Mengjie Xu
Med-LEGO: Editing and Adapting toward Generalist Medical Image Diagnosis
Mar 03, 2025


Abstract:The adoption of visual foundation models has become a common practice in computer-aided diagnosis (CAD). While these foundation models provide a viable solution for creating generalist medical AI, privacy concerns make it difficult to pre-train or continuously update such models across multiple domains and datasets, leading many studies to focus on specialist models. To address this challenge, we propose Med-LEGO, a training-free framework that enables the seamless integration or updating of a generalist CAD model by combining multiple specialist models, similar to assembling LEGO bricks. Med-LEGO enhances LoRA (low-rank adaptation) by incorporating singular value decomposition (SVD) to efficiently capture the domain expertise of each specialist model with minimal additional parameters. By combining these adapted weights through simple operations, Med-LEGO allows for the easy integration or modification of specific diagnostic capabilities without the need for original data or retraining. Finally, the combined model can be further adapted to new diagnostic tasks, making it a versatile generalist model. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that Med-LEGO outperforms existing methods in both cross-domain and in-domain medical tasks while using only 0.18% of full model parameters. These merged models show better convergence and generalization to new tasks, providing an effective path toward generalist medical AI.
MITracker: Multi-View Integration for Visual Object Tracking
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Multi-view object tracking (MVOT) offers promising solutions to challenges such as occlusion and target loss, which are common in traditional single-view tracking. However, progress has been limited by the lack of comprehensive multi-view datasets and effective cross-view integration methods. To overcome these limitations, we compiled a Multi-View object Tracking (MVTrack) dataset of 234K high-quality annotated frames featuring 27 distinct objects across various scenes. In conjunction with this dataset, we introduce a novel MVOT method, Multi-View Integration Tracker (MITracker), to efficiently integrate multi-view object features and provide stable tracking outcomes. MITracker can track any object in video frames of arbitrary length from arbitrary viewpoints. The key advancements of our method over traditional single-view approaches come from two aspects: (1) MITracker transforms 2D image features into a 3D feature volume and compresses it into a bird's eye view (BEV) plane, facilitating inter-view information fusion; (2) we propose an attention mechanism that leverages geometric information from fused 3D feature volume to refine the tracking results at each view. MITracker outperforms existing methods on the MVTrack and GMTD datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance. The code and the new dataset will be available at https://mii-laboratory.github.io/MITracker/.
MUC: Mixture of Uncalibrated Cameras for Robust 3D Human Body Reconstruction
Mar 08, 2024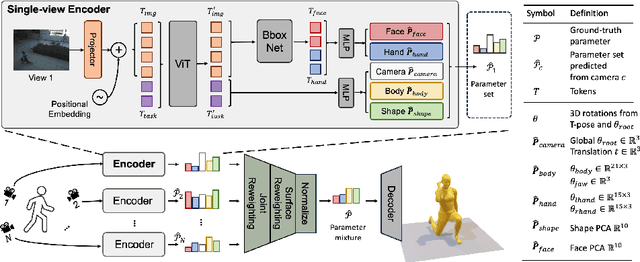
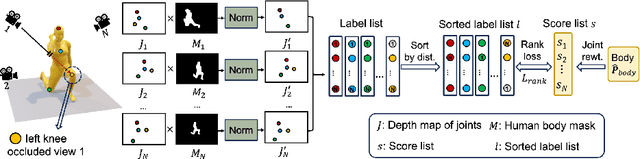
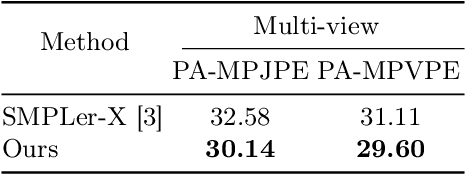
Abstract:Multiple cameras can provide multi-view video coverage of a person. It is necessary to fuse multi-view data, e.g., for subsequent behavioral analysis, while such fusion often relies on calibration of cameras in traditional solutions. However, it is non-trivial to calibrate multiple cameras. In this work, we propose a method to reconstruct 3D human body from multiple uncalibrated camera views. First, we adopt a pre-trained human body encoder to process each individual camera view, such that human body models and parameters can be reconstructed for each view. Next, instead of simply averaging models across views, we train a network to determine the weights of individual views for their fusion, based on the parameters estimated for joints and hands of human body as well as camera positions. Further, we turn to the mesh surface of human body for dynamic fusion, such that facial expression can be seamlessly integrated into the model of human body. Our method has demonstrated superior performance in reconstructing human body upon two public datasets. More importantly, our method can flexibly support ad-hoc deployment of an arbitrary number of cameras, which has significant potential in related applications. We will release source code upon acceptance of the paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge