Yuxiao Liu
GR-Dexter Technical Report
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Vision-language-action (VLA) models have enabled language-conditioned, long-horizon robot manipulation, but most existing systems are limited to grippers. Scaling VLA policies to bimanual robots with high degree-of-freedom (DoF) dexterous hands remains challenging due to the expanded action space, frequent hand-object occlusions, and the cost of collecting real-robot data. We present GR-Dexter, a holistic hardware-model-data framework for VLA-based generalist manipulation on a bimanual dexterous-hand robot. Our approach combines the design of a compact 21-DoF robotic hand, an intuitive bimanual teleoperation system for real-robot data collection, and a training recipe that leverages teleoperated robot trajectories together with large-scale vision-language and carefully curated cross-embodiment datasets. Across real-world evaluations spanning long-horizon everyday manipulation and generalizable pick-and-place, GR-Dexter achieves strong in-domain performance and improved robustness to unseen objects and unseen instructions. We hope GR-Dexter serves as a practical step toward generalist dexterous-hand robotic manipulation.
AInsteinBench: Benchmarking Coding Agents on Scientific Repositories
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:We introduce AInsteinBench, a large-scale benchmark for evaluating whether large language model (LLM) agents can operate as scientific computing development agents within real research software ecosystems. Unlike existing scientific reasoning benchmarks which focus on conceptual knowledge, or software engineering benchmarks that emphasize generic feature implementation and issue resolving, AInsteinBench evaluates models in end-to-end scientific development settings grounded in production-grade scientific repositories. The benchmark consists of tasks derived from maintainer-authored pull requests across six widely used scientific codebases, spanning quantum chemistry, quantum computing, molecular dynamics, numerical relativity, fluid dynamics, and cheminformatics. All benchmark tasks are carefully curated through multi-stage filtering and expert review to ensure scientific challenge, adequate test coverage, and well-calibrated difficulty. By leveraging evaluation in executable environments, scientifically meaningful failure modes, and test-driven verification, AInsteinBench measures a model's ability to move beyond surface-level code generation toward the core competencies required for computational scientific research.
GR-2: A Generative Video-Language-Action Model with Web-Scale Knowledge for Robot Manipulation
Oct 08, 2024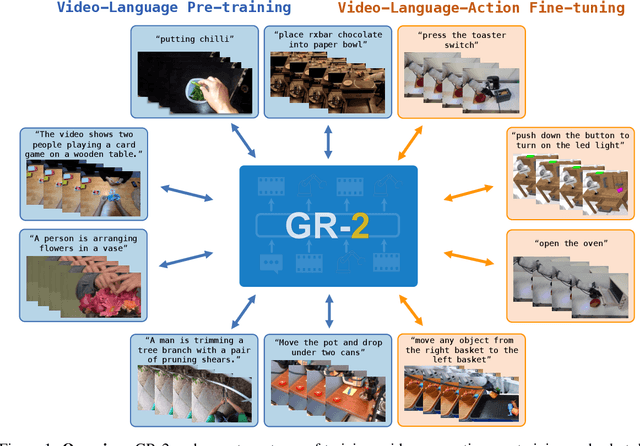
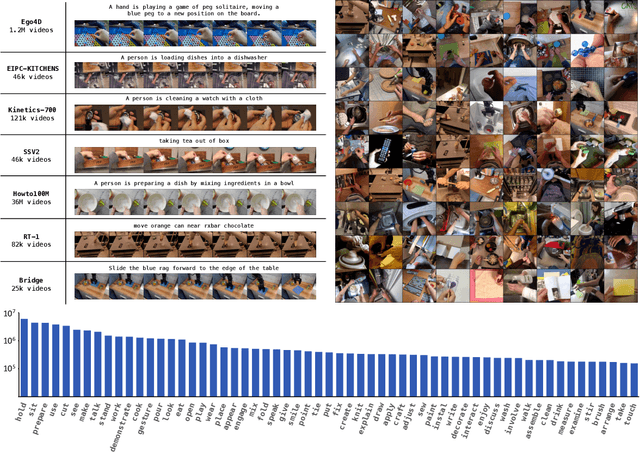


Abstract:We present GR-2, a state-of-the-art generalist robot agent for versatile and generalizable robot manipulation. GR-2 is first pre-trained on a vast number of Internet videos to capture the dynamics of the world. This large-scale pre-training, involving 38 million video clips and over 50 billion tokens, equips GR-2 with the ability to generalize across a wide range of robotic tasks and environments during subsequent policy learning. Following this, GR-2 is fine-tuned for both video generation and action prediction using robot trajectories. It exhibits impressive multi-task learning capabilities, achieving an average success rate of 97.7% across more than 100 tasks. Moreover, GR-2 demonstrates exceptional generalization to new, previously unseen scenarios, including novel backgrounds, environments, objects, and tasks. Notably, GR-2 scales effectively with model size, underscoring its potential for continued growth and application. Project page: \url{https://gr2-manipulation.github.io}.
A Progressive Single-Modality to Multi-Modality Classification Framework for Alzheimer's Disease Sub-type Diagnosis
Jul 26, 2024
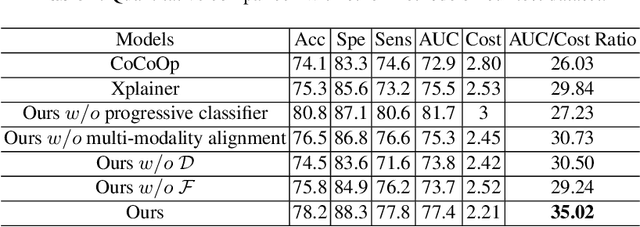
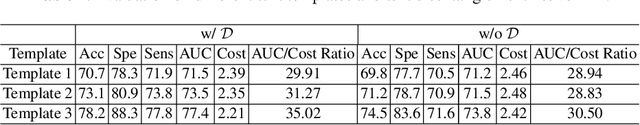
Abstract:The current clinical diagnosis framework of Alzheimer's disease (AD) involves multiple modalities acquired from multiple diagnosis stages, each with distinct usage and cost. Previous AD diagnosis research has predominantly focused on how to directly fuse multiple modalities for an end-to-end one-stage diagnosis, which practically requires a high cost in data acquisition. Moreover, a significant part of these methods diagnose AD without considering clinical guideline and cannot offer accurate sub-type diagnosis. In this paper, by exploring inter-correlation among multiple modalities, we propose a novel progressive AD sub-type diagnosis framework, aiming to give diagnosis results based on easier-to-access modalities in earlier low-cost stages, instead of modalities from all stages. Specifically, first, we design 1) a text disentanglement network for better processing tabular data collected in the initial stage, and 2) a modality fusion module for fusing multi-modality features separately. Second, we align features from modalities acquired in earlier low-cost stage(s) with later high-cost stage(s) to give accurate diagnosis without actual modality acquisition in later-stage(s) for saving cost. Furthermore, we follow the clinical guideline to align features at each stage for achieving sub-type diagnosis. Third, we leverage a progressive classifier that can progressively include additional acquired modalities (if needed) for diagnosis, to achieve the balance between diagnosis cost and diagnosis performance. We evaluate our proposed framework on large diverse public and in-home datasets (8280 in total) and achieve superior performance over state-of-the-art methods. Our codes will be released after the acceptance.
Potential of Multimodal Large Language Models for Data Mining of Medical Images and Free-text Reports
Jul 08, 2024



Abstract:Medical images and radiology reports are crucial for diagnosing medical conditions, highlighting the importance of quantitative analysis for clinical decision-making. However, the diversity and cross-source heterogeneity of these data challenge the generalizability of current data-mining methods. Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have recently transformed many domains, significantly affecting the medical field. Notably, Gemini-Vision-series (Gemini) and GPT-4-series (GPT-4) models have epitomized a paradigm shift in Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) for computer vision, showcasing their potential in the biomedical domain. In this study, we evaluated the performance of the Gemini, GPT-4, and 4 popular large models for an exhaustive evaluation across 14 medical imaging datasets, including 5 medical imaging categories (dermatology, radiology, dentistry, ophthalmology, and endoscopy), and 3 radiology report datasets. The investigated tasks encompass disease classification, lesion segmentation, anatomical localization, disease diagnosis, report generation, and lesion detection. Our experimental results demonstrated that Gemini-series models excelled in report generation and lesion detection but faces challenges in disease classification and anatomical localization. Conversely, GPT-series models exhibited proficiency in lesion segmentation and anatomical localization but encountered difficulties in disease diagnosis and lesion detection. Additionally, both the Gemini series and GPT series contain models that have demonstrated commendable generation efficiency. While both models hold promise in reducing physician workload, alleviating pressure on limited healthcare resources, and fostering collaboration between clinical practitioners and artificial intelligence technologies, substantial enhancements and comprehensive validations remain imperative before clinical deployment.
IRASim: Learning Interactive Real-Robot Action Simulators
Jun 20, 2024



Abstract:Scalable robot learning in the real world is limited by the cost and safety issues of real robots. In addition, rolling out robot trajectories in the real world can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. In this paper, we propose to learn an interactive real-robot action simulator as an alternative. We introduce a novel method, IRASim, which leverages the power of generative models to generate extremely realistic videos of a robot arm that executes a given action trajectory, starting from an initial given frame. To validate the effectiveness of our method, we create a new benchmark, IRASim Benchmark, based on three real-robot datasets and perform extensive experiments on the benchmark. Results show that IRASim outperforms all the baseline methods and is more preferable in human evaluations. We hope that IRASim can serve as an effective and scalable approach to enhance robot learning in the real world. To promote research for generative real-robot action simulators, we open-source code, benchmark, and checkpoints at https: //gen-irasim.github.io.
TexVocab: Texture Vocabulary-conditioned Human Avatars
Mar 31, 2024



Abstract:To adequately utilize the available image evidence in multi-view video-based avatar modeling, we propose TexVocab, a novel avatar representation that constructs a texture vocabulary and associates body poses with texture maps for animation. Given multi-view RGB videos, our method initially back-projects all the available images in the training videos to the posed SMPL surface, producing texture maps in the SMPL UV domain. Then we construct pairs of human poses and texture maps to establish a texture vocabulary for encoding dynamic human appearances under various poses. Unlike the commonly used joint-wise manner, we further design a body-part-wise encoding strategy to learn the structural effects of the kinematic chain. Given a driving pose, we query the pose feature hierarchically by decomposing the pose vector into several body parts and interpolating the texture features for synthesizing fine-grained human dynamics. Overall, our method is able to create animatable human avatars with detailed and dynamic appearances from RGB videos, and the experiments show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches. The project page can be found at https://texvocab.github.io/.
CLIP in Medical Imaging: A Comprehensive Survey
Dec 26, 2023



Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP), a simple yet effective pre-training paradigm, successfully introduces text supervision to vision models. It has shown promising results across various tasks, attributable to its generalizability and interpretability. The use of CLIP has recently gained increasing interest in the medical imaging domain, serving both as a pre-training paradigm for aligning medical vision and language, and as a critical component in diverse clinical tasks. With the aim of facilitating a deeper understanding of this promising direction, this survey offers an in-depth exploration of the CLIP paradigm within the domain of medical imaging, regarding both refined CLIP pre-training and CLIP-driven applications. In this study, We (1) start with a brief introduction to the fundamentals of CLIP methodology. (2) Then, we investigate the adaptation of CLIP pre-training in the medical domain, focusing on how to optimize CLIP given characteristics of medical images and reports. (3) Furthermore, we explore the practical utilization of CLIP pre-trained models in various tasks, including classification, dense prediction, and cross-modal tasks. (4) Finally, we discuss existing limitations of CLIP in the context of medical imaging and propose forward-looking directions to address the demands of medical imaging domain. We expect that this comprehensive survey will provide researchers in the field of medical image analysis with a holistic understanding of the CLIP paradigm and its potential implications. The project page can be found on https://github.com/zhaozh10/Awesome-CLIP-in-Medical-Imaging.
ChatRadio-Valuer: A Chat Large Language Model for Generalizable Radiology Report Generation Based on Multi-institution and Multi-system Data
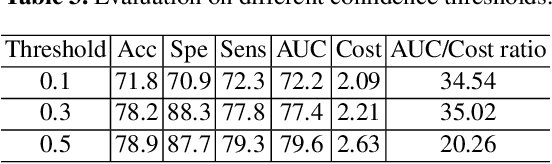
Oct 10, 2023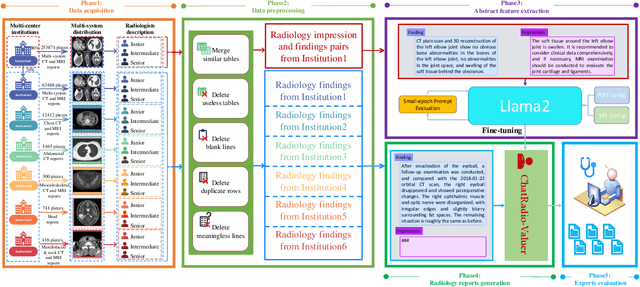
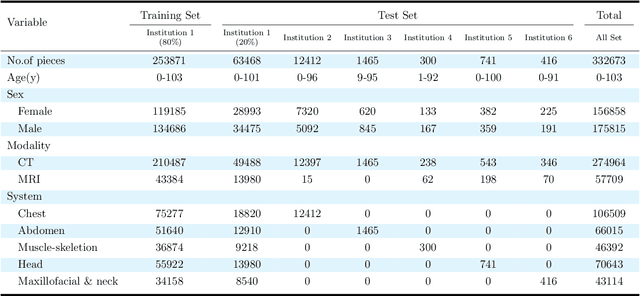
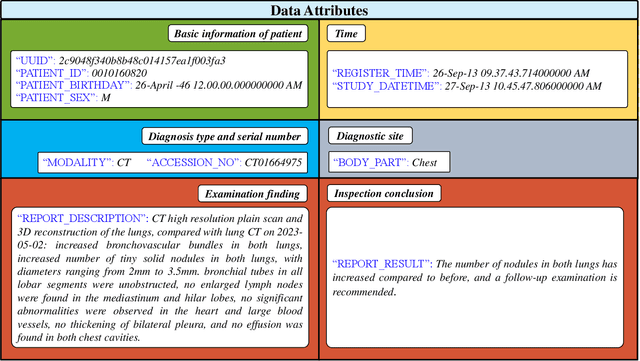
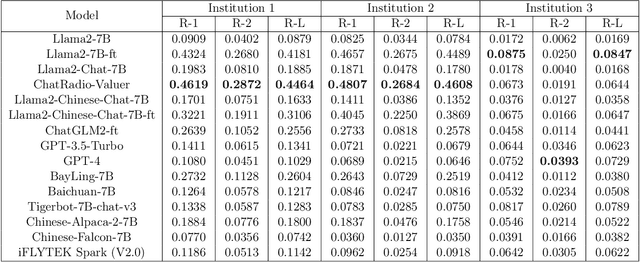
Abstract:Radiology report generation, as a key step in medical image analysis, is critical to the quantitative analysis of clinically informed decision-making levels. However, complex and diverse radiology reports with cross-source heterogeneity pose a huge generalizability challenge to the current methods under massive data volume, mainly because the style and normativity of radiology reports are obviously distinctive among institutions, body regions inspected and radiologists. Recently, the advent of large language models (LLM) offers great potential for recognizing signs of health conditions. To resolve the above problem, we collaborate with the Second Xiangya Hospital in China and propose ChatRadio-Valuer based on the LLM, a tailored model for automatic radiology report generation that learns generalizable representations and provides a basis pattern for model adaptation in sophisticated analysts' cases. Specifically, ChatRadio-Valuer is trained based on the radiology reports from a single institution by means of supervised fine-tuning, and then adapted to disease diagnosis tasks for human multi-system evaluation (i.e., chest, abdomen, muscle-skeleton, head, and maxillofacial $\&$ neck) from six different institutions in clinical-level events. The clinical dataset utilized in this study encompasses a remarkable total of \textbf{332,673} observations. From the comprehensive results on engineering indicators, clinical efficacy and deployment cost metrics, it can be shown that ChatRadio-Valuer consistently outperforms state-of-the-art models, especially ChatGPT (GPT-3.5-Turbo) and GPT-4 et al., in terms of the diseases diagnosis from radiology reports. ChatRadio-Valuer provides an effective avenue to boost model generalization performance and alleviate the annotation workload of experts to enable the promotion of clinical AI applications in radiology reports.
Evaluating Large Language Models for Radiology Natural Language Processing
Jul 27, 2023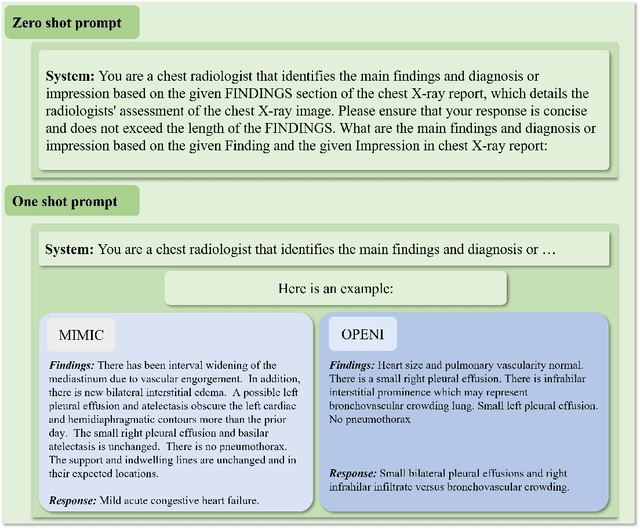
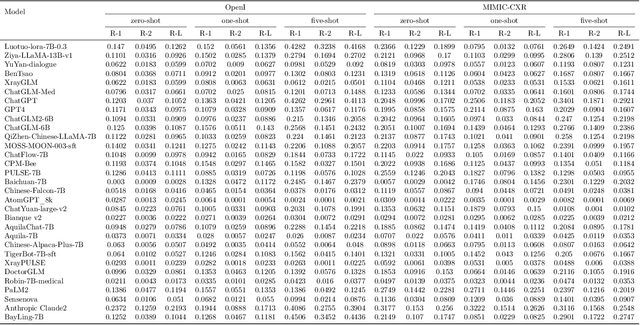
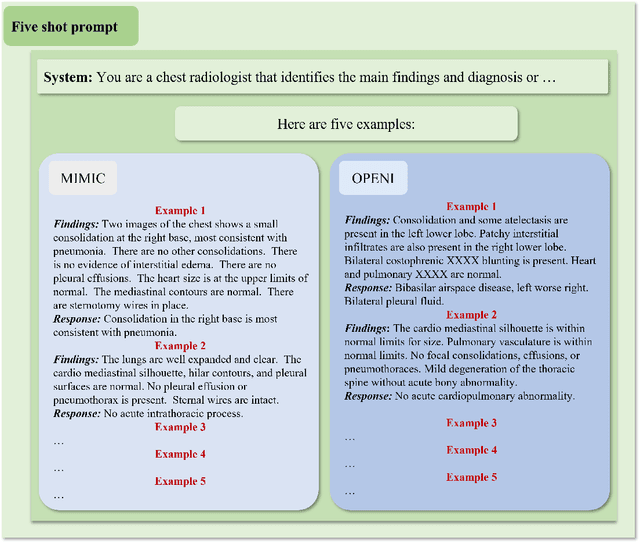
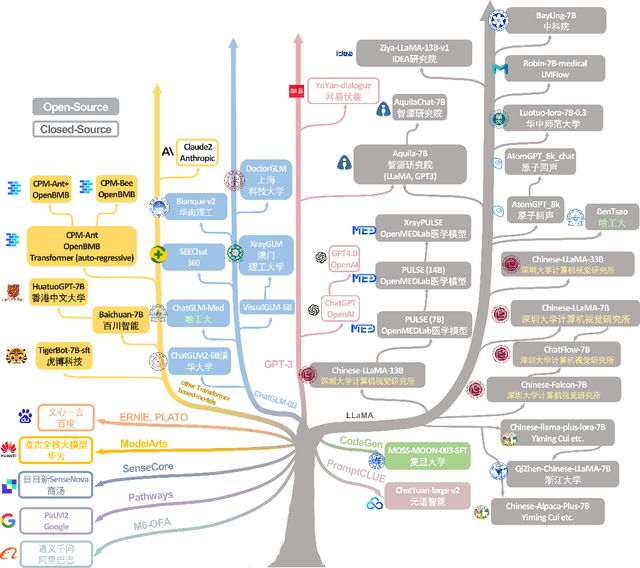
Abstract:The rise of large language models (LLMs) has marked a pivotal shift in the field of natural language processing (NLP). LLMs have revolutionized a multitude of domains, and they have made a significant impact in the medical field. Large language models are now more abundant than ever, and many of these models exhibit bilingual capabilities, proficient in both English and Chinese. However, a comprehensive evaluation of these models remains to be conducted. This lack of assessment is especially apparent within the context of radiology NLP. This study seeks to bridge this gap by critically evaluating thirty two LLMs in interpreting radiology reports, a crucial component of radiology NLP. Specifically, the ability to derive impressions from radiologic findings is assessed. The outcomes of this evaluation provide key insights into the performance, strengths, and weaknesses of these LLMs, informing their practical applications within the medical domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge