Hangguan Shan
RayFusion: Ray Fusion Enhanced Collaborative Visual Perception
Oct 09, 2025



Abstract:Collaborative visual perception methods have gained widespread attention in the autonomous driving community in recent years due to their ability to address sensor limitation problems. However, the absence of explicit depth information often makes it difficult for camera-based perception systems, e.g., 3D object detection, to generate accurate predictions. To alleviate the ambiguity in depth estimation, we propose RayFusion, a ray-based fusion method for collaborative visual perception. Using ray occupancy information from collaborators, RayFusion reduces redundancy and false positive predictions along camera rays, enhancing the detection performance of purely camera-based collaborative perception systems. Comprehensive experiments show that our method consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art models, substantially advancing the performance of collaborative visual perception. The code is available at https://github.com/wangsh0111/RayFusion.
IFTR: An Instance-Level Fusion Transformer for Visual Collaborative Perception
Jul 13, 2024



Abstract:Multi-agent collaborative perception has emerged as a widely recognized technology in the field of autonomous driving in recent years. However, current collaborative perception predominantly relies on LiDAR point clouds, with significantly less attention given to methods using camera images. This severely impedes the development of budget-constrained collaborative systems and the exploitation of the advantages offered by the camera modality. This work proposes an instance-level fusion transformer for visual collaborative perception (IFTR), which enhances the detection performance of camera-only collaborative perception systems through the communication and sharing of visual features. To capture the visual information from multiple agents, we design an instance feature aggregation that interacts with the visual features of individual agents using predefined grid-shaped bird eye view (BEV) queries, generating more comprehensive and accurate BEV features. Additionally, we devise a cross-domain query adaptation as a heuristic to fuse 2D priors, implicitly encoding the candidate positions of targets. Furthermore, IFTR optimizes communication efficiency by sending instance-level features, achieving an optimal performance-bandwidth trade-off. We evaluate the proposed IFTR on a real dataset, DAIR-V2X, and two simulated datasets, OPV2V and V2XSet, achieving performance improvements of 57.96%, 9.23% and 12.99% in AP@70 metrics compared to the previous SOTAs, respectively. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of IFTR and the effectiveness of its key components. The code is available at https://github.com/wangsh0111/IFTR.
Byzantine-resilient Federated Learning With Adaptivity to Data Heterogeneity
Mar 27, 2024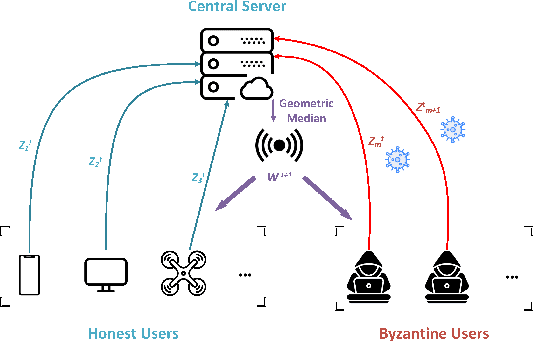
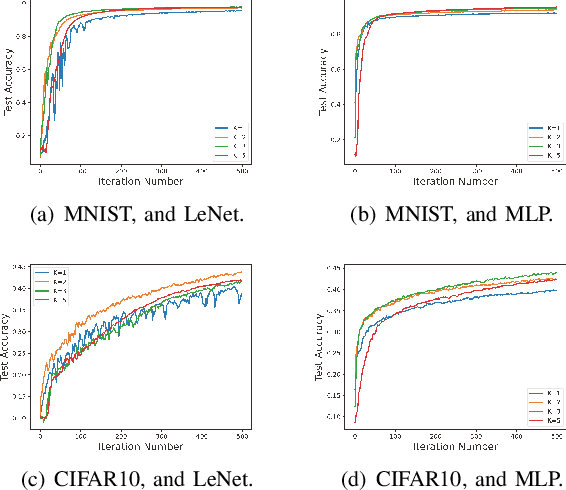
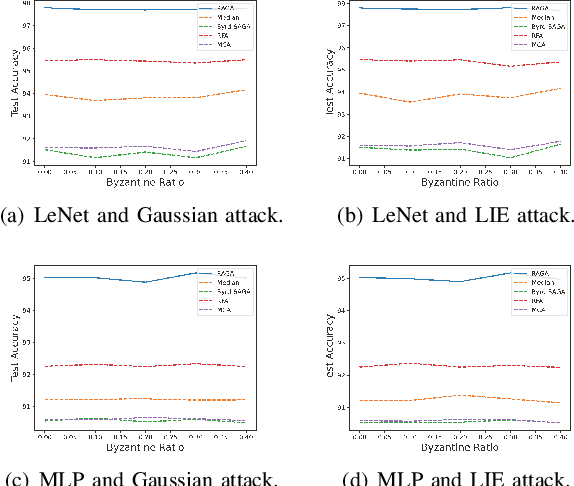
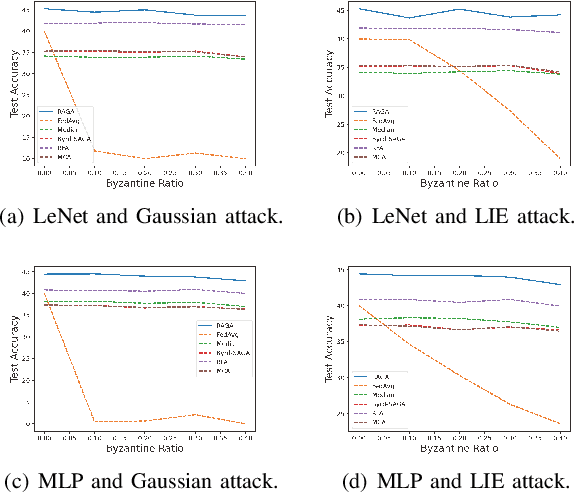
Abstract:This paper deals with federated learning (FL) in the presence of malicious Byzantine attacks and data heterogeneity. A novel Robust Average Gradient Algorithm (RAGA) is proposed, which leverages the geometric median for aggregation and can freely select the round number for local updating. Different from most existing resilient approaches, which perform convergence analysis based on strongly-convex loss function or homogeneously distributed dataset, we conduct convergence analysis for not only strongly-convex but also non-convex loss function over heterogeneous dataset. According to our theoretical analysis, as long as the fraction of dataset from malicious users is less than half, RAGA can achieve convergence at rate $\mathcal{O}({1}/{T^{2/3- \delta}})$ where $T$ is the iteration number and $\delta \in (0, 2/3)$ for non-convex loss function, and at linear rate for strongly-convex loss function. Moreover, stationary point or global optimal solution is proved to obtainable as data heterogeneity vanishes. Experimental results corroborate the robustness of RAGA to Byzantine attacks and verifies the advantage of RAGA over baselines on convergence performance under various intensity of Byzantine attacks, for heterogeneous dataset.
Adaptive Base-class Suppression and Prior Guidance Network for One-Shot Object Detection
Mar 24, 2023



Abstract:One-shot object detection (OSOD) aims to detect all object instances towards the given category specified by a query image. Most existing studies in OSOD endeavor to explore effective cross-image correlation and alleviate the semantic feature misalignment, however, ignoring the phenomenon of the model bias towards the base classes and the generalization degradation on the novel classes. Observing this, we propose a novel framework, namely Base-class Suppression and Prior Guidance (BSPG) network to overcome the problem. Specifically, the objects of base categories can be explicitly detected by a base-class predictor and adaptively eliminated by our base-class suppression module. Moreover, a prior guidance module is designed to calculate the correlation of high-level features in a non-parametric manner, producing a class-agnostic prior map to provide the target features with rich semantic cues and guide the subsequent detection process. Equipped with the proposed two modules, we endow the model with a strong discriminative ability to distinguish the target objects from distractors belonging to the base classes. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms the previous techniques by a large margin and achieves new state-of-the-art performance under various evaluation settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge