Chengyue Wang
Predict and Resist: Long-Term Accident Anticipation under Sensor Noise
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Accident anticipation is essential for proactive and safe autonomous driving, where even a brief advance warning can enable critical evasive actions. However, two key challenges hinder real-world deployment: (1) noisy or degraded sensory inputs from weather, motion blur, or hardware limitations, and (2) the need to issue timely yet reliable predictions that balance early alerts with false-alarm suppression. We propose a unified framework that integrates diffusion-based denoising with a time-aware actor-critic model to address these challenges. The diffusion module reconstructs noise-resilient image and object features through iterative refinement, preserving critical motion and interaction cues under sensor degradation. In parallel, the actor-critic architecture leverages long-horizon temporal reasoning and time-weighted rewards to determine the optimal moment to raise an alert, aligning early detection with reliability. Experiments on three benchmark datasets (DAD, CCD, A3D) demonstrate state-of-the-art accuracy and significant gains in mean time-to-accident, while maintaining robust performance under Gaussian and impulse noise. Qualitative analyses further show that our model produces earlier, more stable, and human-aligned predictions in both routine and highly complex traffic scenarios, highlighting its potential for real-world, safety-critical deployment.
AMD: Adaptive Momentum and Decoupled Contrastive Learning Framework for Robust Long-Tail Trajectory Prediction
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Accurately predicting the future trajectories of traffic agents is essential in autonomous driving. However, due to the inherent imbalance in trajectory distributions, tail data in natural datasets often represents more complex and hazardous scenarios. Existing studies typically rely solely on a base model's prediction error, without considering the diversity and uncertainty of long-tail trajectory patterns. We propose an adaptive momentum and decoupled contrastive learning framework (AMD), which integrates unsupervised and supervised contrastive learning strategies. By leveraging an improved momentum contrast learning (MoCo-DT) and decoupled contrastive learning (DCL) module, our framework enhances the model's ability to recognize rare and complex trajectories. Additionally, we design four types of trajectory random augmentation methods and introduce an online iterative clustering strategy, allowing the model to dynamically update pseudo-labels and better adapt to the distributional shifts in long-tail data. We propose three different criteria to define long-tail trajectories and conduct extensive comparative experiments on the nuScenes and ETH$/$UCY datasets. The results show that AMD not only achieves optimal performance in long-tail trajectory prediction but also demonstrates outstanding overall prediction accuracy.
LLM-DSE: Searching Accelerator Parameters with LLM Agents
May 18, 2025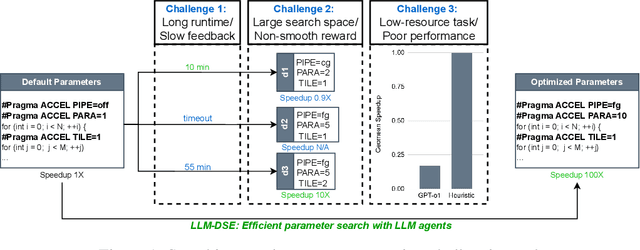
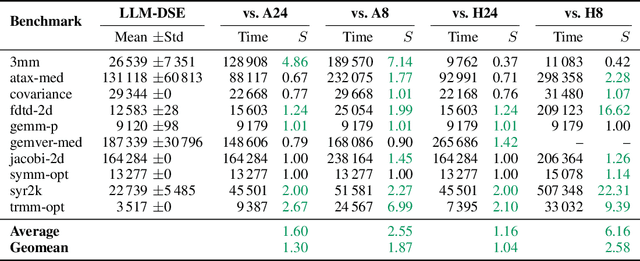
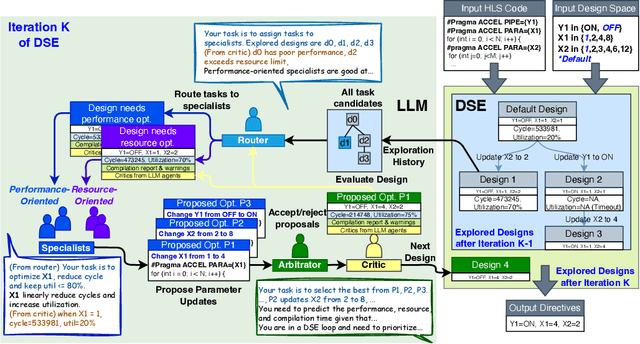
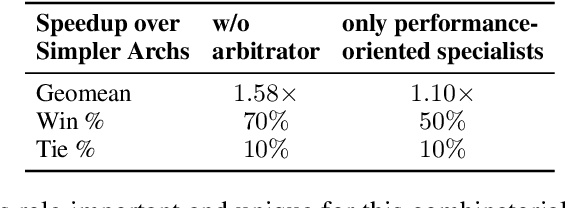
Abstract:Even though high-level synthesis (HLS) tools mitigate the challenges of programming domain-specific accelerators (DSAs) by raising the abstraction level, optimizing hardware directive parameters remains a significant hurdle. Existing heuristic and learning-based methods struggle with adaptability and sample efficiency.We present LLM-DSE, a multi-agent framework designed specifically for optimizing HLS directives. Combining LLM with design space exploration (DSE), our explorer coordinates four agents: Router, Specialists, Arbitrator, and Critic. These multi-agent components interact with various tools to accelerate the optimization process. LLM-DSE leverages essential domain knowledge to identify efficient parameter combinations while maintaining adaptability through verbal learning from online interactions. Evaluations on the HLSyn dataset demonstrate that LLM-DSE achieves substantial $2.55\times$ performance gains over state-of-the-art methods, uncovering novel designs while reducing runtime. Ablation studies validate the effectiveness and necessity of the proposed agent interactions. Our code is open-sourced here: https://github.com/Nozidoali/LLM-DSE.
Beyond Patterns: Harnessing Causal Logic for Autonomous Driving Trajectory Prediction
May 11, 2025Abstract:Accurate trajectory prediction has long been a major challenge for autonomous driving (AD). Traditional data-driven models predominantly rely on statistical correlations, often overlooking the causal relationships that govern traffic behavior. In this paper, we introduce a novel trajectory prediction framework that leverages causal inference to enhance predictive robustness, generalization, and accuracy. By decomposing the environment into spatial and temporal components, our approach identifies and mitigates spurious correlations, uncovering genuine causal relationships. We also employ a progressive fusion strategy to integrate multimodal information, simulating human-like reasoning processes and enabling real-time inference. Evaluations on five real-world datasets--ApolloScape, nuScenes, NGSIM, HighD, and MoCAD--demonstrate our model's superiority over existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, with improvements in key metrics such as RMSE and FDE. Our findings highlight the potential of causal reasoning to transform trajectory prediction, paving the way for robust AD systems.
SafeCast: Risk-Responsive Motion Forecasting for Autonomous Vehicles
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:Accurate motion forecasting is essential for the safety and reliability of autonomous driving (AD) systems. While existing methods have made significant progress, they often overlook explicit safety constraints and struggle to capture the complex interactions among traffic agents, environmental factors, and motion dynamics. To address these challenges, we present SafeCast, a risk-responsive motion forecasting model that integrates safety-aware decision-making with uncertainty-aware adaptability. SafeCast is the first to incorporate the Responsibility-Sensitive Safety (RSS) framework into motion forecasting, encoding interpretable safety rules--such as safe distances and collision avoidance--based on traffic norms and physical principles. To further enhance robustness, we introduce the Graph Uncertainty Feature (GUF), a graph-based module that injects learnable noise into Graph Attention Networks, capturing real-world uncertainties and enhancing generalization across diverse scenarios. We evaluate SafeCast on four real-world benchmark datasets--Next Generation Simulation (NGSIM), Highway Drone (HighD), ApolloScape, and the Macao Connected Autonomous Driving (MoCAD)--covering highway, urban, and mixed-autonomy traffic environments. Our model achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) accuracy while maintaining a lightweight architecture and low inference latency, underscoring its potential for real-time deployment in safety-critical AD systems.
CoT-Drive: Efficient Motion Forecasting for Autonomous Driving with LLMs and Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Mar 10, 2025
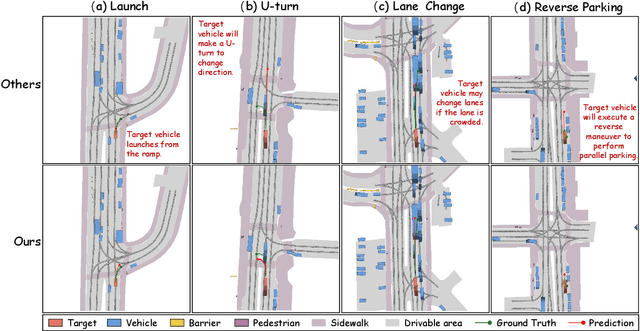
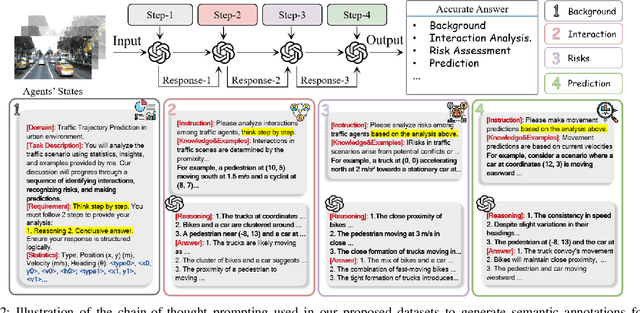

Abstract:Accurate motion forecasting is crucial for safe autonomous driving (AD). This study proposes CoT-Drive, a novel approach that enhances motion forecasting by leveraging large language models (LLMs) and a chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting method. We introduce a teacher-student knowledge distillation strategy to effectively transfer LLMs' advanced scene understanding capabilities to lightweight language models (LMs), ensuring that CoT-Drive operates in real-time on edge devices while maintaining comprehensive scene understanding and generalization capabilities. By leveraging CoT prompting techniques for LLMs without additional training, CoT-Drive generates semantic annotations that significantly improve the understanding of complex traffic environments, thereby boosting the accuracy and robustness of predictions. Additionally, we present two new scene description datasets, Highway-Text and Urban-Text, designed for fine-tuning lightweight LMs to generate context-specific semantic annotations. Comprehensive evaluations of five real-world datasets demonstrate that CoT-Drive outperforms existing models, highlighting its effectiveness and efficiency in handling complex traffic scenarios. Overall, this study is the first to consider the practical application of LLMs in this field. It pioneers the training and use of a lightweight LLM surrogate for motion forecasting, setting a new benchmark and showcasing the potential of integrating LLMs into AD systems.
Minds on the Move: Decoding Trajectory Prediction in Autonomous Driving with Cognitive Insights
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:In mixed autonomous driving environments, accurately predicting the future trajectories of surrounding vehicles is crucial for the safe operation of autonomous vehicles (AVs). In driving scenarios, a vehicle's trajectory is determined by the decision-making process of human drivers. However, existing models primarily focus on the inherent statistical patterns in the data, often neglecting the critical aspect of understanding the decision-making processes of human drivers. This oversight results in models that fail to capture the true intentions of human drivers, leading to suboptimal performance in long-term trajectory prediction. To address this limitation, we introduce a Cognitive-Informed Transformer (CITF) that incorporates a cognitive concept, Perceived Safety, to interpret drivers' decision-making mechanisms. Perceived Safety encapsulates the varying risk tolerances across drivers with different driving behaviors. Specifically, we develop a Perceived Safety-aware Module that includes a Quantitative Safety Assessment for measuring the subject risk levels within scenarios, and Driver Behavior Profiling for characterizing driver behaviors. Furthermore, we present a novel module, Leanformer, designed to capture social interactions among vehicles. CITF demonstrates significant performance improvements on three well-established datasets. In terms of long-term prediction, it surpasses existing benchmarks by 12.0% on the NGSIM, 28.2% on the HighD, and 20.8% on the MoCAD dataset. Additionally, its robustness in scenarios with limited or missing data is evident, surpassing most state-of-the-art (SOTA) baselines, and paving the way for real-world applications.
DEMO: A Dynamics-Enhanced Learning Model for Multi-Horizon Trajectory Prediction in Autonomous Vehicles
Dec 30, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous vehicles (AVs) rely on accurate trajectory prediction of surrounding vehicles to ensure the safety of both passengers and other road users. Trajectory prediction spans both short-term and long-term horizons, each requiring distinct considerations: short-term predictions rely on accurately capturing the vehicle's dynamics, while long-term predictions rely on accurately modeling the interaction patterns within the environment. However current approaches, either physics-based or learning-based models, always ignore these distinct considerations, making them struggle to find the optimal prediction for both short-term and long-term horizon. In this paper, we introduce the Dynamics-Enhanced Learning MOdel (DEMO), a novel approach that combines a physics-based Vehicle Dynamics Model with advanced deep learning algorithms. DEMO employs a two-stage architecture, featuring a Dynamics Learning Stage and an Interaction Learning Stage, where the former stage focuses on capturing vehicle motion dynamics and the latter focuses on modeling interaction. By capitalizing on the respective strengths of both methods, DEMO facilitates multi-horizon predictions for future trajectories. Experimental results on the Next Generation Simulation (NGSIM), Macau Connected Autonomous Driving (MoCAD), Highway Drone (HighD), and nuScenes datasets demonstrate that DEMO outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) baselines in both short-term and long-term prediction horizons.
NEST: A Neuromodulated Small-world Hypergraph Trajectory Prediction Model for Autonomous Driving
Dec 16, 2024Abstract:Accurate trajectory prediction is essential for the safety and efficiency of autonomous driving. Traditional models often struggle with real-time processing, capturing non-linearity and uncertainty in traffic environments, efficiency in dense traffic, and modeling temporal dynamics of interactions. We introduce NEST (Neuromodulated Small-world Hypergraph Trajectory Prediction), a novel framework that integrates Small-world Networks and hypergraphs for superior interaction modeling and prediction accuracy. This integration enables the capture of both local and extended vehicle interactions, while the Neuromodulator component adapts dynamically to changing traffic conditions. We validate the NEST model on several real-world datasets, including nuScenes, MoCAD, and HighD. The results consistently demonstrate that NEST outperforms existing methods in various traffic scenarios, showcasing its exceptional generalization capability, efficiency, and temporal foresight. Our comprehensive evaluation illustrates that NEST significantly improves the reliability and operational efficiency of autonomous driving systems, making it a robust solution for trajectory prediction in complex traffic environments.
Real-time Accident Anticipation for Autonomous Driving Through Monocular Depth-Enhanced 3D Modeling
Sep 02, 2024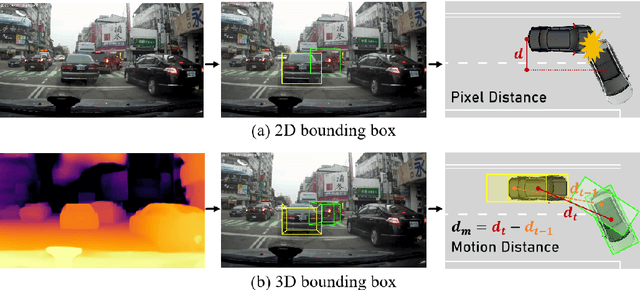
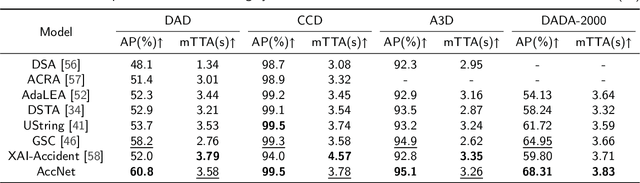
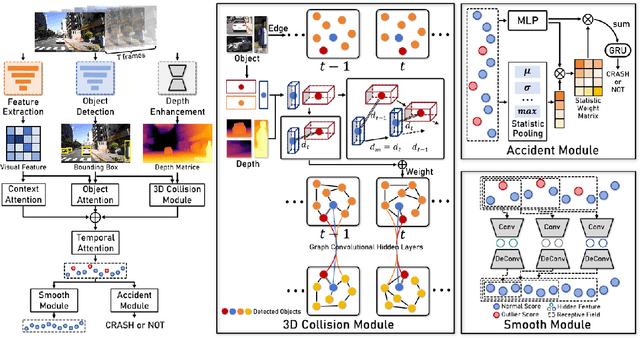
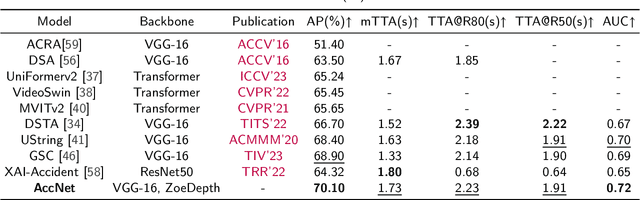
Abstract:The primary goal of traffic accident anticipation is to foresee potential accidents in real time using dashcam videos, a task that is pivotal for enhancing the safety and reliability of autonomous driving technologies. In this study, we introduce an innovative framework, AccNet, which significantly advances the prediction capabilities beyond the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) 2D-based methods by incorporating monocular depth cues for sophisticated 3D scene modeling. Addressing the prevalent challenge of skewed data distribution in traffic accident datasets, we propose the Binary Adaptive Loss for Early Anticipation (BA-LEA). This novel loss function, together with a multi-task learning strategy, shifts the focus of the predictive model towards the critical moments preceding an accident. {We rigorously evaluate the performance of our framework on three benchmark datasets--Dashcam Accident Dataset (DAD), Car Crash Dataset (CCD), and AnAn Accident Detection (A3D), and DADA-2000 Dataset--demonstrating its superior predictive accuracy through key metrics such as Average Precision (AP) and mean Time-To-Accident (mTTA).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge