Bowen Pang
RayFusion: Ray Fusion Enhanced Collaborative Visual Perception
Oct 09, 2025



Abstract:Collaborative visual perception methods have gained widespread attention in the autonomous driving community in recent years due to their ability to address sensor limitation problems. However, the absence of explicit depth information often makes it difficult for camera-based perception systems, e.g., 3D object detection, to generate accurate predictions. To alleviate the ambiguity in depth estimation, we propose RayFusion, a ray-based fusion method for collaborative visual perception. Using ray occupancy information from collaborators, RayFusion reduces redundancy and false positive predictions along camera rays, enhancing the detection performance of purely camera-based collaborative perception systems. Comprehensive experiments show that our method consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art models, substantially advancing the performance of collaborative visual perception. The code is available at https://github.com/wangsh0111/RayFusion.
Automatic Operator-level Parallelism Planning for Distributed Deep Learning -- A Mixed-Integer Programming Approach
Mar 12, 2025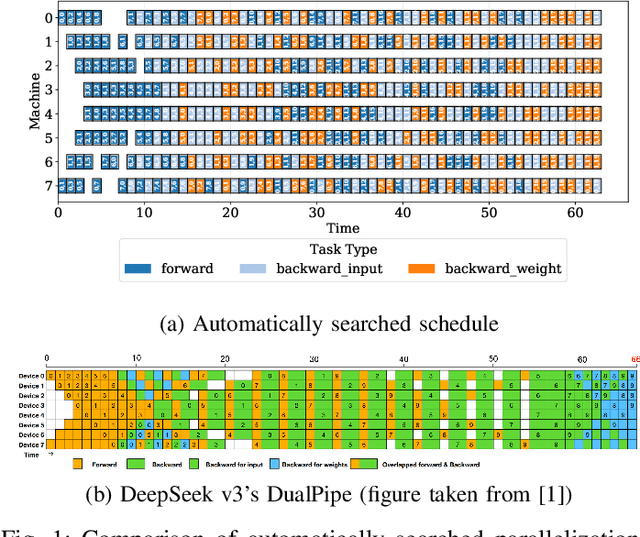
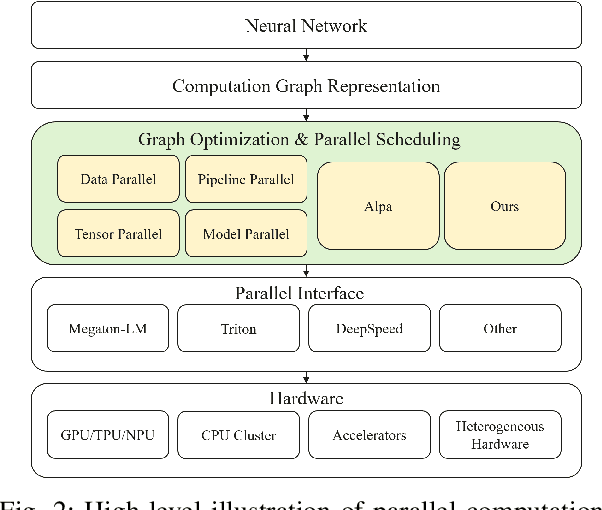
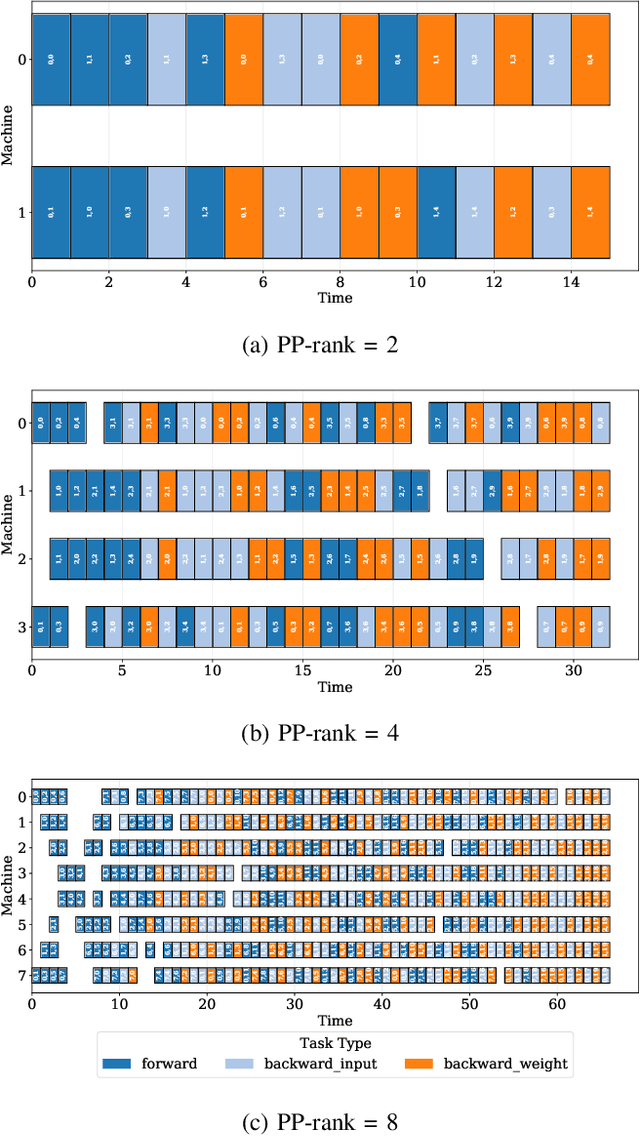
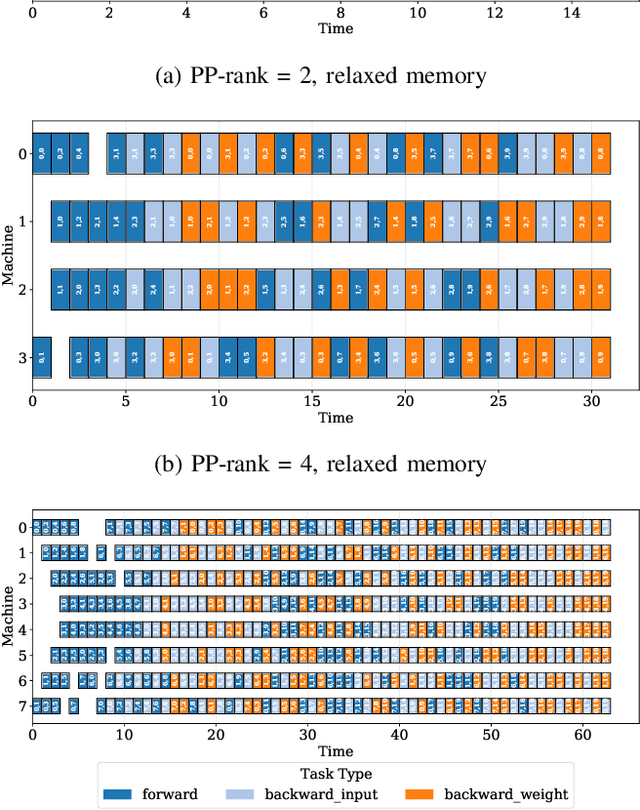
Abstract:As the artificial intelligence community advances into the era of large models with billions of parameters, distributed training and inference have become essential. While various parallelism strategies-data, model, sequence, and pipeline-have been successfully implemented for popular neural networks on main-stream hardware, optimizing the distributed deployment schedule requires extensive expertise and manual effort. Further more, while existing frameworks with most simple chain-like structures, they struggle with complex non-linear architectures. Mixture-of-experts and multi-modal models feature intricate MIMO and branch-rich topologies that require fine-grained operator-level parallelization beyond the capabilities of existing frameworks. We propose formulating parallelism planning as a scheduling optimization problem using mixed-integer programming. We propose a bi-level solution framework balancing optimality with computational efficiency, automatically generating effective distributed plans that capture both the heterogeneous structure of modern neural networks and the underlying hardware constraints. In experiments comparing against expert-designed strategies like DeepSeek's DualPipe, our framework achieves comparable or superior performance, reducing computational bubbles by half under the same memory constraints. The framework's versatility extends beyond throughput optimization to incorporate hardware utilization maximization, memory capacity constraints, and other considerations or potential strategies. Such capabilities position our solution as both a valuable research tool for exploring optimal parallelization strategies and a practical industrial solution for large-scale AI deployment.
Language Driven Occupancy Prediction
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:We introduce LOcc, an effective and generalizable framework for open-vocabulary occupancy (OVO) prediction. Previous approaches typically supervise the networks through coarse voxel-to-text correspondences via image features as intermediates or noisy and sparse correspondences from voxel-based model-view projections. To alleviate the inaccurate supervision, we propose a semantic transitive labeling pipeline to generate dense and finegrained 3D language occupancy ground truth. Our pipeline presents a feasible way to dig into the valuable semantic information of images, transferring text labels from images to LiDAR point clouds and utimately to voxels, to establish precise voxel-to-text correspondences. By replacing the original prediction head of supervised occupancy models with a geometry head for binary occupancy states and a language head for language features, LOcc effectively uses the generated language ground truth to guide the learning of 3D language volume. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our semantic transitive labeling pipeline can produce more accurate pseudo-labeled ground truth, diminishing labor-intensive human annotations. Additionally, we validate LOcc across various architectures, where all models consistently outperform state-ofthe-art zero-shot occupancy prediction approaches on the Occ3D-nuScenes dataset. Notably, even based on the simpler BEVDet model, with an input resolution of 256 * 704,Occ-BEVDet achieves an mIoU of 20.29, surpassing previous approaches that rely on temporal images, higher-resolution inputs, or larger backbone networks. The code for the proposed method is available at https://github.com/pkqbajng/LOcc.
LVIC: Multi-modality segmentation by Lifting Visual Info as Cue
Mar 08, 2024


Abstract:Multi-modality fusion is proven an effective method for 3d perception for autonomous driving. However, most current multi-modality fusion pipelines for LiDAR semantic segmentation have complicated fusion mechanisms. Point painting is a quite straight forward method which directly bind LiDAR points with visual information. Unfortunately, previous point painting like methods suffer from projection error between camera and LiDAR. In our experiments, we find that this projection error is the devil in point painting. As a result of that, we propose a depth aware point painting mechanism, which significantly boosts the multi-modality fusion. Apart from that, we take a deeper look at the desired visual feature for LiDAR to operate semantic segmentation. By Lifting Visual Information as Cue, LVIC ranks 1st on nuScenes LiDAR semantic segmentation benchmark. Our experiments show the robustness and effectiveness. Codes would be make publicly available soon.
The FlySpeech Audio-Visual Speaker Diarization System for MISP Challenge 2022
Jul 28, 2023


Abstract:This paper describes the FlySpeech speaker diarization system submitted to the second \textbf{M}ultimodal \textbf{I}nformation Based \textbf{S}peech \textbf{P}rocessing~(\textbf{MISP}) Challenge held in ICASSP 2022. We develop an end-to-end audio-visual speaker diarization~(AVSD) system, which consists of a lip encoder, a speaker encoder, and an audio-visual decoder. Specifically, to mitigate the degradation of diarization performance caused by separate training, we jointly train the speaker encoder and the audio-visual decoder. In addition, we leverage the large-data pretrained speaker extractor to initialize the speaker encoder.
TSUP Speaker Diarization System for Conversational Short-phrase Speaker Diarization Challenge
Oct 26, 2022Abstract:This paper describes the TSUP team's submission to the ISCSLP 2022 conversational short-phrase speaker diarization (CSSD) challenge which particularly focuses on short-phrase conversations with a new evaluation metric called conversational diarization error rate (CDER). In this challenge, we explore three kinds of typical speaker diarization systems, which are spectral clustering(SC) based diarization, target-speaker voice activity detection(TS-VAD) and end-to-end neural diarization(EEND) respectively. Our major findings are summarized as follows. First, the SC approach is more favored over the other two approaches under the new CDER metric. Second, tuning on hyperparameters is essential to CDER for all three types of speaker diarization systems. Specifically, CDER becomes smaller when the length of sub-segments setting longer. Finally, multi-system fusion through DOVER-LAP will worsen the CDER metric on the challenge data. Our submitted SC system eventually ranks the third place in the challenge.
Parameter Convex Neural Networks
Jun 11, 2022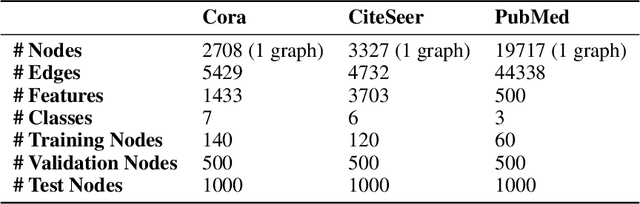
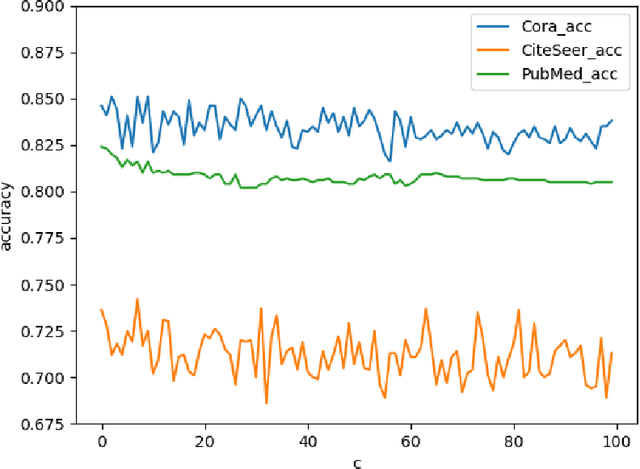
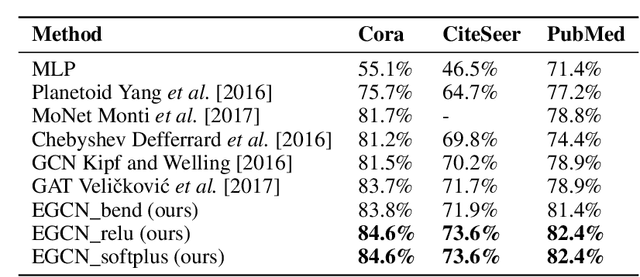
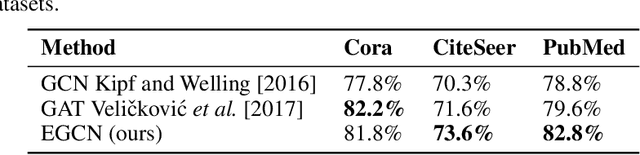
Abstract:Deep learning utilizing deep neural networks (DNNs) has achieved a lot of success recently in many important areas such as computer vision, natural language processing, and recommendation systems. The lack of convexity for DNNs has been seen as a major disadvantage of many optimization methods, such as stochastic gradient descent, which greatly reduces the genelization of neural network applications. We realize that the convexity make sense in the neural network and propose the exponential multilayer neural network (EMLP), a class of parameter convex neural network (PCNN) which is convex with regard to the parameters of the neural network under some conditions that can be realized. Besides, we propose the convexity metric for the two-layer EGCN and test the accuracy when the convexity metric changes. For late experiments, we use the same architecture to make the exponential graph convolutional network (EGCN) and do the experiment on the graph classificaion dataset in which our model EGCN performs better than the graph convolutional network (GCN) and the graph attention network (GAT).
Enhance Ambiguous Community Structure via Multi-strategy Community Related Link Prediction Method with Evolutionary Process
Apr 28, 2022Abstract:Most real-world networks suffer from incompleteness or incorrectness, which is an inherent attribute to real-world datasets. As a consequence, those downstream machine learning tasks in complex network like community detection methods may yield less satisfactory results, i.e., a proper preprocessing measure is required here. To address this issue, in this paper, we design a new community attribute based link prediction strategy HAP and propose a two-step community enhancement algorithm with automatic evolution process based on HAP. This paper aims at providing a community enhancement measure through adding links to clarify ambiguous community structures. The HAP method takes the neighbourhood uncertainty and Shannon entropy to identify boundary nodes, and establishes links by considering the nodes' community attributes and community size at the same time. The experimental results on twelve real-world datasets with ground truth community indicate that the proposed link prediction method outperforms other baseline methods and the enhancement of community follows the expected evolution process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge