Eryun Liu
RayFusion: Ray Fusion Enhanced Collaborative Visual Perception
Oct 09, 2025



Abstract:Collaborative visual perception methods have gained widespread attention in the autonomous driving community in recent years due to their ability to address sensor limitation problems. However, the absence of explicit depth information often makes it difficult for camera-based perception systems, e.g., 3D object detection, to generate accurate predictions. To alleviate the ambiguity in depth estimation, we propose RayFusion, a ray-based fusion method for collaborative visual perception. Using ray occupancy information from collaborators, RayFusion reduces redundancy and false positive predictions along camera rays, enhancing the detection performance of purely camera-based collaborative perception systems. Comprehensive experiments show that our method consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art models, substantially advancing the performance of collaborative visual perception. The code is available at https://github.com/wangsh0111/RayFusion.
MIDAS: Modeling Ground-Truth Distributions with Dark Knowledge for Domain Generalized Stereo Matching
Mar 06, 2025



Abstract:Despite the significant advances in domain generalized stereo matching, existing methods still exhibit domain-specific preferences when transferring from synthetic to real domains, hindering their practical applications in complex and diverse scenarios. The probability distributions predicted by the stereo network naturally encode rich similarity and uncertainty information. Inspired by this observation, we propose to extract these two types of dark knowledge from the pre-trained network to model intuitive multi-modal ground-truth distributions for both edge and non-edge regions. To mitigate the inherent domain preferences of a single network, we adopt network ensemble and further distinguish between objective and biased knowledge in the Laplace parameter space. Finally, the objective knowledge and the original disparity labels are jointly modeled as a mixture of Laplacians to provide fine-grained supervision for the stereo network training. Extensive experiments demonstrate that: 1) Our method is generic and effectively improves the generalization of existing networks. 2) PCWNet with our method achieves the state-of-the-art generalization performance on both KITTI 2015 and 2012 datasets. 3) Our method outperforms existing methods in comprehensive ranking across four popular real-world datasets.
SCKD: Semi-Supervised Cross-Modality Knowledge Distillation for 4D Radar Object Detection
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:3D object detection is one of the fundamental perception tasks for autonomous vehicles. Fulfilling such a task with a 4D millimeter-wave radar is very attractive since the sensor is able to acquire 3D point clouds similar to Lidar while maintaining robust measurements under adverse weather. However, due to the high sparsity and noise associated with the radar point clouds, the performance of the existing methods is still much lower than expected. In this paper, we propose a novel Semi-supervised Cross-modality Knowledge Distillation (SCKD) method for 4D radar-based 3D object detection. It characterizes the capability of learning the feature from a Lidar-radar-fused teacher network with semi-supervised distillation. We first propose an adaptive fusion module in the teacher network to boost its performance. Then, two feature distillation modules are designed to facilitate the cross-modality knowledge transfer. Finally, a semi-supervised output distillation is proposed to increase the effectiveness and flexibility of the distillation framework. With the same network structure, our radar-only student trained by SCKD boosts the mAP by 10.38% over the baseline and outperforms the state-of-the-art works on the VoD dataset. The experiment on ZJUODset also shows 5.12% mAP improvements on the moderate difficulty level over the baseline when extra unlabeled data are available. Code is available at https://github.com/Ruoyu-Xu/SCKD.
IFTR: An Instance-Level Fusion Transformer for Visual Collaborative Perception
Jul 13, 2024



Abstract:Multi-agent collaborative perception has emerged as a widely recognized technology in the field of autonomous driving in recent years. However, current collaborative perception predominantly relies on LiDAR point clouds, with significantly less attention given to methods using camera images. This severely impedes the development of budget-constrained collaborative systems and the exploitation of the advantages offered by the camera modality. This work proposes an instance-level fusion transformer for visual collaborative perception (IFTR), which enhances the detection performance of camera-only collaborative perception systems through the communication and sharing of visual features. To capture the visual information from multiple agents, we design an instance feature aggregation that interacts with the visual features of individual agents using predefined grid-shaped bird eye view (BEV) queries, generating more comprehensive and accurate BEV features. Additionally, we devise a cross-domain query adaptation as a heuristic to fuse 2D priors, implicitly encoding the candidate positions of targets. Furthermore, IFTR optimizes communication efficiency by sending instance-level features, achieving an optimal performance-bandwidth trade-off. We evaluate the proposed IFTR on a real dataset, DAIR-V2X, and two simulated datasets, OPV2V and V2XSet, achieving performance improvements of 57.96%, 9.23% and 12.99% in AP@70 metrics compared to the previous SOTAs, respectively. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of IFTR and the effectiveness of its key components. The code is available at https://github.com/wangsh0111/IFTR.
A Two-stage Based Social Preference Recognition in Multi-Agent Autonomous Driving System
Oct 05, 2023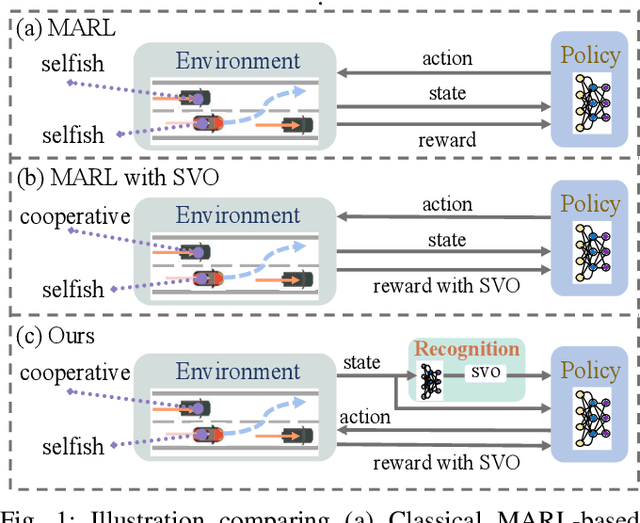
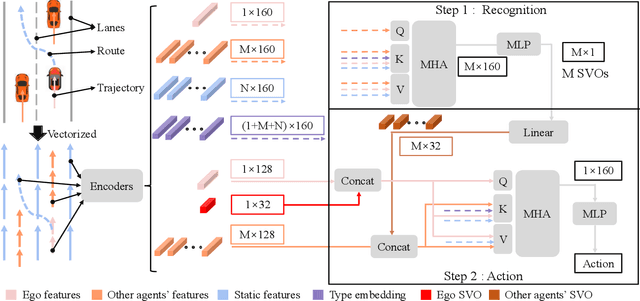
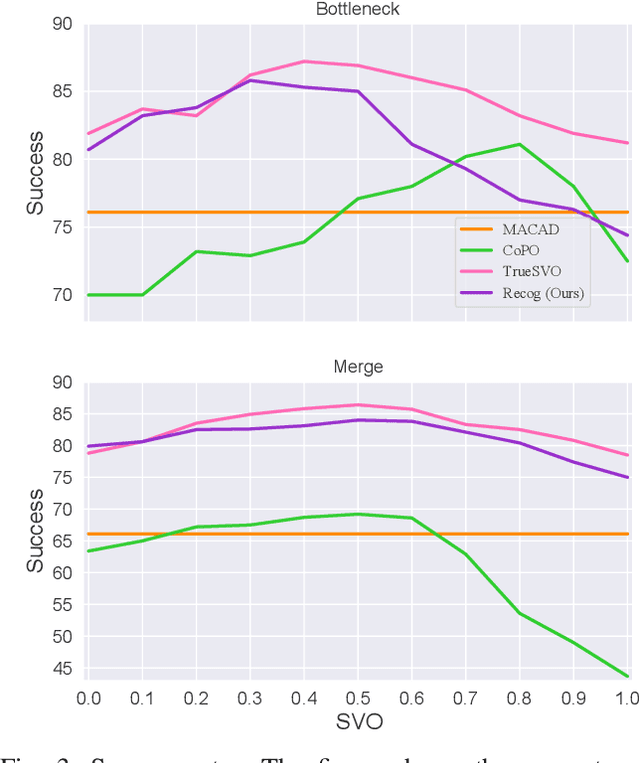
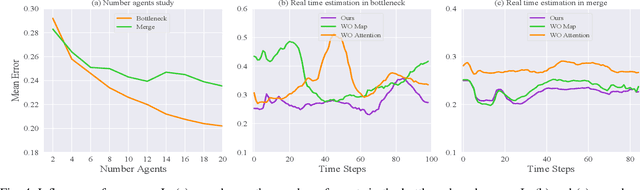
Abstract:Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) has become a promising solution for constructing a multi-agent autonomous driving system (MADS) in complex and dense scenarios. But most methods consider agents acting selfishly, which leads to conflict behaviors. Some existing works incorporate the concept of social value orientation (SVO) to promote coordination, but they lack the knowledge of other agents' SVOs, resulting in conservative maneuvers. In this paper, we aim to tackle the mentioned problem by enabling the agents to understand other agents' SVOs. To accomplish this, we propose a two-stage system framework. Firstly, we train a policy by allowing the agents to share their ground truth SVOs to establish a coordinated traffic flow. Secondly, we develop a recognition network that estimates agents' SVOs and integrates it with the policy trained in the first stage. Experiments demonstrate that our developed method significantly improves the performance of the driving policy in MADS compared to two state-of-the-art MARL algorithms.
Zero-shot Transfer Learning of Driving Policy via Socially Adversarial Traffic Flow
Apr 25, 2023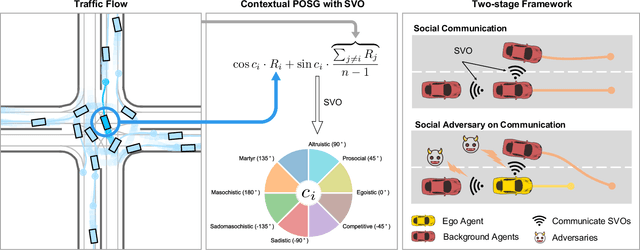
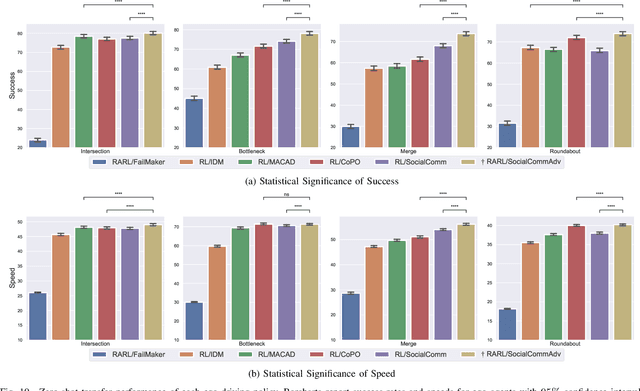
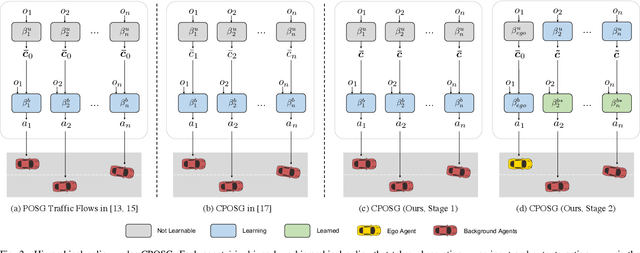
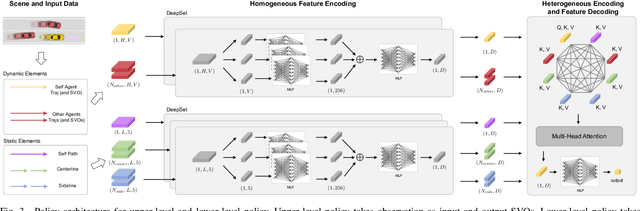
Abstract:Acquiring driving policies that can transfer to unseen environments is challenging when driving in dense traffic flows. The design of traffic flow is essential and previous studies are unable to balance interaction and safety-criticism. To tackle this problem, we propose a socially adversarial traffic flow. We propose a Contextual Partially-Observable Stochastic Game to model traffic flow and assign Social Value Orientation (SVO) as context. We then adopt a two-stage framework. In Stage 1, each agent in our socially-aware traffic flow is driven by a hierarchical policy where upper-level policy communicates genuine SVOs of all agents, which the lower-level policy takes as input. In Stage 2, each agent in the socially adversarial traffic flow is driven by the hierarchical policy where upper-level communicates mistaken SVOs, taken by the lower-level policy trained in Stage 1. Driving policy is adversarially trained through a zero-sum game formulation with upper-level policies, resulting in a policy with enhanced zero-shot transfer capability to unseen traffic flows. Comprehensive experiments on cross-validation verify the superior zero-shot transfer performance of our method.
Adaptive Base-class Suppression and Prior Guidance Network for One-Shot Object Detection
Mar 24, 2023



Abstract:One-shot object detection (OSOD) aims to detect all object instances towards the given category specified by a query image. Most existing studies in OSOD endeavor to explore effective cross-image correlation and alleviate the semantic feature misalignment, however, ignoring the phenomenon of the model bias towards the base classes and the generalization degradation on the novel classes. Observing this, we propose a novel framework, namely Base-class Suppression and Prior Guidance (BSPG) network to overcome the problem. Specifically, the objects of base categories can be explicitly detected by a base-class predictor and adaptively eliminated by our base-class suppression module. Moreover, a prior guidance module is designed to calculate the correlation of high-level features in a non-parametric manner, producing a class-agnostic prior map to provide the target features with rich semantic cues and guide the subsequent detection process. Equipped with the proposed two modules, we endow the model with a strong discriminative ability to distinguish the target objects from distractors belonging to the base classes. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms the previous techniques by a large margin and achieves new state-of-the-art performance under various evaluation settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge