Dongliang Xu
Mind the Third Eye! Benchmarking Privacy Awareness in MLLM-powered Smartphone Agents
Aug 27, 2025



Abstract:Smartphones bring significant convenience to users but also enable devices to extensively record various types of personal information. Existing smartphone agents powered by Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable performance in automating different tasks. However, as the cost, these agents are granted substantial access to sensitive users' personal information during this operation. To gain a thorough understanding of the privacy awareness of these agents, we present the first large-scale benchmark encompassing 7,138 scenarios to the best of our knowledge. In addition, for privacy context in scenarios, we annotate its type (e.g., Account Credentials), sensitivity level, and location. We then carefully benchmark seven available mainstream smartphone agents. Our results demonstrate that almost all benchmarked agents show unsatisfying privacy awareness (RA), with performance remaining below 60% even with explicit hints. Overall, closed-source agents show better privacy ability than open-source ones, and Gemini 2.0-flash achieves the best, achieving an RA of 67%. We also find that the agents' privacy detection capability is highly related to scenario sensitivity level, i.e., the scenario with a higher sensitivity level is typically more identifiable. We hope the findings enlighten the research community to rethink the unbalanced utility-privacy tradeoff about smartphone agents. Our code and benchmark are available at https://zhixin-l.github.io/SAPA-Bench.
Simple Radiology VLLM Test-time Scaling with Thought Graph Traversal
Jun 13, 2025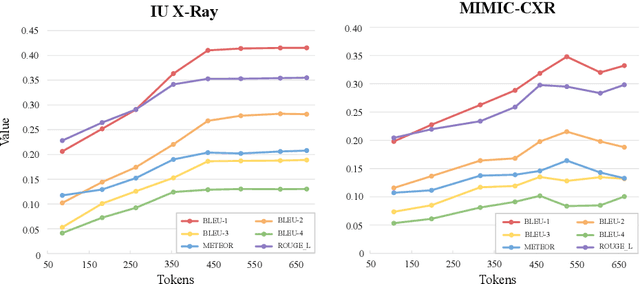
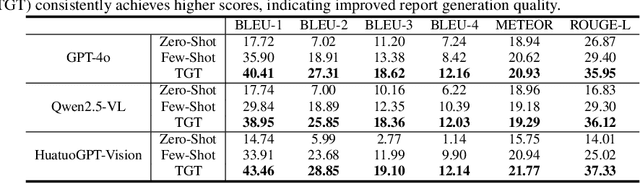
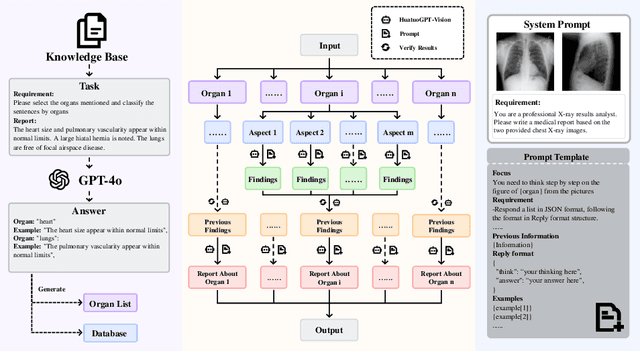
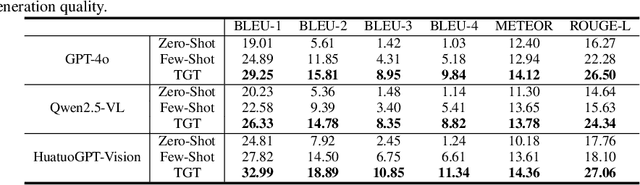
Abstract:Test-time scaling offers a promising way to improve the reasoning performance of vision-language large models (VLLMs) without additional training. In this paper, we explore a simple but effective approach for applying test-time scaling to radiology report generation. Specifically, we introduce a lightweight Thought Graph Traversal (TGT) framework that guides the model to reason through organ-specific findings in a medically coherent order. This framework integrates structured medical priors into the prompt, enabling deeper and more logical analysis with no changes to the underlying model. To further enhance reasoning depth, we apply a reasoning budget forcing strategy that adjusts the model's inference depth at test time by dynamically extending its generation process. This simple yet powerful combination allows a frozen radiology VLLM to self-correct and generate more accurate, consistent chest X-ray reports. Our method outperforms baseline prompting approaches on standard benchmarks, and also reveals dataset biases through traceable reasoning paths. Code and prompts are open-sourced for reproducibility at https://github.com/glerium/Thought-Graph-Traversal.
Advancing Large Language Model Attribution through Self-Improving
Oct 17, 2024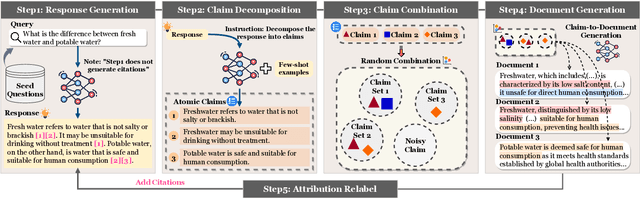
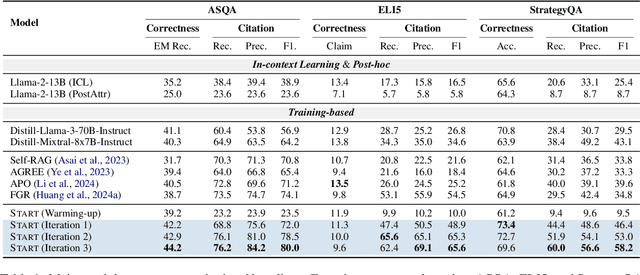
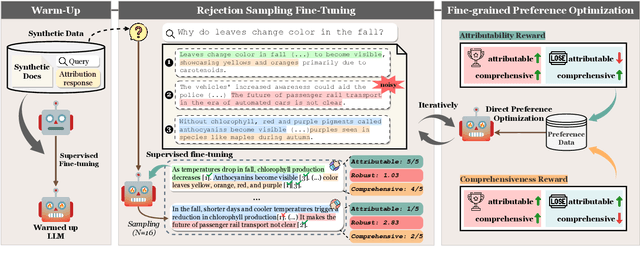
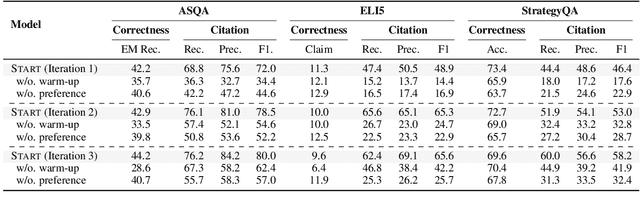
Abstract:Teaching large language models (LLMs) to generate text with citations to evidence sources can mitigate hallucinations and enhance verifiability in information-seeking systems. However, improving this capability requires high-quality attribution data, which is costly and labor-intensive. Inspired by recent advances in self-improvement that enhance LLMs without manual annotation, we present START, a Self-Taught AttRibuTion framework for iteratively improving the attribution capability of LLMs. First, to prevent models from stagnating due to initially insufficient supervision signals, START leverages the model to self-construct synthetic training data for warming up. To further self-improve the model's attribution ability, START iteratively utilizes fine-grained preference supervision signals constructed from its sampled responses to encourage robust, comprehensive, and attributable generation. Experiments on three open-domain question-answering datasets, covering long-form QA and multi-step reasoning, demonstrate significant performance gains of 25.13% on average without relying on human annotations and more advanced models. Further analysis reveals that START excels in aggregating information across multiple sources.
GlobeSumm: A Challenging Benchmark Towards Unifying Multi-lingual, Cross-lingual and Multi-document News Summarization
Oct 05, 2024



Abstract:News summarization in today's global scene can be daunting with its flood of multilingual content and varied viewpoints from different sources. However, current studies often neglect such real-world scenarios as they tend to focus solely on either single-language or single-document tasks. To bridge this gap, we aim to unify Multi-lingual, Cross-lingual and Multi-document Summarization into a novel task, i.e., MCMS, which encapsulates the real-world requirements all-in-one. Nevertheless, the lack of a benchmark inhibits researchers from adequately studying this invaluable problem. To tackle this, we have meticulously constructed the GLOBESUMM dataset by first collecting a wealth of multilingual news reports and restructuring them into event-centric format. Additionally, we introduce the method of protocol-guided prompting for high-quality and cost-effective reference annotation. In MCMS, we also highlight the challenge of conflicts between news reports, in addition to the issues of redundancies and omissions, further enhancing the complexity of GLOBESUMM. Through extensive experimental analysis, we validate the quality of our dataset and elucidate the inherent challenges of the task. We firmly believe that GLOBESUMM, given its challenging nature, will greatly contribute to the multilingual communities and the evaluation of LLMs.
Turning Trash into Treasure: Accelerating Inference of Large Language Models with Token Recycling
Aug 16, 2024



Abstract:The rapid growth in the parameters of large language models (LLMs) has made inference latency a fundamental bottleneck, limiting broader application of LLMs. Speculative decoding represents a lossless approach to accelerate inference through a guess-and-verify paradigm, leveraging the parallel capabilities of modern hardware. Some speculative decoding methods rely on additional structures to guess draft tokens, such as small models or parameter-efficient architectures, which need extra training before use. Alternatively, retrieval-based train-free techniques build libraries from pre-existing corpora or by n-gram generation. However, they face challenges like large storage requirements, time-consuming retrieval, and limited adaptability. Observing that candidate tokens generated during the decoding process are likely to reoccur in future sequences, we propose Token Recycling. This approach stores candidate tokens in an adjacency matrix and employs a breadth-first search (BFS)-like algorithm on the matrix to construct a draft tree. The tree is then validated through tree attention. New candidate tokens from the decoding process are then used to update the matrix. Token Recycling requires \textless2MB of additional storage and achieves approximately 2x speedup across all sizes of LLMs. It significantly outperforms existing train-free methods by 30\% and even a training method by 25\%. It can be directly applied to any existing LLMs and tasks without the need for adaptation.
Make Some Noise: Unlocking Language Model Parallel Inference Capability through Noisy Training
Jun 25, 2024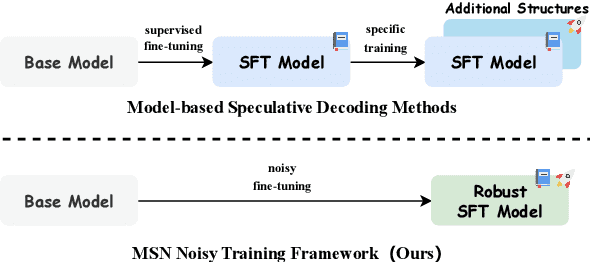
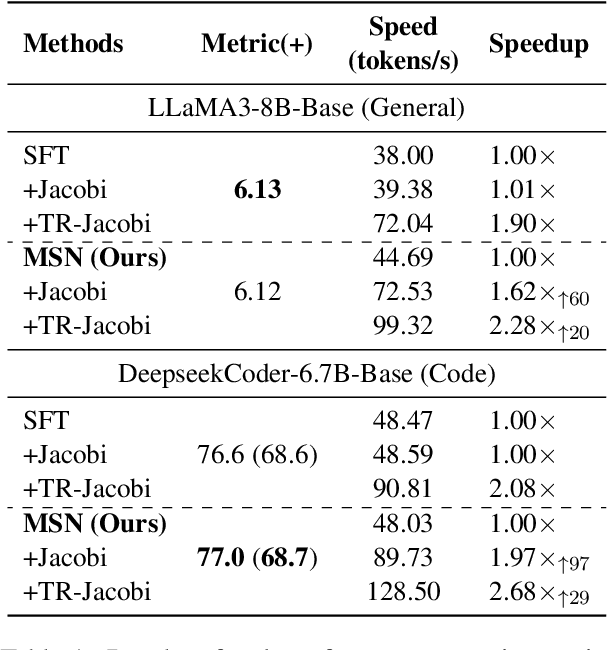
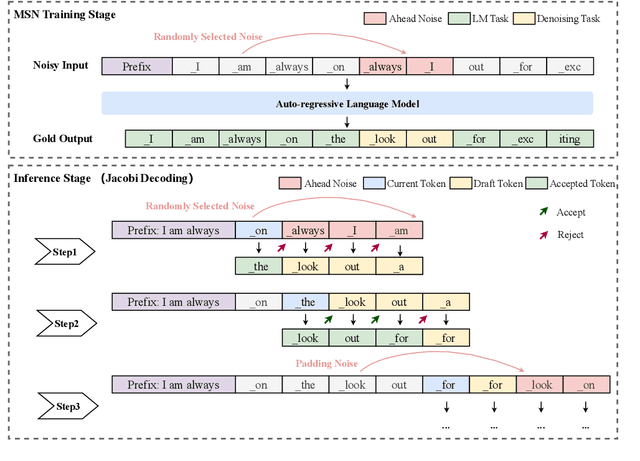
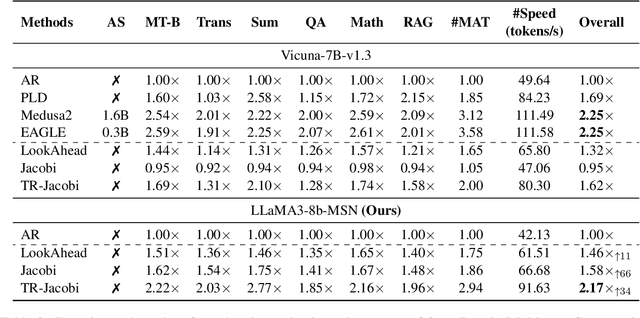
Abstract:Existing speculative decoding methods typically require additional model structure and training processes to assist the model for draft token generation. This makes the migration of acceleration methods to the new model more costly and more demanding on device memory. To address this problem, we propose the Make Some Noise (MSN) training framework as a replacement for the supervised fine-tuning stage of the large language model. The training method simply introduces some noise at the input for the model to learn the denoising task. It significantly enhances the parallel decoding capability of the model without affecting the original task capability. In addition, we propose a tree-based retrieval-augmented Jacobi (TR-Jacobi) decoding strategy to further improve the inference speed of MSN models. Experiments in both the general and code domains have shown that MSN can improve inference speed by 2.3-2.7x times without compromising model performance. The MSN model also achieves comparable acceleration ratios to the SOTA model with additional model structure on Spec-Bench.
MoGU: A Framework for Enhancing Safety of Open-Sourced LLMs While Preserving Their Usability
May 23, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in various applications. As their usage grows, concerns regarding their safety are rising, especially in maintaining harmless responses when faced with malicious instructions. Many defense strategies have been developed to enhance the safety of LLMs. However, our research finds that existing defense strategies lead LLMs to predominantly adopt a rejection-oriented stance, thereby diminishing the usability of their responses to benign instructions. To solve this problem, we introduce the MoGU framework, designed to enhance LLMs' safety while preserving their usability. Our MoGU framework transforms the base LLM into two variants: the usable LLM and the safe LLM, and further employs dynamic routing to balance their contribution. When encountering malicious instructions, the router will assign a higher weight to the safe LLM to ensure that responses are harmless. Conversely, for benign instructions, the router prioritizes the usable LLM, facilitating usable and helpful responses. On various open-sourced LLMs, we compare multiple defense strategies to verify the superiority of our MoGU framework. Besides, our analysis provides key insights into the effectiveness of MoGU and verifies that our designed routing mechanism can effectively balance the contribution of each variant by assigning weights. Our work released the safer Llama2, Vicuna, Falcon, Dolphin, and Baichuan2.
Meaningful Learning: Advancing Abstract Reasoning in Large Language Models via Generic Fact Guidance
Mar 14, 2024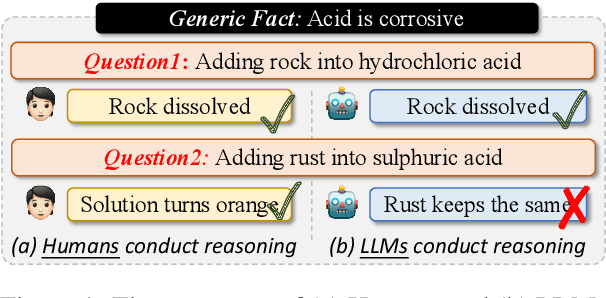


Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have developed impressive performance and strong explainability across various reasoning scenarios, marking a significant stride towards mimicking human-like intelligence. Despite this, when tasked with simple questions supported by a generic fact, LLMs often fail to provide consistent and precise answers, indicating a deficiency in abstract reasoning abilities. This has sparked a vigorous debate about whether LLMs are genuinely reasoning or merely memorizing. In light of this, we design a preliminary study to quantify and delve into the abstract reasoning abilities of existing LLMs. Our findings reveal a substantial discrepancy between their general reasoning and abstract reasoning performances. To relieve this problem, we tailor an abstract reasoning dataset (AbsR) together with a meaningful learning paradigm to teach LLMs how to leverage generic facts for reasoning purposes. The results show that our approach not only boosts the general reasoning performance of LLMs but also makes considerable strides towards their capacity for abstract reasoning, moving beyond simple memorization or imitation to a more nuanced understanding and application of generic facts.
Semi-Instruct: Bridging Natural-Instruct and Self-Instruct for Code Large Language Models
Mar 01, 2024


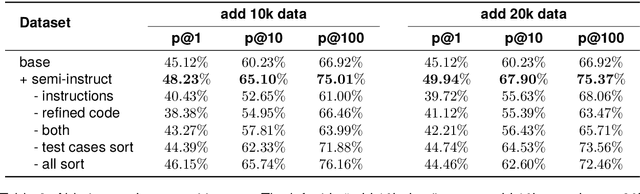
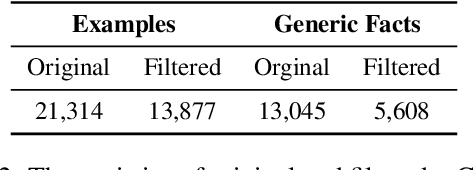
Abstract:Instruction tuning plays a pivotal role in Code Large Language Models (Code LLMs) for the task of program synthesis. Presently, two dominant paradigms for collecting tuning data are natural-instruct (human-written) and self-instruct (automatically generated). Natural-instruct includes diverse and correct codes but lacks instruction-code pairs, and exists improper code formats like nested single-line codes. In contrast, self-instruct automatically generates proper paired data. However, it suffers from low diversity due to generating duplicates and cannot ensure the correctness of codes. To bridge the both paradigms, we propose \textbf{Semi-Instruct}. It first converts diverse but improper codes from natural-instruct into proper instruction-code pairs through a method similar to self-instruct. To verify the correctness of generated codes, we design a novel way to construct test cases by generating cases' inputs and executing correct codes from natural-instruct to get outputs. Finally, diverse and correct instruction-code pairs are retained for instruction tuning. Experiments show that semi-instruct is significantly better than natural-instruct and self-instruct. Furthermore, the performance steadily improves as data scale increases.
MultiPoT: Multilingual Program of Thoughts Harnesses Multiple Programming Languages
Feb 16, 2024



Abstract:Program of Thoughts (PoT) is an approach characterized by its executable intermediate steps, which ensure the accuracy of the numerical calculations in the reasoning process. Currently, PoT primarily uses Python. However, relying solely on a single language may result in suboptimal solutions and overlook the potential benefits of other programming languages. In this paper, we conduct comprehensive experiments on the programming languages used in PoT and find that no single language consistently delivers optimal performance across all tasks and models. The effectiveness of each language varies depending on the specific scenarios. Inspired by this, we propose a task and model agnostic approach called MultiPoT, which harnesses strength and diversity from various languages. Experimental results reveal that it significantly outperforms Python Self-Consistency. Furthermore, it achieves comparable or superior performance compared to the best monolingual PoT in almost all tasks across all models. In particular, MultiPoT achieves more than 4.6\% improvement on average on both Starcoder and ChatGPT (gpt-3.5-turbo).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge