Honglin Xiong
ReactDiff: Latent Diffusion for Facial Reaction Generation
May 20, 2025Abstract:Given the audio-visual clip of the speaker, facial reaction generation aims to predict the listener's facial reactions. The challenge lies in capturing the relevance between video and audio while balancing appropriateness, realism, and diversity. While prior works have mostly focused on uni-modal inputs or simplified reaction mappings, recent approaches such as PerFRDiff have explored multi-modal inputs and the one-to-many nature of appropriate reaction mappings. In this work, we propose the Facial Reaction Diffusion (ReactDiff) framework that uniquely integrates a Multi-Modality Transformer with conditional diffusion in the latent space for enhanced reaction generation. Unlike existing methods, ReactDiff leverages intra- and inter-class attention for fine-grained multi-modal interaction, while the latent diffusion process between the encoder and decoder enables diverse yet contextually appropriate outputs. Experimental results demonstrate that ReactDiff significantly outperforms existing approaches, achieving a facial reaction correlation of 0.26 and diversity score of 0.094 while maintaining competitive realism. The code is open-sourced at \href{https://github.com/Hunan-Tiger/ReactDiff}{github}.
Pathology Image Restoration via Mixture of Prompts
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:In digital pathology, acquiring all-in-focus images is essential to high-quality imaging and high-efficient clinical workflow. Traditional scanners achieve this by scanning at multiple focal planes of varying depths and then merging them, which is relatively slow and often struggles with complex tissue defocus. Recent prevailing image restoration technique provides a means to restore high-quality pathology images from scans of single focal planes. However, existing image restoration methods are inadequate, due to intricate defocus patterns in pathology images and their domain-specific semantic complexities. In this work, we devise a two-stage restoration solution cascading a transformer and a diffusion model, to benefit from their powers in preserving image fidelity and perceptual quality, respectively. We particularly propose a novel mixture of prompts for the two-stage solution. Given initial prompt that models defocus in microscopic imaging, we design two prompts that describe the high-level image semantics from pathology foundation model and the fine-grained tissue structures via edge extraction. We demonstrate that, by feeding the prompt mixture to our method, we can restore high-quality pathology images from single-focal-plane scans, implying high potentials of the mixture of prompts to clinical usage. Code will be publicly available at https://github.com/caijd2000/MoP.
LSA: Latent Style Augmentation Towards Stain-Agnostic Cervical Cancer Screening
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:The deployment of computer-aided diagnosis systems for cervical cancer screening using whole slide images (WSIs) faces critical challenges due to domain shifts caused by staining variations across different scanners and imaging environments. While existing stain augmentation methods improve patch-level robustness, they fail to scale to WSIs due to two key limitations: (1) inconsistent stain patterns when extending patch operations to gigapixel slides, and (2) prohibitive computational/storage costs from offline processing of augmented WSIs.To address this, we propose Latent Style Augmentation (LSA), a framework that performs efficient, online stain augmentation directly on WSI-level latent features. We first introduce WSAug, a WSI-level stain augmentation method ensuring consistent stain across patches within a WSI. Using offline-augmented WSIs by WSAug, we design and train Stain Transformer, which can simulate targeted style in the latent space, efficiently enhancing the robustness of the WSI-level classifier. We validate our method on a multi-scanner WSI dataset for cervical cancer diagnosis. Despite being trained on data from a single scanner, our approach achieves significant performance improvements on out-of-distribution data from other scanners. Code will be available at https://github.com/caijd2000/LSA.
Med-LEGO: Editing and Adapting toward Generalist Medical Image Diagnosis
Mar 03, 2025


Abstract:The adoption of visual foundation models has become a common practice in computer-aided diagnosis (CAD). While these foundation models provide a viable solution for creating generalist medical AI, privacy concerns make it difficult to pre-train or continuously update such models across multiple domains and datasets, leading many studies to focus on specialist models. To address this challenge, we propose Med-LEGO, a training-free framework that enables the seamless integration or updating of a generalist CAD model by combining multiple specialist models, similar to assembling LEGO bricks. Med-LEGO enhances LoRA (low-rank adaptation) by incorporating singular value decomposition (SVD) to efficiently capture the domain expertise of each specialist model with minimal additional parameters. By combining these adapted weights through simple operations, Med-LEGO allows for the easy integration or modification of specific diagnostic capabilities without the need for original data or retraining. Finally, the combined model can be further adapted to new diagnostic tasks, making it a versatile generalist model. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that Med-LEGO outperforms existing methods in both cross-domain and in-domain medical tasks while using only 0.18% of full model parameters. These merged models show better convergence and generalization to new tasks, providing an effective path toward generalist medical AI.
Towards General Text-guided Image Synthesis for Customized Multimodal Brain MRI Generation
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal brain magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is indispensable in neuroscience and neurology. However, due to the accessibility of MRI scanners and their lengthy acquisition time, multimodal MR images are not commonly available. Current MR image synthesis approaches are typically trained on independent datasets for specific tasks, leading to suboptimal performance when applied to novel datasets and tasks. Here, we present TUMSyn, a Text-guided Universal MR image Synthesis generalist model, which can flexibly generate brain MR images with demanded imaging metadata from routinely acquired scans guided by text prompts. To ensure TUMSyn's image synthesis precision, versatility, and generalizability, we first construct a brain MR database comprising 31,407 3D images with 7 MRI modalities from 13 centers. We then pre-train an MRI-specific text encoder using contrastive learning to effectively control MR image synthesis based on text prompts. Extensive experiments on diverse datasets and physician assessments indicate that TUMSyn can generate clinically meaningful MR images with specified imaging metadata in supervised and zero-shot scenarios. Therefore, TUMSyn can be utilized along with acquired MR scan(s) to facilitate large-scale MRI-based screening and diagnosis of brain diseases.
Progressive Attention Guidance for Whole Slide Vulvovaginal Candidiasis Screening
Sep 06, 2023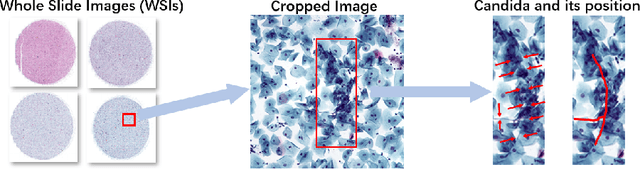
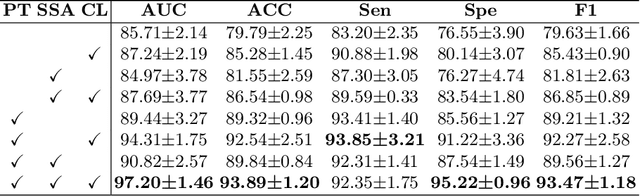
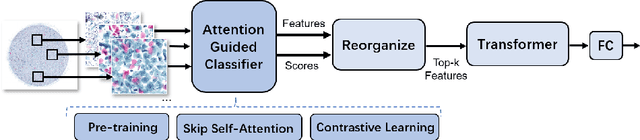
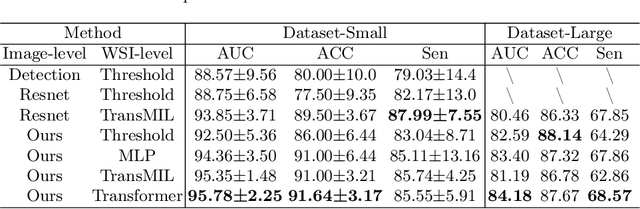
Abstract:Vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) is the most prevalent human candidal infection, estimated to afflict approximately 75% of all women at least once in their lifetime. It will lead to several symptoms including pruritus, vaginal soreness, and so on. Automatic whole slide image (WSI) classification is highly demanded, for the huge burden of disease control and prevention. However, the WSI-based computer-aided VCC screening method is still vacant due to the scarce labeled data and unique properties of candida. Candida in WSI is challenging to be captured by conventional classification models due to its distinctive elongated shape, the small proportion of their spatial distribution, and the style gap from WSIs. To make the model focus on the candida easier, we propose an attention-guided method, which can obtain a robust diagnosis classification model. Specifically, we first use a pre-trained detection model as prior instruction to initialize the classification model. Then we design a Skip Self-Attention module to refine the attention onto the fined-grained features of candida. Finally, we use a contrastive learning method to alleviate the overfitting caused by the style gap of WSIs and suppress the attention to false positive regions. Our experimental results demonstrate that our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance. Code and example data are available at https://github.com/cjdbehumble/MICCAI2023-VVC-Screening.
* Accepted in the main conference MICCAI 2023
DoctorGLM: Fine-tuning your Chinese Doctor is not a Herculean Task
Apr 17, 2023



Abstract:The recent progress of large language models (LLMs), including ChatGPT and GPT-4, in comprehending and responding to human instructions has been remarkable. Nevertheless, these models typically perform better in English and have not been explicitly trained for the medical domain, resulting in suboptimal precision in diagnoses, drug recommendations, and other medical advice. Additionally, training and deploying a dialogue model is still believed to be impossible for hospitals, hindering the promotion of LLMs. To tackle these challenges, we have collected databases of medical dialogues in Chinese with ChatGPT's help and adopted several techniques to train an easy-deploy LLM. Remarkably, we were able to fine-tune the ChatGLM-6B on a single A100 80G in 13 hours, which means having a healthcare-purpose LLM can be very affordable. DoctorGLM is currently an early-stage engineering attempt and contain various mistakes. We are sharing it with the broader community to invite feedback and suggestions to improve its healthcare-focused capabilities: https://github.com/xionghonglin/DoctorGLM.
Arbitrary Reduction of MRI Slice Spacing Based on Local-Aware Implicit Representation
May 23, 2022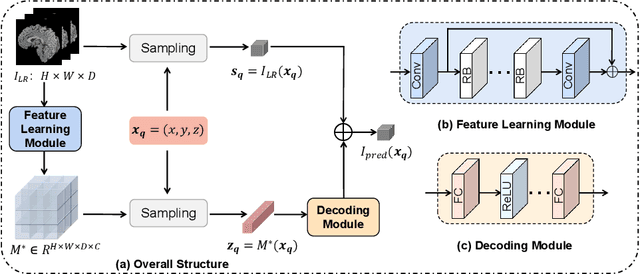
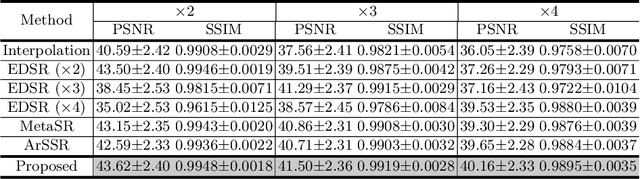

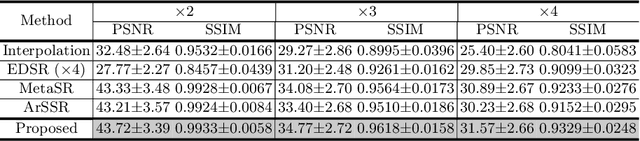
Abstract:Magnetic resonance (MR) images are often acquired in 2D settings for real clinical applications. The 3D volumes reconstructed by stacking multiple 2D slices have large inter-slice spacing, resulting in lower inter-slice resolution than intra-slice resolution. Super-resolution is a powerful tool to reduce the inter-slice spacing of 3D images to facilitate subsequent visualization and computation tasks. However, most existing works train the super-resolution network at a fixed ratio, which is inconvenient in clinical scenes due to the heterogeneous parameters in MR scanning. In this paper, we propose a single super-resolution network to reduce the inter-slice spacing of MR images at an arbitrarily adjustable ratio. Specifically, we view the input image as a continuous implicit function of coordinates. The intermediate slices of different spacing ratios could be constructed according to the implicit representation up-sampled in the continuous domain. We particularly propose a novel local-aware spatial attention mechanism and long-range residual learning to boost the quality of the output image. The experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method, even compared to the models trained at a fixed ratio.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge