Sheng Yang
State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Survering, Mapping and Remote Sensing, Wuhan University
TIGaussian: Disentangle Gaussians for Spatial-Awared Text-Image-3D Alignment
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:While visual-language models have profoundly linked features between texts and images, the incorporation of 3D modality data, such as point clouds and 3D Gaussians, further enables pretraining for 3D-related tasks, e.g., cross-modal retrieval, zero-shot classification, and scene recognition. As challenges remain in extracting 3D modal features and bridging the gap between different modalities, we propose TIGaussian, a framework that harnesses 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) characteristics to strengthen cross-modality alignment through multi-branch 3DGS tokenizer and modality-specific 3D feature alignment strategies. Specifically, our multi-branch 3DGS tokenizer decouples the intrinsic properties of 3DGS structures into compact latent representations, enabling more generalizable feature extraction. To further bridge the modality gap, we develop a bidirectional cross-modal alignment strategies: a multi-view feature fusion mechanism that leverages diffusion priors to resolve perspective ambiguity in image-3D alignment, while a text-3D projection module adaptively maps 3D features to text embedding space for better text-3D alignment. Extensive experiments on various datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of TIGaussian in multiple tasks.
GUIDE: Gaussian Unified Instance Detection for Enhanced Obstacle Perception in Autonomous Driving
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:In the realm of autonomous driving, accurately detecting surrounding obstacles is crucial for effective decision-making. Traditional methods primarily rely on 3D bounding boxes to represent these obstacles, which often fail to capture the complexity of irregularly shaped, real-world objects. To overcome these limitations, we present GUIDE, a novel framework that utilizes 3D Gaussians for instance detection and occupancy prediction. Unlike conventional occupancy prediction methods, GUIDE also offers robust tracking capabilities. Our framework employs a sparse representation strategy, using Gaussian-to-Voxel Splatting to provide fine-grained, instance-level occupancy data without the computational demands associated with dense voxel grids. Experimental validation on the nuScenes dataset demonstrates GUIDE's performance, with an instance occupancy mAP of 21.61, marking a 50\% improvement over existing methods, alongside competitive tracking capabilities. GUIDE establishes a new benchmark in autonomous perception systems, effectively combining precision with computational efficiency to better address the complexities of real-world driving environments.
LiDAR-GS++:Improving LiDAR Gaussian Reconstruction via Diffusion Priors
Nov 15, 2025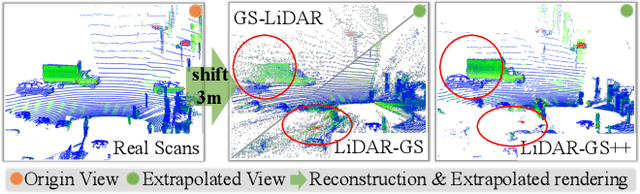
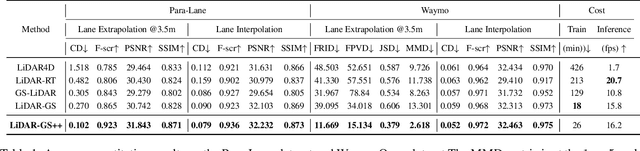
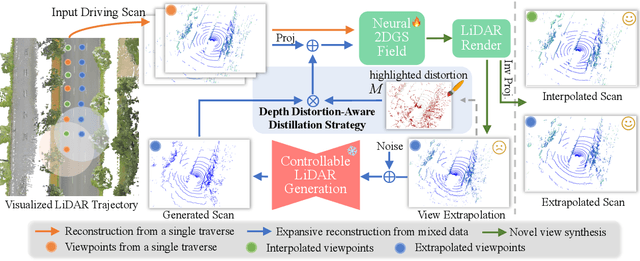
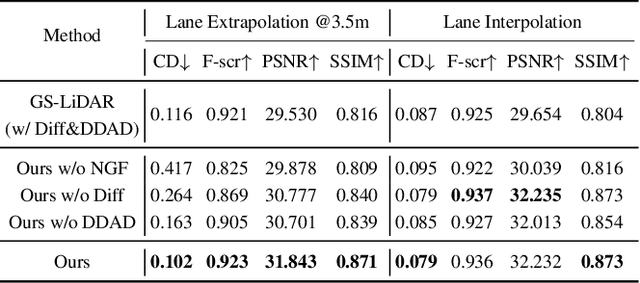
Abstract:Recent GS-based rendering has made significant progress for LiDAR, surpassing Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) in both quality and speed. However, these methods exhibit artifacts in extrapolated novel view synthesis due to the incomplete reconstruction from single traversal scans. To address this limitation, we present LiDAR-GS++, a LiDAR Gaussian Splatting reconstruction method enhanced by diffusion priors for real-time and high-fidelity re-simulation on public urban roads. Specifically, we introduce a controllable LiDAR generation model conditioned on coarsely extrapolated rendering to produce extra geometry-consistent scans and employ an effective distillation mechanism for expansive reconstruction. By extending reconstruction to under-fitted regions, our approach ensures global geometric consistency for extrapolative novel views while preserving detailed scene surfaces captured by sensors. Experiments on multiple public datasets demonstrate that LiDAR-GS++ achieves state-of-the-art performance for both interpolated and extrapolated viewpoints, surpassing existing GS and NeRF-based methods.
ProFusion: 3D Reconstruction of Protein Complex Structures from Multi-view AFM Images
Sep 17, 2025



Abstract:AI-based in silico methods have improved protein structure prediction but often struggle with large protein complexes (PCs) involving multiple interacting proteins due to missing 3D spatial cues. Experimental techniques like Cryo-EM are accurate but costly and time-consuming. We present ProFusion, a hybrid framework that integrates a deep learning model with Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), which provides high-resolution height maps from random orientations, naturally yielding multi-view data for 3D reconstruction. However, generating a large-scale AFM imaging data set sufficient to train deep learning models is impractical. Therefore, we developed a virtual AFM framework that simulates the imaging process and generated a dataset of ~542,000 proteins with multi-view synthetic AFM images. We train a conditional diffusion model to synthesize novel views from unposed inputs and an instance-specific Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) model to reconstruct 3D structures. Our reconstructed 3D protein structures achieve an average Chamfer Distance within the AFM imaging resolution, reflecting high structural fidelity. Our method is extensively validated on experimental AFM images of various PCs, demonstrating strong potential for accurate, cost-effective protein complex structure prediction and rapid iterative validation using AFM experiments.
GLM-4.1V-Thinking: Towards Versatile Multimodal Reasoning with Scalable Reinforcement Learning
Jul 02, 2025



Abstract:We present GLM-4.1V-Thinking, a vision-language model (VLM) designed to advance general-purpose multimodal understanding and reasoning. In this report, we share our key findings in the development of the reasoning-centric training framework. We first develop a capable vision foundation model with significant potential through large-scale pre-training, which arguably sets the upper bound for the final performance. We then propose Reinforcement Learning with Curriculum Sampling (RLCS) to unlock the full potential of the model, leading to comprehensive capability enhancement across a diverse range of tasks, including STEM problem solving, video understanding, content recognition, coding, grounding, GUI-based agents, and long document understanding. We open-source GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking, which achieves state-of-the-art performance among models of comparable size. In a comprehensive evaluation across 28 public benchmarks, our model outperforms Qwen2.5-VL-7B on nearly all tasks and achieves comparable or even superior performance on 18 benchmarks relative to the significantly larger Qwen2.5-VL-72B. Notably, GLM-4.1V-9B-Thinking also demonstrates competitive or superior performance compared to closed-source models such as GPT-4o on challenging tasks including long document understanding and STEM reasoning, further underscoring its strong capabilities. Code, models and more information are released at https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4.1V-Thinking.
RTMap: Real-Time Recursive Mapping with Change Detection and Localization
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:While recent online HD mapping methods relieve burdened offline pipelines and solve map freshness, they remain limited by perceptual inaccuracies, occlusion in dense traffic, and an inability to fuse multi-agent observations. We propose RTMap to enhance these single-traversal methods by persistently crowdsourcing a multi-traversal HD map as a self-evolutional memory. On onboard agents, RTMap simultaneously addresses three core challenges in an end-to-end fashion: (1) Uncertainty-aware positional modeling for HD map elements, (2) probabilistic-aware localization w.r.t. the crowdsourced prior-map, and (3) real-time detection for possible road structural changes. Experiments on several public autonomous driving datasets demonstrate our solid performance on both the prior-aided map quality and the localization accuracy, demonstrating our effectiveness of robustly serving downstream prediction and planning modules while gradually improving the accuracy and freshness of the crowdsourced prior-map asynchronously. Our source-code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/CN-ADLab/RTMap (Camera ready version incorporating reviewer suggestions will be updated soon).
SAM4D: Segment Anything in Camera and LiDAR Streams
Jun 26, 2025



Abstract:We present SAM4D, a multi-modal and temporal foundation model designed for promptable segmentation across camera and LiDAR streams. Unified Multi-modal Positional Encoding (UMPE) is introduced to align camera and LiDAR features in a shared 3D space, enabling seamless cross-modal prompting and interaction. Additionally, we propose Motion-aware Cross-modal Memory Attention (MCMA), which leverages ego-motion compensation to enhance temporal consistency and long-horizon feature retrieval, ensuring robust segmentation across dynamically changing autonomous driving scenes. To avoid annotation bottlenecks, we develop a multi-modal automated data engine that synergizes VFM-driven video masklets, spatiotemporal 4D reconstruction, and cross-modal masklet fusion. This framework generates camera-LiDAR aligned pseudo-labels at a speed orders of magnitude faster than human annotation while preserving VFM-derived semantic fidelity in point cloud representations. We conduct extensive experiments on the constructed Waymo-4DSeg, which demonstrate the powerful cross-modal segmentation ability and great potential in data annotation of proposed SAM4D.
PixelThink: Towards Efficient Chain-of-Pixel Reasoning
May 29, 2025Abstract:Existing reasoning segmentation approaches typically fine-tune multimodal large language models (MLLMs) using image-text pairs and corresponding mask labels. However, they exhibit limited generalization to out-of-distribution scenarios without an explicit reasoning process. Although recent efforts leverage reinforcement learning through group-relative policy optimization (GRPO) to enhance reasoning ability, they often suffer from overthinking - producing uniformly verbose reasoning chains irrespective of task complexity. This results in elevated computational costs and limited control over reasoning quality. To address this problem, we propose PixelThink, a simple yet effective scheme that integrates externally estimated task difficulty and internally measured model uncertainty to regulate reasoning generation within a reinforcement learning paradigm. The model learns to compress reasoning length in accordance with scene complexity and predictive confidence. To support comprehensive evaluation, we introduce ReasonSeg-Diff, an extended benchmark with annotated reasoning references and difficulty scores, along with a suite of metrics designed to assess segmentation accuracy, reasoning quality, and efficiency jointly. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach improves both reasoning efficiency and overall segmentation performance. Our work contributes novel perspectives towards efficient and interpretable multimodal understanding. The code and model will be publicly available.
ZFusion: An Effective Fuser of Camera and 4D Radar for 3D Object Perception in Autonomous Driving
Apr 07, 2025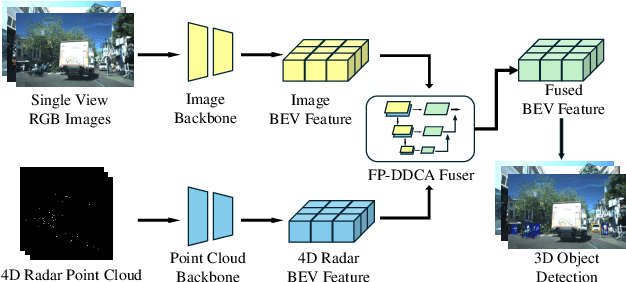
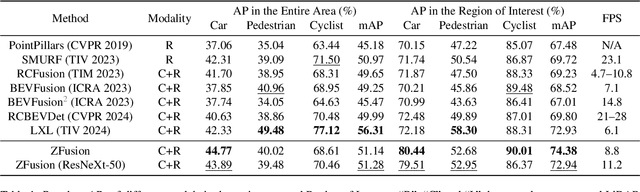
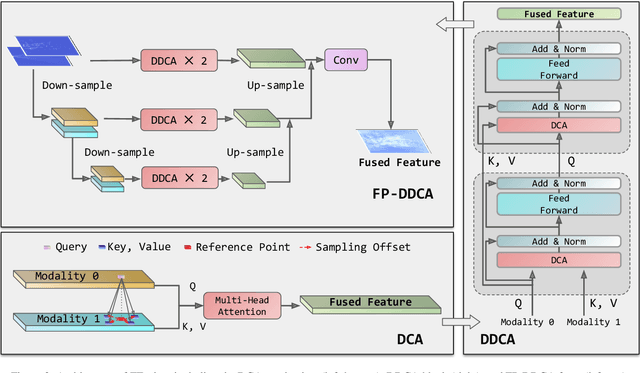
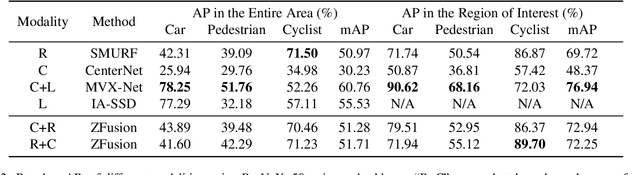
Abstract:Reliable 3D object perception is essential in autonomous driving. Owing to its sensing capabilities in all weather conditions, 4D radar has recently received much attention. However, compared to LiDAR, 4D radar provides much sparser point cloud. In this paper, we propose a 3D object detection method, termed ZFusion, which fuses 4D radar and vision modality. As the core of ZFusion, our proposed FP-DDCA (Feature Pyramid-Double Deformable Cross Attention) fuser complements the (sparse) radar information and (dense) vision information, effectively. Specifically, with a feature-pyramid structure, the FP-DDCA fuser packs Transformer blocks to interactively fuse multi-modal features at different scales, thus enhancing perception accuracy. In addition, we utilize the Depth-Context-Split view transformation module due to the physical properties of 4D radar. Considering that 4D radar has a much lower cost than LiDAR, ZFusion is an attractive alternative to LiDAR-based methods. In typical traffic scenarios like the VoD (View-of-Delft) dataset, experiments show that with reasonable inference speed, ZFusion achieved the state-of-the-art mAP (mean average precision) in the region of interest, while having competitive mAP in the entire area compared to the baseline methods, which demonstrates performance close to LiDAR and greatly outperforms those camera-only methods.
Industrial-Grade Sensor Simulation via Gaussian Splatting: A Modular Framework for Scalable Editing and Full-Stack Validation
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Sensor simulation is pivotal for scalable validation of autonomous driving systems, yet existing Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) based methods face applicability and efficiency challenges in industrial workflows. This paper introduces a Gaussian Splatting (GS) based system to address these challenges: We first break down sensor simulator components and analyze the possible advantages of GS over NeRF. Then in practice, we refactor three crucial components through GS, to leverage its explicit scene representation and real-time rendering: (1) choosing the 2D neural Gaussian representation for physics-compliant scene and sensor modeling, (2) proposing a scene editing pipeline to leverage Gaussian primitives library for data augmentation, and (3) coupling a controllable diffusion model for scene expansion and harmonization. We implement this framework on a proprietary autonomous driving dataset supporting cameras and LiDAR sensors. We demonstrate through ablation studies that our approach reduces frame-wise simulation latency, achieves better geometric and photometric consistency, and enables interpretable explicit scene editing and expansion. Furthermore, we showcase how integrating such a GS-based sensor simulator with traffic and dynamic simulators enables full-stack testing of end-to-end autonomy algorithms. Our work provides both algorithmic insights and practical validation, establishing GS as a cornerstone for industrial-grade sensor simulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge