Disheng Liu
When 'YES' Meets 'BUT': Can Large Models Comprehend Contradictory Humor Through Comparative Reasoning?
Mar 29, 2025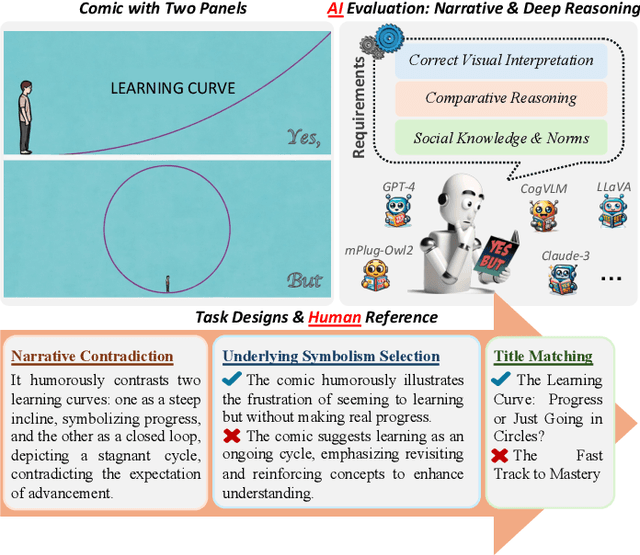

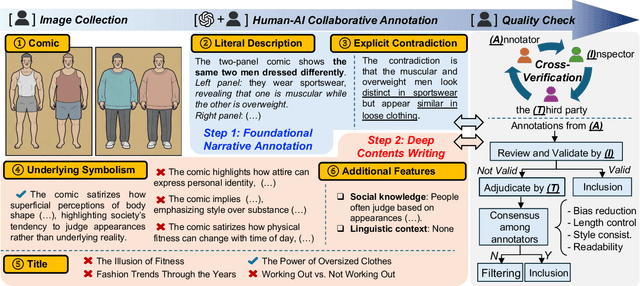

Abstract:Understanding humor-particularly when it involves complex, contradictory narratives that require comparative reasoning-remains a significant challenge for large vision-language models (VLMs). This limitation hinders AI's ability to engage in human-like reasoning and cultural expression. In this paper, we investigate this challenge through an in-depth analysis of comics that juxtapose panels to create humor through contradictions. We introduce the YesBut (V2), a novel benchmark with 1,262 comic images from diverse multilingual and multicultural contexts, featuring comprehensive annotations that capture various aspects of narrative understanding. Using this benchmark, we systematically evaluate a wide range of VLMs through four complementary tasks spanning from surface content comprehension to deep narrative reasoning, with particular emphasis on comparative reasoning between contradictory elements. Our extensive experiments reveal that even the most advanced models significantly underperform compared to humans, with common failures in visual perception, key element identification, comparative analysis and hallucinations. We further investigate text-based training strategies and social knowledge augmentation methods to enhance model performance. Our findings not only highlight critical weaknesses in VLMs' understanding of cultural and creative expressions but also provide pathways toward developing context-aware models capable of deeper narrative understanding though comparative reasoning.
BARD-GS: Blur-Aware Reconstruction of Dynamic Scenes via Gaussian Splatting
Mar 20, 2025



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has shown remarkable potential for static scene reconstruction, and recent advancements have extended its application to dynamic scenes. However, the quality of reconstructions depends heavily on high-quality input images and precise camera poses, which are not that trivial to fulfill in real-world scenarios. Capturing dynamic scenes with handheld monocular cameras, for instance, typically involves simultaneous movement of both the camera and objects within a single exposure. This combined motion frequently results in image blur that existing methods cannot adequately handle. To address these challenges, we introduce BARD-GS, a novel approach for robust dynamic scene reconstruction that effectively handles blurry inputs and imprecise camera poses. Our method comprises two main components: 1) camera motion deblurring and 2) object motion deblurring. By explicitly decomposing motion blur into camera motion blur and object motion blur and modeling them separately, we achieve significantly improved rendering results in dynamic regions. In addition, we collect a real-world motion blur dataset of dynamic scenes to evaluate our approach. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BARD-GS effectively reconstructs high-quality dynamic scenes under realistic conditions, significantly outperforming existing methods.
CAUSAL3D: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Causal Learning from Visual Data
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:True intelligence hinges on the ability to uncover and leverage hidden causal relations. Despite significant progress in AI and computer vision (CV), there remains a lack of benchmarks for assessing models' abilities to infer latent causality from complex visual data. In this paper, we introduce \textsc{\textbf{Causal3D}}, a novel and comprehensive benchmark that integrates structured data (tables) with corresponding visual representations (images) to evaluate causal reasoning. Designed within a systematic framework, Causal3D comprises 19 3D-scene datasets capturing diverse causal relations, views, and backgrounds, enabling evaluations across scenes of varying complexity. We assess multiple state-of-the-art methods, including classical causal discovery, causal representation learning, and large/vision-language models (LLMs/VLMs). Our experiments show that as causal structures grow more complex without prior knowledge, performance declines significantly, highlighting the challenges even advanced methods face in complex causal scenarios. Causal3D serves as a vital resource for advancing causal reasoning in CV and fostering trustworthy AI in critical domains.
CLIP in Medical Imaging: A Comprehensive Survey
Dec 26, 2023



Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP), a simple yet effective pre-training paradigm, successfully introduces text supervision to vision models. It has shown promising results across various tasks, attributable to its generalizability and interpretability. The use of CLIP has recently gained increasing interest in the medical imaging domain, serving both as a pre-training paradigm for aligning medical vision and language, and as a critical component in diverse clinical tasks. With the aim of facilitating a deeper understanding of this promising direction, this survey offers an in-depth exploration of the CLIP paradigm within the domain of medical imaging, regarding both refined CLIP pre-training and CLIP-driven applications. In this study, We (1) start with a brief introduction to the fundamentals of CLIP methodology. (2) Then, we investigate the adaptation of CLIP pre-training in the medical domain, focusing on how to optimize CLIP given characteristics of medical images and reports. (3) Furthermore, we explore the practical utilization of CLIP pre-trained models in various tasks, including classification, dense prediction, and cross-modal tasks. (4) Finally, we discuss existing limitations of CLIP in the context of medical imaging and propose forward-looking directions to address the demands of medical imaging domain. We expect that this comprehensive survey will provide researchers in the field of medical image analysis with a holistic understanding of the CLIP paradigm and its potential implications. The project page can be found on https://github.com/zhaozh10/Awesome-CLIP-in-Medical-Imaging.
Prediction of COVID-19 Patients' Emergency Room Revisit using Multi-Source Transfer Learning
Jun 29, 2023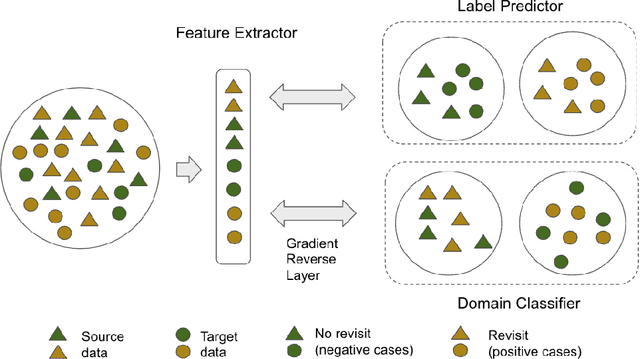
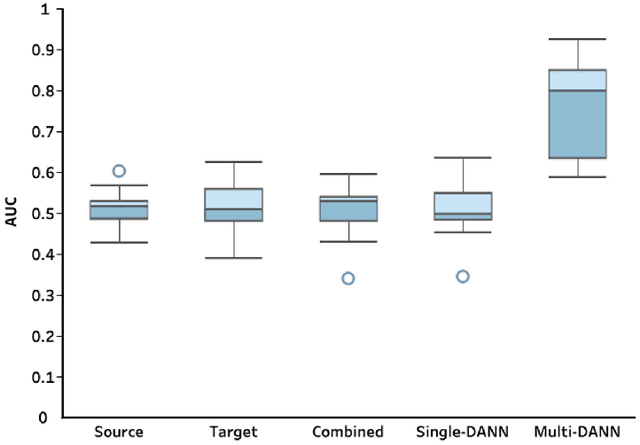
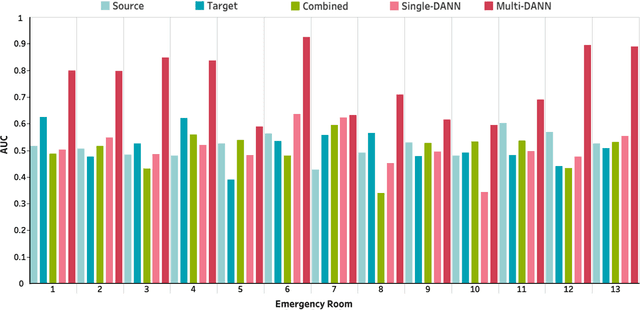
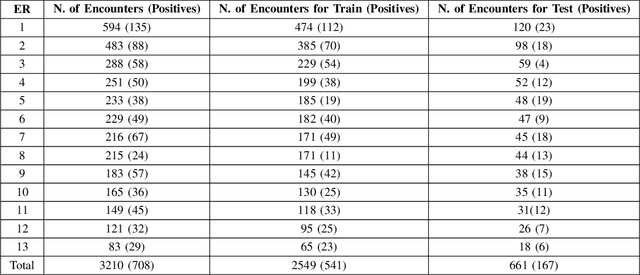
Abstract:The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has led to a global pandemic of significant severity. In addition to its high level of contagiousness, COVID-19 can have a heterogeneous clinical course, ranging from asymptomatic carriers to severe and potentially life-threatening health complications. Many patients have to revisit the emergency room (ER) within a short time after discharge, which significantly increases the workload for medical staff. Early identification of such patients is crucial for helping physicians focus on treating life-threatening cases. In this study, we obtained Electronic Health Records (EHRs) of 3,210 encounters from 13 affiliated ERs within the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center between March 2020 and January 2021. We leveraged a Natural Language Processing technique, ScispaCy, to extract clinical concepts and used the 1001 most frequent concepts to develop 7-day revisit models for COVID-19 patients in ERs. The research data we collected from 13 ERs may have distributional differences that could affect the model development. To address this issue, we employed a classic deep transfer learning method called the Domain Adversarial Neural Network (DANN) and evaluated different modeling strategies, including the Multi-DANN algorithm, the Single-DANN algorithm, and three baseline methods. Results showed that the Multi-DANN models outperformed the Single-DANN models and baseline models in predicting revisits of COVID-19 patients to the ER within 7 days after discharge. Notably, the Multi-DANN strategy effectively addressed the heterogeneity among multiple source domains and improved the adaptation of source data to the target domain. Moreover, the high performance of Multi-DANN models indicates that EHRs are informative for developing a prediction model to identify COVID-19 patients who are very likely to revisit an ER within 7 days after discharge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge