Xiaoyue Yang
Low-Cost and Detunable Wireless Resonator Glasses for Enhanced Eye MRI with Concurrent High-Quality Whole Brain MRI
Sep 10, 2025
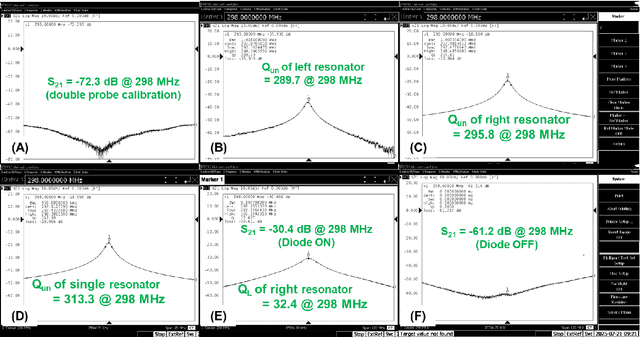
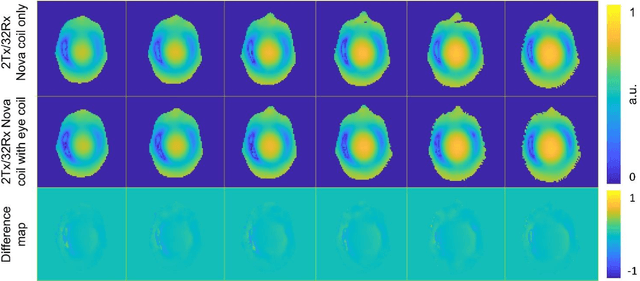

Abstract:Purpose: To develop and evaluate a wearable wireless resonator glasses design that enhances eye MRI signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) without compromising whole-brain image quality at 7 T. Methods: The device integrates two detunable LC loop resonators into a lightweight, 3D-printed frame positioned near the eyes. The resonators passively couple to a standard 2Tx/32Rx head coil without hardware modifications. Bench tests assessed tuning, isolation, and detuning performance. B1$^+$ maps were measured in a head/shoulder phantom, and SNR maps were obtained in both phantom and in vivo experiments. Results: Bench measurements confirmed accurate tuning, strong inter-element isolation, and effective passive detuning. Phantom B1$^+$ mapping showed negligible differences between configurations with and without the resonators. Phantom and in vivo imaging demonstrated up to about a 3-fold SNR gain in the eye region, with no measurable SNR loss in the brain. Conclusion: The wireless resonator glasses provide a low-cost, easy-to-use solution that improves ocular SNR while preserving whole-brain image quality, enabling both dedicated eye MRI and simultaneous eye-brain imaging at ultrahigh field.
Transsion TSUP's speech recognition system for ASRU 2023 MADASR Challenge
Jul 20, 2023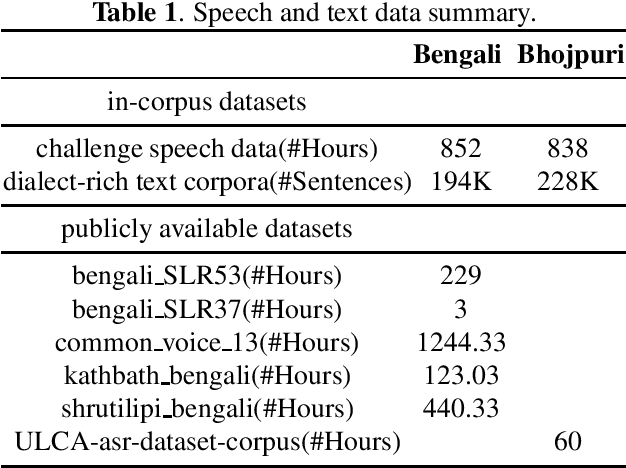

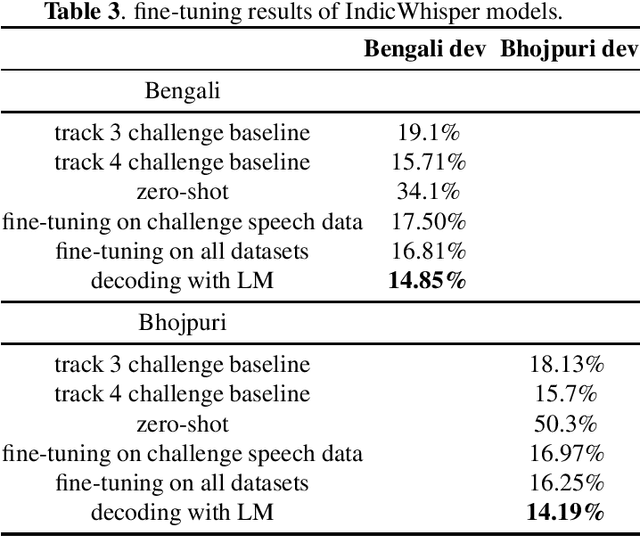
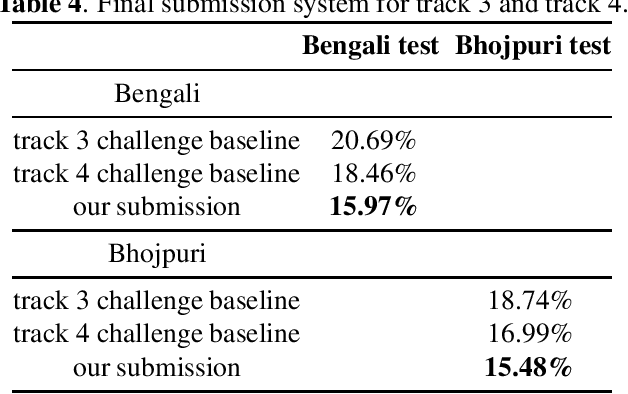
Abstract:This paper presents a speech recognition system developed by the Transsion Speech Understanding Processing Team (TSUP) for the ASRU 2023 MADASR Challenge. The system focuses on adapting ASR models for low-resource Indian languages and covers all four tracks of the challenge. For tracks 1 and 2, the acoustic model utilized a squeezeformer encoder and bidirectional transformer decoder with joint CTC-Attention training loss. Additionally, an external KenLM language model was used during TLG beam search decoding. For tracks 3 and 4, pretrained IndicWhisper models were employed and finetuned on both the challenge dataset and publicly available datasets. The whisper beam search decoding was also modified to support an external KenLM language model, which enabled better utilization of the additional text provided by the challenge. The proposed method achieved word error rates (WER) of 24.17%, 24.43%, 15.97%, and 15.97% for Bengali language in the four tracks, and WER of 19.61%, 19.54%, 15.48%, and 15.48% for Bhojpuri language in the four tracks. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
TSUP Speaker Diarization System for Conversational Short-phrase Speaker Diarization Challenge
Oct 26, 2022Abstract:This paper describes the TSUP team's submission to the ISCSLP 2022 conversational short-phrase speaker diarization (CSSD) challenge which particularly focuses on short-phrase conversations with a new evaluation metric called conversational diarization error rate (CDER). In this challenge, we explore three kinds of typical speaker diarization systems, which are spectral clustering(SC) based diarization, target-speaker voice activity detection(TS-VAD) and end-to-end neural diarization(EEND) respectively. Our major findings are summarized as follows. First, the SC approach is more favored over the other two approaches under the new CDER metric. Second, tuning on hyperparameters is essential to CDER for all three types of speaker diarization systems. Specifically, CDER becomes smaller when the length of sub-segments setting longer. Finally, multi-system fusion through DOVER-LAP will worsen the CDER metric on the challenge data. Our submitted SC system eventually ranks the third place in the challenge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge