Qing Yang
FCMBench: A Comprehensive Financial Credit Multimodal Benchmark for Real-world Applications
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:As multimodal AI becomes widely used for credit risk assessment and document review, a domain-specific benchmark is urgently needed that (1) reflects documents and workflows specific to financial credit applications, (2) includes credit-specific understanding and real-world robustness, and (3) preserves privacy compliance without sacrificing practical utility. Here, we introduce FCMBench-V1.0 -- a large-scale financial credit multimodal benchmark for real-world applications, covering 18 core certificate types, with 4,043 privacy-compliant images and 8,446 QA samples. The FCMBench evaluation framework consists of three dimensions: Perception, Reasoning, and Robustness, including 3 foundational perception tasks, 4 credit-specific reasoning tasks that require decision-oriented understanding of visual evidence, and 10 real-world acquisition artifact types for robustness stress testing. To reconcile compliance with realism, we construct all samples via a closed synthesis-capture pipeline: we manually synthesize document templates with virtual content and capture scenario-aware images in-house. This design also mitigates pre-training data leakage by avoiding web-sourced or publicly released images. FCMBench can effectively discriminate performance disparities and robustness across modern vision-language models. Extensive experiments were conducted on 23 state-of-the-art vision-language models (VLMs) from 14 top AI companies and research institutes. Among them, Gemini 3 Pro achieves the best F1(\%) score as a commercial model (64.61), Qwen3-VL-235B achieves the best score as an open-source baseline (57.27), and our financial credit-specific model, Qfin-VL-Instruct, achieves the top overall score (64.92). Robustness evaluations show that even top-performing models suffer noticeable performance drops under acquisition artifacts.
M3CAD: Towards Generic Cooperative Autonomous Driving Benchmark
May 10, 2025Abstract:We introduce M$^3$CAD, a novel benchmark designed to advance research in generic cooperative autonomous driving. M$^3$CAD comprises 204 sequences with 30k frames, spanning a diverse range of cooperative driving scenarios. Each sequence includes multiple vehicles and sensing modalities, e.g., LiDAR point clouds, RGB images, and GPS/IMU, supporting a variety of autonomous driving tasks, including object detection and tracking, mapping, motion forecasting, occupancy prediction, and path planning. This rich multimodal setup enables M$^3$CAD to support both single-vehicle and multi-vehicle autonomous driving research, significantly broadening the scope of research in the field. To our knowledge, M$^3$CAD is the most comprehensive benchmark specifically tailored for cooperative multi-task autonomous driving research. We evaluate the state-of-the-art end-to-end solution on M$^3$CAD to establish baseline performance. To foster cooperative autonomous driving research, we also propose E2EC, a simple yet effective framework for cooperative driving solution that leverages inter-vehicle shared information for improved path planning. We release M$^3$CAD, along with our baseline models and evaluation results, to support the development of robust cooperative autonomous driving systems. All resources will be made publicly available on https://github.com/zhumorui/M3CAD
Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning in Large Language Models with One Training Example
Apr 29, 2025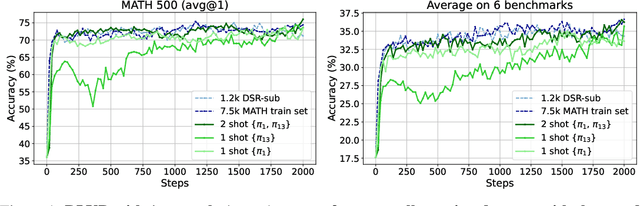
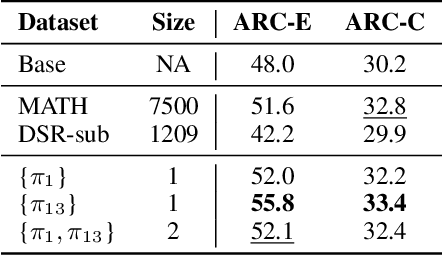
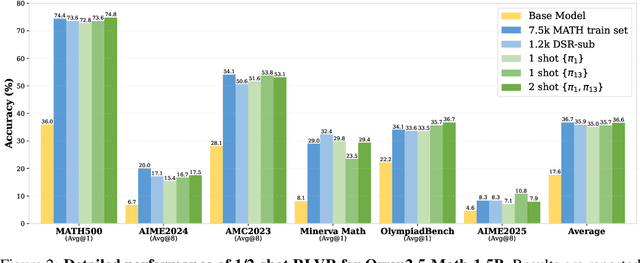

Abstract:We show that reinforcement learning with verifiable reward using one training example (1-shot RLVR) is effective in incentivizing the math reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Applying RLVR to the base model Qwen2.5-Math-1.5B, we identify a single example that elevates model performance on MATH500 from 36.0% to 73.6%, and improves the average performance across six common mathematical reasoning benchmarks from 17.6% to 35.7%. This result matches the performance obtained using the 1.2k DeepScaleR subset (MATH500: 73.6%, average: 35.9%), which includes the aforementioned example. Similar substantial improvements are observed across various models (Qwen2.5-Math-7B, Llama3.2-3B-Instruct, DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B), RL algorithms (GRPO and PPO), and different math examples (many of which yield approximately 30% or greater improvement on MATH500 when employed as a single training example). In addition, we identify some interesting phenomena during 1-shot RLVR, including cross-domain generalization, increased frequency of self-reflection, and sustained test performance improvement even after the training accuracy has saturated, a phenomenon we term post-saturation generalization. Moreover, we verify that the effectiveness of 1-shot RLVR primarily arises from the policy gradient loss, distinguishing it from the "grokking" phenomenon. We also show the critical role of promoting exploration (e.g., by adding entropy loss with an appropriate coefficient) in 1-shot RLVR training. As a bonus, we observe that applying entropy loss alone, without any outcome reward, significantly enhances Qwen2.5-Math-1.5B's performance on MATH500 by 27.4%. These findings can inspire future work on RLVR data efficiency and encourage a re-examination of both recent progress and the underlying mechanisms in RLVR. Our code, model, and data are open source at https://github.com/ypwang61/One-Shot-RLVR
ZFusion: An Effective Fuser of Camera and 4D Radar for 3D Object Perception in Autonomous Driving
Apr 07, 2025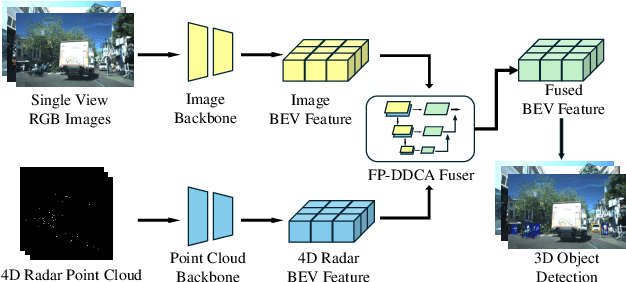
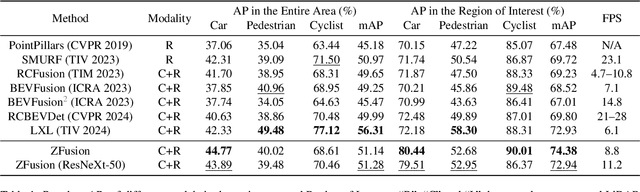
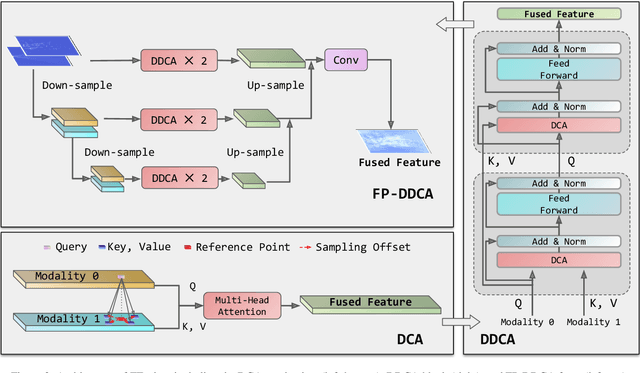
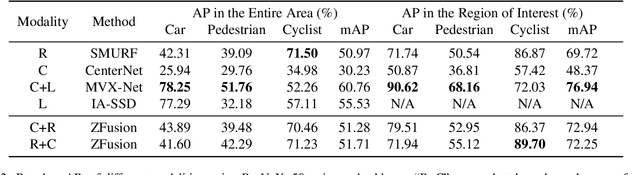
Abstract:Reliable 3D object perception is essential in autonomous driving. Owing to its sensing capabilities in all weather conditions, 4D radar has recently received much attention. However, compared to LiDAR, 4D radar provides much sparser point cloud. In this paper, we propose a 3D object detection method, termed ZFusion, which fuses 4D radar and vision modality. As the core of ZFusion, our proposed FP-DDCA (Feature Pyramid-Double Deformable Cross Attention) fuser complements the (sparse) radar information and (dense) vision information, effectively. Specifically, with a feature-pyramid structure, the FP-DDCA fuser packs Transformer blocks to interactively fuse multi-modal features at different scales, thus enhancing perception accuracy. In addition, we utilize the Depth-Context-Split view transformation module due to the physical properties of 4D radar. Considering that 4D radar has a much lower cost than LiDAR, ZFusion is an attractive alternative to LiDAR-based methods. In typical traffic scenarios like the VoD (View-of-Delft) dataset, experiments show that with reasonable inference speed, ZFusion achieved the state-of-the-art mAP (mean average precision) in the region of interest, while having competitive mAP in the entire area compared to the baseline methods, which demonstrates performance close to LiDAR and greatly outperforms those camera-only methods.
Zero-Knowledge Federated Learning: A New Trustworthy and Privacy-Preserving Distributed Learning Paradigm
Mar 18, 2025


Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a promising paradigm in distributed machine learning, enabling collaborative model training while preserving data privacy. However, despite its many advantages, FL still contends with significant challenges -- most notably regarding security and trust. Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) offer a potential solution by establishing trust and enhancing system integrity throughout the FL process. Although several studies have explored ZKP-based FL (ZK-FL), a systematic framework and comprehensive analysis are still lacking. This article makes two key contributions. First, we propose a structured ZK-FL framework that categorizes and analyzes the technical roles of ZKPs across various FL stages and tasks. Second, we introduce a novel algorithm, Verifiable Client Selection FL (Veri-CS-FL), which employs ZKPs to refine the client selection process. In Veri-CS-FL, participating clients generate verifiable proofs for the performance metrics of their local models and submit these concise proofs to the server for efficient verification. The server then selects clients with high-quality local models for uploading, subsequently aggregating the contributions from these selected clients. By integrating ZKPs, Veri-CS-FL not only ensures the accuracy of performance metrics but also fortifies trust among participants while enhancing the overall efficiency and security of FL systems.
MITracker: Multi-View Integration for Visual Object Tracking
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Multi-view object tracking (MVOT) offers promising solutions to challenges such as occlusion and target loss, which are common in traditional single-view tracking. However, progress has been limited by the lack of comprehensive multi-view datasets and effective cross-view integration methods. To overcome these limitations, we compiled a Multi-View object Tracking (MVTrack) dataset of 234K high-quality annotated frames featuring 27 distinct objects across various scenes. In conjunction with this dataset, we introduce a novel MVOT method, Multi-View Integration Tracker (MITracker), to efficiently integrate multi-view object features and provide stable tracking outcomes. MITracker can track any object in video frames of arbitrary length from arbitrary viewpoints. The key advancements of our method over traditional single-view approaches come from two aspects: (1) MITracker transforms 2D image features into a 3D feature volume and compresses it into a bird's eye view (BEV) plane, facilitating inter-view information fusion; (2) we propose an attention mechanism that leverages geometric information from fused 3D feature volume to refine the tracking results at each view. MITracker outperforms existing methods on the MVTrack and GMTD datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance. The code and the new dataset will be available at https://mii-laboratory.github.io/MITracker/.
A Survey of Zero-Knowledge Proof Based Verifiable Machine Learning
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:As machine learning technologies advance rapidly across various domains, concerns over data privacy and model security have grown significantly. These challenges are particularly pronounced when models are trained and deployed on cloud platforms or third-party servers due to the computational resource limitations of users' end devices. In response, zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) technology has emerged as a promising solution, enabling effective validation of model performance and authenticity in both training and inference processes without disclosing sensitive data. Thus, ZKP ensures the verifiability and security of machine learning models, making it a valuable tool for privacy-preserving AI. Although some research has explored the verifiable machine learning solutions that exploit ZKP, a comprehensive survey and summary of these efforts remain absent. This survey paper aims to bridge this gap by reviewing and analyzing all the existing Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning (ZKML) research from June 2017 to December 2024. We begin by introducing the concept of ZKML and outlining its ZKP algorithmic setups under three key categories: verifiable training, verifiable inference, and verifiable testing. Next, we provide a comprehensive categorization of existing ZKML research within these categories and analyze the works in detail. Furthermore, we explore the implementation challenges faced in this field and discuss the improvement works to address these obstacles. Additionally, we highlight several commercial applications of ZKML technology. Finally, we propose promising directions for future advancements in this domain.
GSOT3D: Towards Generic 3D Single Object Tracking in the Wild
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel benchmark, GSOT3D, that aims at facilitating development of generic 3D single object tracking (SOT) in the wild. Specifically, GSOT3D offers 620 sequences with 123K frames, and covers a wide selection of 54 object categories. Each sequence is offered with multiple modalities, including the point cloud (PC), RGB image, and depth. This allows GSOT3D to support various 3D tracking tasks, such as single-modal 3D SOT on PC and multi-modal 3D SOT on RGB-PC or RGB-D, and thus greatly broadens research directions for 3D object tracking. To provide highquality per-frame 3D annotations, all sequences are labeled manually with multiple rounds of meticulous inspection and refinement. To our best knowledge, GSOT3D is the largest benchmark dedicated to various generic 3D object tracking tasks. To understand how existing 3D trackers perform and to provide comparisons for future research on GSOT3D, we assess eight representative point cloud-based tracking models. Our evaluation results exhibit that these models heavily degrade on GSOT3D, and more efforts are required for robust and generic 3D object tracking. Besides, to encourage future research, we present a simple yet effective generic 3D tracker, named PROT3D, that localizes the target object via a progressive spatial-temporal network and outperforms all current solutions by a large margin. By releasing GSOT3D, we expect to advance further 3D tracking in future research and applications. Our benchmark and model as well as the evaluation results will be publicly released at our webpage https://github.com/ailovejinx/GSOT3D.
Advancing Large Language Model Attribution through Self-Improving
Oct 17, 2024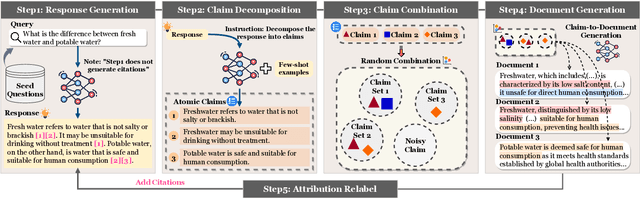
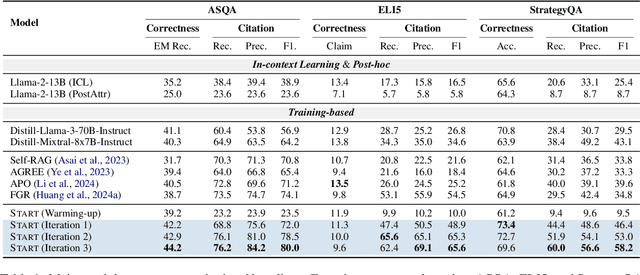
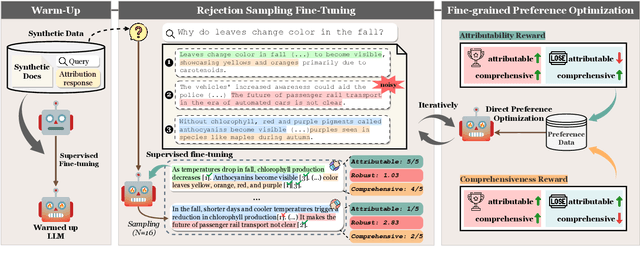
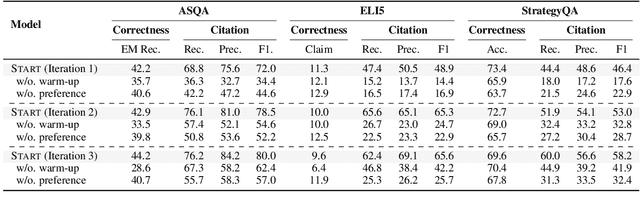
Abstract:Teaching large language models (LLMs) to generate text with citations to evidence sources can mitigate hallucinations and enhance verifiability in information-seeking systems. However, improving this capability requires high-quality attribution data, which is costly and labor-intensive. Inspired by recent advances in self-improvement that enhance LLMs without manual annotation, we present START, a Self-Taught AttRibuTion framework for iteratively improving the attribution capability of LLMs. First, to prevent models from stagnating due to initially insufficient supervision signals, START leverages the model to self-construct synthetic training data for warming up. To further self-improve the model's attribution ability, START iteratively utilizes fine-grained preference supervision signals constructed from its sampled responses to encourage robust, comprehensive, and attributable generation. Experiments on three open-domain question-answering datasets, covering long-form QA and multi-step reasoning, demonstrate significant performance gains of 25.13% on average without relying on human annotations and more advanced models. Further analysis reveals that START excels in aggregating information across multiple sources.
GlobeSumm: A Challenging Benchmark Towards Unifying Multi-lingual, Cross-lingual and Multi-document News Summarization
Oct 05, 2024



Abstract:News summarization in today's global scene can be daunting with its flood of multilingual content and varied viewpoints from different sources. However, current studies often neglect such real-world scenarios as they tend to focus solely on either single-language or single-document tasks. To bridge this gap, we aim to unify Multi-lingual, Cross-lingual and Multi-document Summarization into a novel task, i.e., MCMS, which encapsulates the real-world requirements all-in-one. Nevertheless, the lack of a benchmark inhibits researchers from adequately studying this invaluable problem. To tackle this, we have meticulously constructed the GLOBESUMM dataset by first collecting a wealth of multilingual news reports and restructuring them into event-centric format. Additionally, we introduce the method of protocol-guided prompting for high-quality and cost-effective reference annotation. In MCMS, we also highlight the challenge of conflicts between news reports, in addition to the issues of redundancies and omissions, further enhancing the complexity of GLOBESUMM. Through extensive experimental analysis, we validate the quality of our dataset and elucidate the inherent challenges of the task. We firmly believe that GLOBESUMM, given its challenging nature, will greatly contribute to the multilingual communities and the evaluation of LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge