Xinyu Xiao
School of Mathematical Science, Peking University
Fast-Slow Efficient Training for Multimodal Large Language Models via Visual Token Pruning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) suffer from severe training inefficiency issue, which is associated with their massive model sizes and visual token numbers. Existing efforts in efficient training focus on reducing model sizes or trainable parameters. Inspired by the success of Visual Token Pruning (VTP) in improving inference efficiency, we are exploring another substantial research direction for efficient training by reducing visual tokens. However, applying VTP at the training stage results in a training-inference mismatch: pruning-trained models perform poorly when inferring on non-pruned full visual token sequences. To close this gap, we propose DualSpeed, a fast-slow framework for efficient training of MLLMs. The fast-mode is the primary mode, which incorporates existing VTP methods as plugins to reduce visual tokens, along with a mode isolator to isolate the model's behaviors. The slow-mode is the auxiliary mode, where the model is trained on full visual sequences to retain training-inference consistency. To boost its training, it further leverages self-distillation to learn from the sufficiently trained fast-mode. Together, DualSpeed can achieve both training efficiency and non-degraded performance. Experiments show DualSpeed accelerates the training of LLaVA-1.5 by 2.1$\times$ and LLaVA-NeXT by 4.0$\times$, retaining over 99% performance. Code: https://github.com/dingkun-zhang/DualSpeed
PruneRAG: Confidence-Guided Query Decomposition Trees for Efficient Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has become a powerful framework for enhancing large language models in knowledge-intensive and reasoning tasks. However, as reasoning chains deepen or search trees expand, RAG systems often face two persistent failures: evidence forgetting, where retrieved knowledge is not effectively used, and inefficiency, caused by uncontrolled query expansions and redundant retrieval. These issues reveal a critical gap between retrieval and evidence utilization in current RAG architectures. We propose PruneRAG, a confidence-guided query decomposition framework that builds a structured query decomposition tree to perform stable and efficient reasoning. PruneRAG introduces three key mechanisms: adaptive node expansion that regulates tree width and depth, confidence-guided decisions that accept reliable answers and prune uncertain branches, and fine-grained retrieval that extracts entity-level anchors to improve retrieval precision. Together, these components preserve salient evidence throughout multi-hop reasoning while significantly reducing retrieval overhead. To better analyze evidence misuse, we define the Evidence Forgetting Rate as a metric to quantify cases where golden evidence is retrieved but not correctly used. Extensive experiments across various multi-hop QA benchmarks show that PruneRAG achieves superior accuracy and efficiency over state-of-the-art baselines.
RayFusion: Ray Fusion Enhanced Collaborative Visual Perception
Oct 09, 2025



Abstract:Collaborative visual perception methods have gained widespread attention in the autonomous driving community in recent years due to their ability to address sensor limitation problems. However, the absence of explicit depth information often makes it difficult for camera-based perception systems, e.g., 3D object detection, to generate accurate predictions. To alleviate the ambiguity in depth estimation, we propose RayFusion, a ray-based fusion method for collaborative visual perception. Using ray occupancy information from collaborators, RayFusion reduces redundancy and false positive predictions along camera rays, enhancing the detection performance of purely camera-based collaborative perception systems. Comprehensive experiments show that our method consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art models, substantially advancing the performance of collaborative visual perception. The code is available at https://github.com/wangsh0111/RayFusion.
Ming-Omni: A Unified Multimodal Model for Perception and Generation
Jun 11, 2025


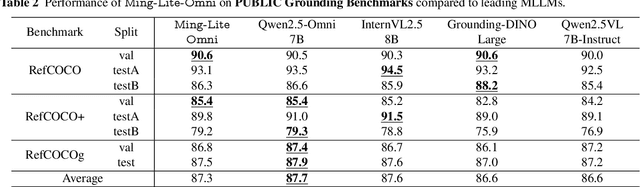
Abstract:We propose Ming-Omni, a unified multimodal model capable of processing images, text, audio, and video, while demonstrating strong proficiency in both speech and image generation. Ming-Omni employs dedicated encoders to extract tokens from different modalities, which are then processed by Ling, an MoE architecture equipped with newly proposed modality-specific routers. This design enables a single model to efficiently process and fuse multimodal inputs within a unified framework, thereby facilitating diverse tasks without requiring separate models, task-specific fine-tuning, or structural redesign. Importantly, Ming-Omni extends beyond conventional multimodal models by supporting audio and image generation. This is achieved through the integration of an advanced audio decoder for natural-sounding speech and Ming-Lite-Uni for high-quality image generation, which also allow the model to engage in context-aware chatting, perform text-to-speech conversion, and conduct versatile image editing. Our experimental results showcase Ming-Omni offers a powerful solution for unified perception and generation across all modalities. Notably, our proposed Ming-Omni is the first open-source model we are aware of to match GPT-4o in modality support, and we release all code and model weights to encourage further research and development in the community.
Ming-Lite-Uni: Advancements in Unified Architecture for Natural Multimodal Interaction
May 05, 2025
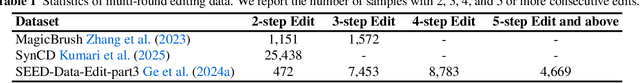
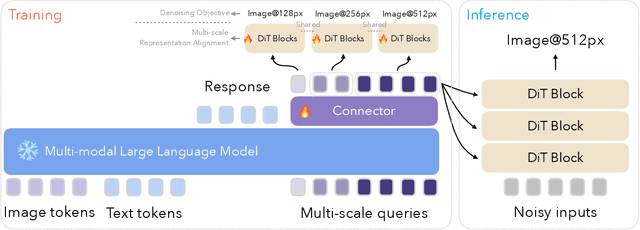
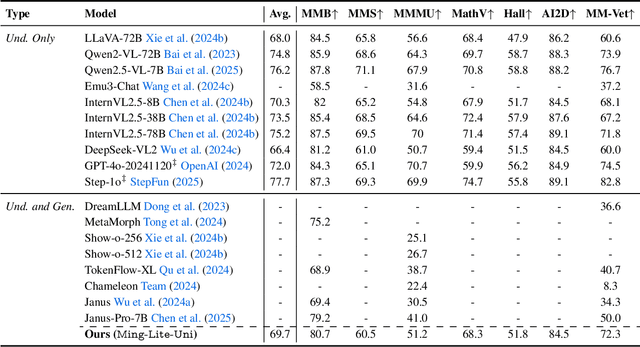
Abstract:We introduce Ming-Lite-Uni, an open-source multimodal framework featuring a newly designed unified visual generator and a native multimodal autoregressive model tailored for unifying vision and language. Specifically, this project provides an open-source implementation of the integrated MetaQueries and M2-omni framework, while introducing the novel multi-scale learnable tokens and multi-scale representation alignment strategy. By leveraging a fixed MLLM and a learnable diffusion model, Ming-Lite-Uni enables native multimodal AR models to perform both text-to-image generation and instruction based image editing tasks, expanding their capabilities beyond pure visual understanding. Our experimental results demonstrate the strong performance of Ming-Lite-Uni and illustrate the impressive fluid nature of its interactive process. All code and model weights are open-sourced to foster further exploration within the community. Notably, this work aligns with concurrent multimodal AI milestones - such as ChatGPT-4o with native image generation updated in March 25, 2025 - underscoring the broader significance of unified models like Ming-Lite-Uni on the path toward AGI. Ming-Lite-Uni is in alpha stage and will soon be further refined.
Merge then Realign: Simple and Effective Modality-Incremental Continual Learning for Multimodal LLMs
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have enhanced their versatility as they integrate a growing number of modalities. Considering the heavy cost of training MLLMs, it is necessary to reuse the existing ones and further extend them to more modalities through Modality-incremental Continual Learning (MCL). However, this often comes with a performance degradation in the previously learned modalities. In this work, we revisit the MCL and investigate a more severe issue it faces in contrast to traditional continual learning, that its degradation comes not only from catastrophic forgetting but also from the misalignment between the modality-agnostic and modality-specific components. To address this problem, we propose an elegantly simple MCL paradigm called "MErge then ReAlign" (MERA). Our method avoids introducing heavy training overhead or modifying the model architecture, hence is easy to deploy and highly reusable in the MLLM community. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, despite the simplicity of MERA, it shows impressive performance, holding up to a 99.84% Backward Relative Gain when extending to four modalities, achieving a nearly lossless MCL performance.
IFTR: An Instance-Level Fusion Transformer for Visual Collaborative Perception
Jul 13, 2024



Abstract:Multi-agent collaborative perception has emerged as a widely recognized technology in the field of autonomous driving in recent years. However, current collaborative perception predominantly relies on LiDAR point clouds, with significantly less attention given to methods using camera images. This severely impedes the development of budget-constrained collaborative systems and the exploitation of the advantages offered by the camera modality. This work proposes an instance-level fusion transformer for visual collaborative perception (IFTR), which enhances the detection performance of camera-only collaborative perception systems through the communication and sharing of visual features. To capture the visual information from multiple agents, we design an instance feature aggregation that interacts with the visual features of individual agents using predefined grid-shaped bird eye view (BEV) queries, generating more comprehensive and accurate BEV features. Additionally, we devise a cross-domain query adaptation as a heuristic to fuse 2D priors, implicitly encoding the candidate positions of targets. Furthermore, IFTR optimizes communication efficiency by sending instance-level features, achieving an optimal performance-bandwidth trade-off. We evaluate the proposed IFTR on a real dataset, DAIR-V2X, and two simulated datasets, OPV2V and V2XSet, achieving performance improvements of 57.96%, 9.23% and 12.99% in AP@70 metrics compared to the previous SOTAs, respectively. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of IFTR and the effectiveness of its key components. The code is available at https://github.com/wangsh0111/IFTR.
Unsupervised Modality-Transferable Video Highlight Detection with Representation Activation Sequence Learning
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:Identifying highlight moments of raw video materials is crucial for improving the efficiency of editing videos that are pervasive on internet platforms. However, the extensive work of manually labeling footage has created obstacles to applying supervised methods to videos of unseen categories. The absence of an audio modality that contains valuable cues for highlight detection in many videos also makes it difficult to use multimodal strategies. In this paper, we propose a novel model with cross-modal perception for unsupervised highlight detection. The proposed model learns representations with visual-audio level semantics from image-audio pair data via a self-reconstruction task. To achieve unsupervised highlight detection, we investigate the latent representations of the network and propose the representation activation sequence learning (RASL) module with k-point contrastive learning to learn significant representation activations. To connect the visual modality with the audio modality, we use the symmetric contrastive learning (SCL) module to learn the paired visual and audio representations. Furthermore, an auxiliary task of masked feature vector sequence (FVS) reconstruction is simultaneously conducted during pretraining for representation enhancement. During inference, the cross-modal pretrained model can generate representations with paired visual-audio semantics given only the visual modality. The RASL module is used to output the highlight scores. The experimental results show that the proposed framework achieves superior performance compared to other state-of-the-art approaches.
Meta-DSP: A Meta-Learning Approach for Data-Driven Nonlinear Compensation in High-Speed Optical Fiber Systems
Nov 17, 2023



Abstract:Non-linear effects in long-haul, high-speed optical fiber systems significantly hinder channel capacity. While the Digital Backward Propagation algorithm (DBP) with adaptive filter (ADF) can mitigate these effects, it suffers from an overwhelming computational complexity. Recent solutions have incorporated deep neural networks in a data-driven strategy to alleviate this complexity in the DBP model. However, these models are often limited to a specific symbol rate and channel number, necessitating retraining for different settings, their performance declines significantly under high-speed and high-power conditions. We introduce Meta-DSP, a novel data-driven nonlinear compensation model based on meta-learning that processes multi-modal data across diverse transmission rates, power levels, and channel numbers. This not only enhances signal quality but also substantially reduces the complexity of the nonlinear processing algorithm. Our model delivers a 0.7 dB increase in the Q-factor over Electronic Dispersion Compensation (EDC), and compared to DBP, it curtails computational complexity by a factor of ten while retaining comparable performance. From the perspective of the entire signal processing system, the core idea of Meta-DSP can be employed in any segment of the overall communication system to enhance the model's scalability and generalization performance. Our research substantiates Meta-DSP's proficiency in addressing the critical parameters defining optical communication networks.
CALM: Contrastive Cross-modal Speaking Style Modeling for Expressive Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Aug 30, 2023



Abstract:To further improve the speaking styles of synthesized speeches, current text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis systems commonly employ reference speeches to stylize their outputs instead of just the input texts. These reference speeches are obtained by manual selection which is resource-consuming, or selected by semantic features. However, semantic features contain not only style-related information, but also style irrelevant information. The information irrelevant to speaking style in the text could interfere the reference audio selection and result in improper speaking styles. To improve the reference selection, we propose Contrastive Acoustic-Linguistic Module (CALM) to extract the Style-related Text Feature (STF) from the text. CALM optimizes the correlation between the speaking style embedding and the extracted STF with contrastive learning. Thus, a certain number of the most appropriate reference speeches for the input text are selected by retrieving the speeches with the top STF similarities. Then the style embeddings are weighted summarized according to their STF similarities and used to stylize the synthesized speech of TTS. Experiment results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach, with both objective evaluations and subjective evaluations on the speaking styles of the synthesized speeches outperform a baseline approach with semantic-feature-based reference selection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge