Our proposed model shows exceptional proficiency in handling corner cases, essential for real-world applications. Moreover, its robustness is evident in scenarios with missing or limited data, outperforming most of the state-of-the-art baselines. This adaptability and resilience position our model as a viable tool for real-world autonomous driving systems, heralding a new standard in vehicle trajectory prediction for enhanced safety and efficiency.
BAT: Behavior-Aware Human-Like Trajectory Prediction for Autonomous Driving
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:The ability to accurately predict the trajectory of surrounding vehicles is a critical hurdle to overcome on the journey to fully autonomous vehicles. To address this challenge, we pioneer a novel behavior-aware trajectory prediction model (BAT) that incorporates insights and findings from traffic psychology, human behavior, and decision-making. Our model consists of behavior-aware, interaction-aware, priority-aware, and position-aware modules that perceive and understand the underlying interactions and account for uncertainty and variability in prediction, enabling higher-level learning and flexibility without rigid categorization of driving behavior. Importantly, this approach eliminates the need for manual labeling in the training process and addresses the challenges of non-continuous behavior labeling and the selection of appropriate time windows. We evaluate BAT's performance across the Next Generation Simulation (NGSIM), Highway Drone (HighD), Roundabout Drone (RounD), and Macao Connected Autonomous Driving (MoCAD) datasets, showcasing its superiority over prevailing state-of-the-art (SOTA) benchmarks in terms of prediction accuracy and efficiency. Remarkably, even when trained on reduced portions of the training data (25%), our model outperforms most of the baselines, demonstrating its robustness and efficiency in predicting vehicle trajectories, and the potential to reduce the amount of data required to train autonomous vehicles, especially in corner cases. In conclusion, the behavior-aware model represents a significant advancement in the development of autonomous vehicles capable of predicting trajectories with the same level of proficiency as human drivers. The project page is available at https://github.com/Petrichor625/BATraj-Behavior-aware-Model.
GPT-4 Enhanced Multimodal Grounding for Autonomous Driving: Leveraging Cross-Modal Attention with Large Language Models
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:In the field of autonomous vehicles (AVs), accurately discerning commander intent and executing linguistic commands within a visual context presents a significant challenge. This paper introduces a sophisticated encoder-decoder framework, developed to address visual grounding in AVs.Our Context-Aware Visual Grounding (CAVG) model is an advanced system that integrates five core encoders-Text, Image, Context, and Cross-Modal-with a Multimodal decoder. This integration enables the CAVG model to adeptly capture contextual semantics and to learn human emotional features, augmented by state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs) including GPT-4. The architecture of CAVG is reinforced by the implementation of multi-head cross-modal attention mechanisms and a Region-Specific Dynamic (RSD) layer for attention modulation. This architectural design enables the model to efficiently process and interpret a range of cross-modal inputs, yielding a comprehensive understanding of the correlation between verbal commands and corresponding visual scenes. Empirical evaluations on the Talk2Car dataset, a real-world benchmark, demonstrate that CAVG establishes new standards in prediction accuracy and operational efficiency. Notably, the model exhibits exceptional performance even with limited training data, ranging from 50% to 75% of the full dataset. This feature highlights its effectiveness and potential for deployment in practical AV applications. Moreover, CAVG has shown remarkable robustness and adaptability in challenging scenarios, including long-text command interpretation, low-light conditions, ambiguous command contexts, inclement weather conditions, and densely populated urban environments. The code for the proposed model is available at our Github.
MSAF: Multimodal Split Attention Fusion
Dec 13, 2020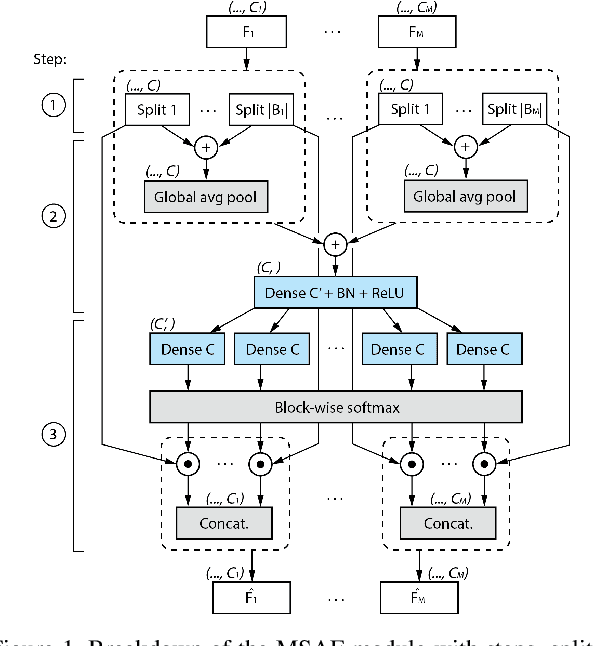
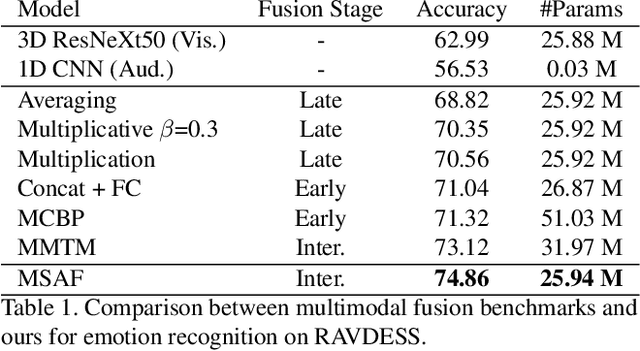
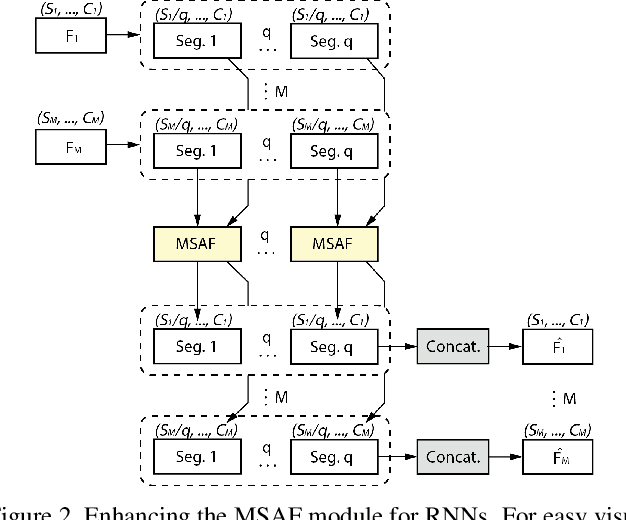
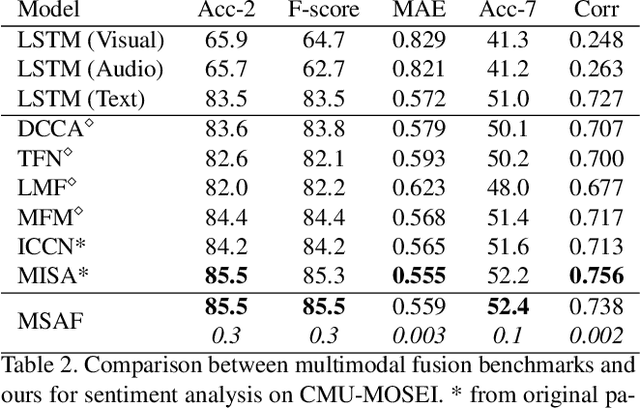
Abstract:Multimodal learning mimics the reasoning process of the human multi-sensory system, which is used to perceive the surrounding world. While making a prediction, the human brain tends to relate crucial cues from multiple sources of information. In this work, we propose a novel multimodal fusion module that learns to emphasize more contributive features across all modalities. Specifically, the proposed Multimodal Split Attention Fusion (MSAF) module splits each modality into channel-wise equal feature blocks and creates a joint representation that is used to generate soft attention for each channel across the feature blocks. Further, the MSAF module is designed to be compatible with features of various spatial dimensions and sequence lengths, suitable for both CNNs and RNNs. Thus, MSAF can be easily added to fuse features of any unimodal networks and utilize existing pretrained unimodal model weights. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our fusion module, we design three multimodal networks with MSAF for emotion recognition, sentiment analysis, and action recognition tasks. Our approach achieves competitive results in each task and outperforms other application-specific networks and multimodal fusion benchmarks.
A Spontaneous Driver Emotion Facial Expression (DEFE) Dataset for Intelligent Vehicles
Apr 26, 2020
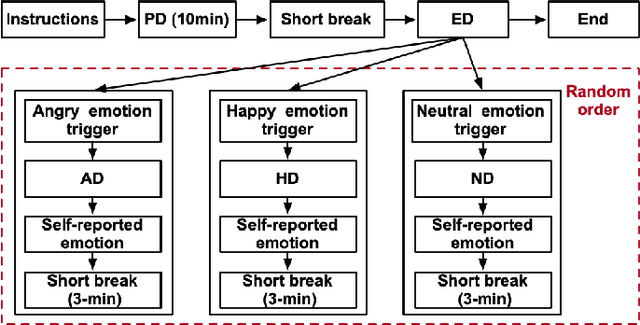

Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a new dataset, the driver emotion facial expression (DEFE) dataset, for driver spontaneous emotions analysis. The dataset includes facial expression recordings from 60 participants during driving. After watching a selected video-audio clip to elicit a specific emotion, each participant completed the driving tasks in the same driving scenario and rated their emotional responses during the driving processes from the aspects of dimensional emotion and discrete emotion. We also conducted classification experiments to recognize the scales of arousal, valence, dominance, as well as the emotion category and intensity to establish baseline results for the proposed dataset. Besides, this paper compared and discussed the differences in facial expressions between driving and non-driving scenarios. The results show that there were significant differences in AUs (Action Units) presence of facial expressions between driving and non-driving scenarios, indicating that human emotional expressions in driving scenarios were different from other life scenarios. Therefore, publishing a human emotion dataset specifically for the driver is necessary for traffic safety improvement. The proposed dataset will be publicly available so that researchers worldwide can use it to develop and examine their driver emotion analysis methods. To the best of our knowledge, this is currently the only public driver facial expression dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge