Chi Sun
CALM: Contrastive Cross-modal Speaking Style Modeling for Expressive Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Aug 30, 2023



Abstract:To further improve the speaking styles of synthesized speeches, current text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis systems commonly employ reference speeches to stylize their outputs instead of just the input texts. These reference speeches are obtained by manual selection which is resource-consuming, or selected by semantic features. However, semantic features contain not only style-related information, but also style irrelevant information. The information irrelevant to speaking style in the text could interfere the reference audio selection and result in improper speaking styles. To improve the reference selection, we propose Contrastive Acoustic-Linguistic Module (CALM) to extract the Style-related Text Feature (STF) from the text. CALM optimizes the correlation between the speaking style embedding and the extracted STF with contrastive learning. Thus, a certain number of the most appropriate reference speeches for the input text are selected by retrieving the speeches with the top STF similarities. Then the style embeddings are weighted summarized according to their STF similarities and used to stylize the synthesized speech of TTS. Experiment results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach, with both objective evaluations and subjective evaluations on the speaking styles of the synthesized speeches outperform a baseline approach with semantic-feature-based reference selection.
GlossBERT: BERT for Word Sense Disambiguation with Gloss Knowledge
Aug 20, 2019
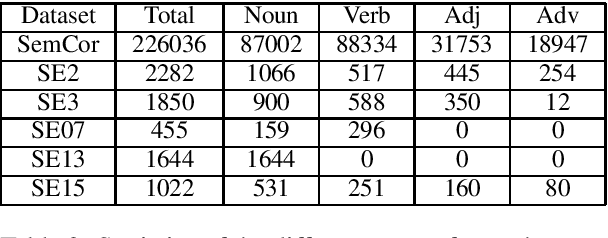
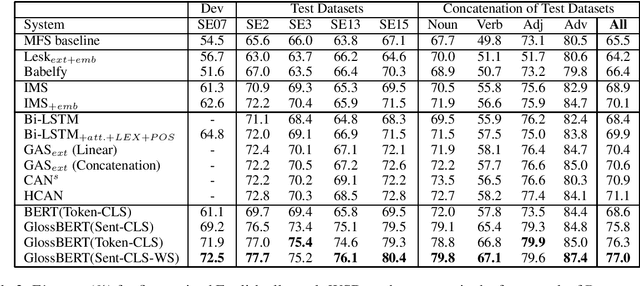
Abstract:Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) aims to find the exact sense of an ambiguous word in a particular context. Traditional supervised methods rarely take into consideration the lexical resources like WordNet, which are widely utilized in knowledge-based methods. Recent studies have shown the effectiveness of incorporating gloss (sense definition) into neural networks for WSD. However, compared with traditional word expert supervised methods, they have not achieved much improvement. In this paper, we focus on how to better leverage gloss knowledge in a supervised neural WSD system. We construct context-gloss pairs and propose three BERT-based models for WSD. We fine-tune the pre-trained BERT model and achieve new state-of-the-art results on WSD task.
How to Fine-Tune BERT for Text Classification?
May 14, 2019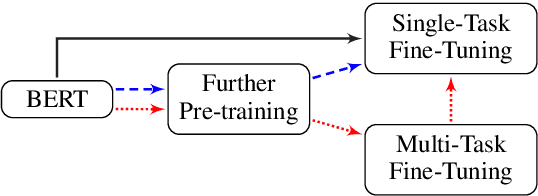
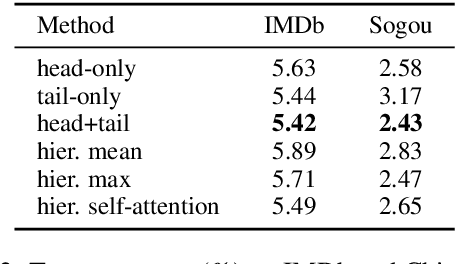
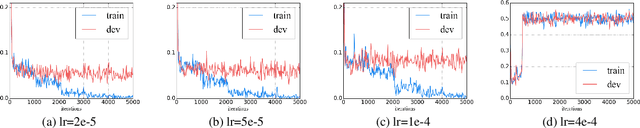
Abstract:Language model pre-training has proven to be useful in learning universal language representations. As a state-of-the-art language model pre-training model, BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) has achieved amazing results in many language understanding tasks. In this paper, we conduct exhaustive experiments to investigate different fine-tuning methods of BERT on text classification task and provide a general solution for BERT fine-tuning. Finally, the proposed solution obtains new state-of-the-art results on eight widely-studied text classification datasets.
VCWE: Visual Character-Enhanced Word Embeddings
Mar 25, 2019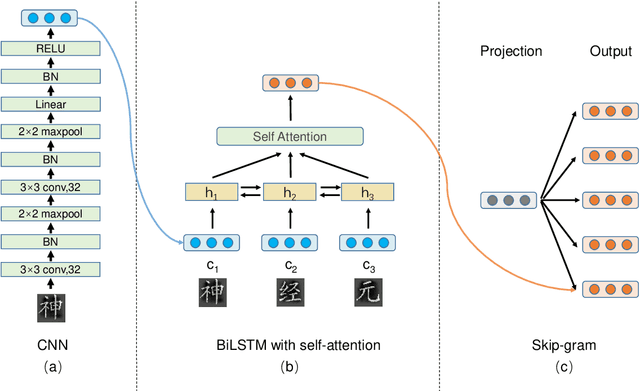
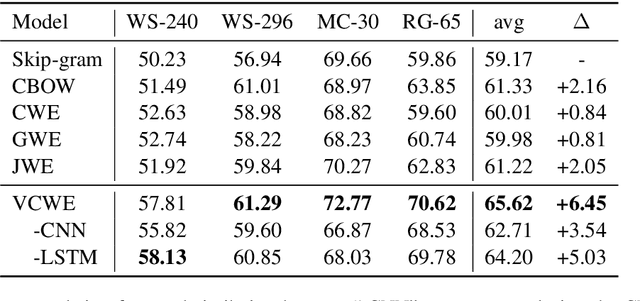
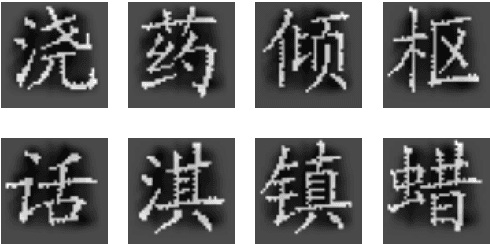
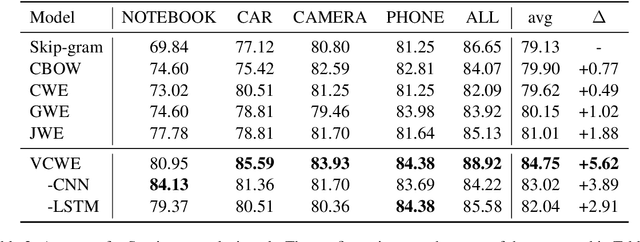
Abstract:Chinese is a logographic writing system, and the shape of Chinese characters contain rich syntactic and semantic information. In this paper, we propose a model to learn Chinese word embeddings via three-level composition: (1) a convolutional neural network to extract the intra-character compositionality from the visual shape of a character; (2) a recurrent neural network with self-attention to compose character representation into word embeddings; (3) the Skip-Gram framework to capture non-compositionality directly from the contextual information. Evaluations demonstrate the superior performance of our model on four tasks: word similarity, sentiment analysis, named entity recognition and part-of-speech tagging.
Utilizing BERT for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis via Constructing Auxiliary Sentence
Mar 22, 2019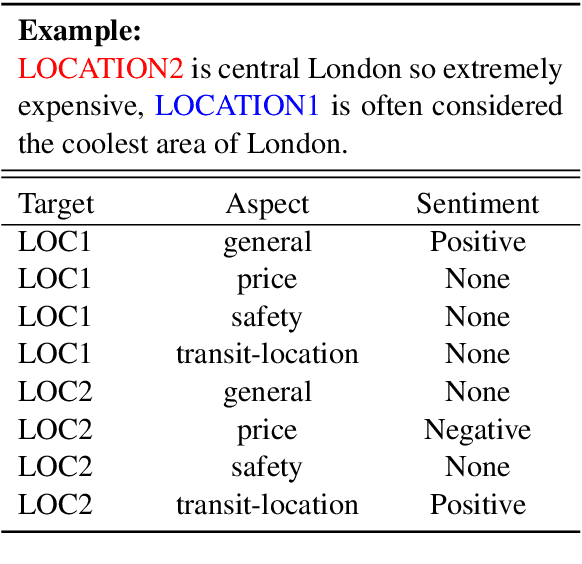
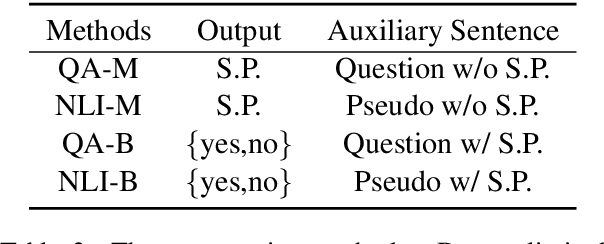
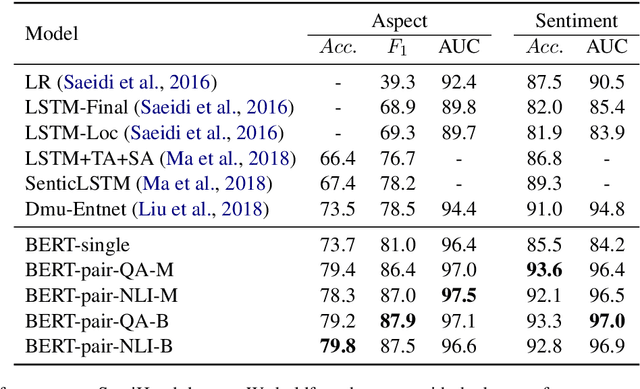
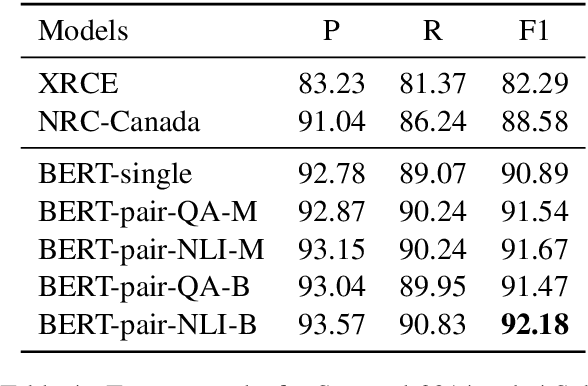
Abstract:Aspect-based sentiment analysis (ABSA), which aims to identify fine-grained opinion polarity towards a specific aspect, is a challenging subtask of sentiment analysis (SA). In this paper, we construct an auxiliary sentence from the aspect and convert ABSA to a sentence-pair classification task, such as question answering (QA) and natural language inference (NLI). We fine-tune the pre-trained model from BERT and achieve new state-of-the-art results on SentiHood and SemEval-2014 Task 4 datasets.
Gaussian Word Embedding with a Wasserstein Distance Loss
Sep 01, 2018
Abstract:Compared with word embedding based on point representation, distribution-based word embedding shows more flexibility in expressing uncertainty and therefore embeds richer semantic information when representing words. The Wasserstein distance provides a natural notion of dissimilarity with probability measures and has a closed-form solution when measuring the distance between two Gaussian distributions. Therefore, with the aim of representing words in a highly efficient way, we propose to operate a Gaussian word embedding model with a loss function based on the Wasserstein distance. Also, external information from ConceptNet will be used to semi-supervise the results of the Gaussian word embedding. Thirteen datasets from the word similarity task, together with one from the word entailment task, and six datasets from the downstream document classification task will be evaluated in this paper to test our hypothesis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge