Yu Yin
HugRAG: Hierarchical Causal Knowledge Graph Design for RAG
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) has enhanced large language models by enabling access to external knowledge, with graph-based RAG emerging as a powerful paradigm for structured retrieval and reasoning. However, existing graph-based methods often over-rely on surface-level node matching and lack explicit causal modeling, leading to unfaithful or spurious answers. Prior attempts to incorporate causality are typically limited to local or single-document contexts and also suffer from information isolation that arises from modular graph structures, which hinders scalability and cross-module causal reasoning. To address these challenges, we propose HugRAG, a framework that rethinks knowledge organization for graph-based RAG through causal gating across hierarchical modules. HugRAG explicitly models causal relationships to suppress spurious correlations while enabling scalable reasoning over large-scale knowledge graphs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HugRAG consistently outperforms competitive graph-based RAG baselines across multiple datasets and evaluation metrics. Our work establishes a principled foundation for structured, scalable, and causally grounded RAG systems.
A Federated and Parameter-Efficient Framework for Large Language Model Training in Medicine
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance on medical benchmarks, including question answering and diagnosis. To enable their use in clinical settings, LLMs are typically further adapted through continued pretraining or post-training using clinical data. However, most medical LLMs are trained on data from a single institution, which faces limitations in generalizability and safety in heterogeneous systems. Federated learning (FL) is a promising solution for enabling collaborative model development across healthcare institutions. Yet applying FL to LLMs in medicine remains fundamentally limited. First, conventional FL requires transmitting the full model during each communication round, which becomes impractical for multi-billion-parameter LLMs given the limited computational resources. Second, many FL algorithms implicitly assume data homogeneity, whereas real-world clinical data are highly heterogeneous across patients, diseases, and institutional practices. We introduce the model-agnostic and parameter-efficient federated learning framework for adapting LLMs to medical applications. Fed-MedLoRA transmits only low-rank adapter parameters, reducing communication and computation overhead, while Fed-MedLoRA+ further incorporates adaptive, data-aware aggregation to improve convergence under cross-site heterogeneity. We apply the framework to clinical information extraction (IE), which transforms patient narratives into structured medical entities and relations. Accuracy was assessed across five patient cohorts through comparisons with BERT models, and LLaMA-3 and DeepSeek-R1, GPT-4o models. Evaluation settings included (1) in-domain training and testing, (2) external validation on independent cohorts, and (3) a low-resource new-site adaptation scenario using real-world clinical notes from the Yale New Haven Health System.
Assessing LLMs for Serendipity Discovery in Knowledge Graphs: A Case for Drug Repurposing
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have greatly advanced knowledge graph question answering (KGQA), yet existing systems are typically optimized for returning highly relevant but predictable answers. A missing yet desired capacity is to exploit LLMs to suggest surprise and novel ("serendipitious") answers. In this paper, we formally define the serendipity-aware KGQA task and propose the SerenQA framework to evaluate LLMs' ability to uncover unexpected insights in scientific KGQA tasks. SerenQA includes a rigorous serendipity metric based on relevance, novelty, and surprise, along with an expert-annotated benchmark derived from the Clinical Knowledge Graph, focused on drug repurposing. Additionally, it features a structured evaluation pipeline encompassing three subtasks: knowledge retrieval, subgraph reasoning, and serendipity exploration. Our experiments reveal that while state-of-the-art LLMs perform well on retrieval, they still struggle to identify genuinely surprising and valuable discoveries, underscoring a significant room for future improvements. Our curated resources and extended version are released at: https://cwru-db-group.github.io/serenQA.
Memorization in Large Language Models in Medicine: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Implications
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in medicine. To date, LLMs have been widely applied to tasks such as diagnostic assistance, medical question answering, and clinical information synthesis. However, a key open question remains: to what extent do LLMs memorize medical training data. In this study, we present the first comprehensive evaluation of memorization of LLMs in medicine, assessing its prevalence (how frequently it occurs), characteristics (what is memorized), volume (how much content is memorized), and potential downstream impacts (how memorization may affect medical applications). We systematically analyze common adaptation scenarios: (1) continued pretraining on medical corpora, (2) fine-tuning on standard medical benchmarks, and (3) fine-tuning on real-world clinical data, including over 13,000 unique inpatient records from Yale New Haven Health System. The results demonstrate that memorization is prevalent across all adaptation scenarios and significantly higher than reported in the general domain. Memorization affects both the development and adoption of LLMs in medicine and can be categorized into three types: beneficial (e.g., accurate recall of clinical guidelines and biomedical references), uninformative (e.g., repeated disclaimers or templated medical document language), and harmful (e.g., regeneration of dataset-specific or sensitive clinical content). Based on these findings, we offer practical recommendations to facilitate beneficial memorization that enhances domain-specific reasoning and factual accuracy, minimize uninformative memorization to promote deeper learning beyond surface-level patterns, and mitigate harmful memorization to prevent the leakage of sensitive or identifiable patient information.
Quantized but Deceptive? A Multi-Dimensional Truthfulness Evaluation of Quantized LLMs
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Quantization enables efficient deployment of large language models (LLMs) in resource-constrained environments by significantly reducing memory and computation costs. While quantized LLMs often maintain performance on perplexity and zero-shot tasks, their impact on truthfulness-whether generating truthful or deceptive responses-remains largely unexplored. In this work, we introduce TruthfulnessEval, a comprehensive evaluation framework for assessing the truthfulness of quantized LLMs across three dimensions: (1) Truthfulness on Logical Reasoning; (2) Truthfulness on Common Sense; and (3) Truthfulness on Imitative Falsehoods. Using this framework, we examine mainstream quantization techniques (ranging from 4-bit to extreme 2-bit) across several open-source LLMs. Surprisingly, we find that while quantized models retain internally truthful representations, they are more susceptible to producing false outputs under misleading prompts. To probe this vulnerability, we test 15 rephrased variants of "honest", "neutral" and "deceptive" prompts and observe that "deceptive" prompts can override truth-consistent behavior, whereas "honest" and "neutral" prompts maintain stable outputs. Further, we reveal that quantized models "know" the truth internally yet still produce false outputs when guided by "deceptive" prompts via layer-wise probing and PCA visualizations. Our findings provide insights into future designs of quantization-aware alignment and truthfulness interventions.
ResSVD: Residual Compensated SVD for Large Language Model Compression
May 26, 2025
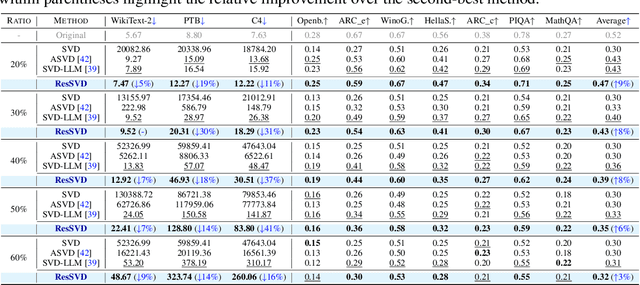


Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in a wide range of downstream natural language processing tasks. Nevertheless, their considerable sizes and memory demands hinder practical deployment, underscoring the importance of developing efficient compression strategies. Singular value decomposition (SVD) decomposes a matrix into orthogonal components, enabling efficient low-rank approximation. This is particularly suitable for LLM compression, where weight matrices often exhibit significant redundancy. However, current SVD-based methods neglect the residual matrix from truncation, resulting in significant truncation loss. Additionally, compressing all layers of the model results in severe performance degradation. To overcome these limitations, we propose ResSVD, a new post-training SVD-based LLM compression method. Specifically, we leverage the residual matrix generated during the truncation process to reduce truncation loss. Moreover, under a fixed overall compression ratio, we selectively compress the last few layers of the model, which mitigates error propagation and significantly improves the performance of compressed models.Comprehensive evaluations of ResSVD on diverse LLM families and multiple benchmark datasets indicate that ResSVD consistently achieves superior performance over existing counterpart methods, demonstrating its practical effectiveness.
When 'YES' Meets 'BUT': Can Large Models Comprehend Contradictory Humor Through Comparative Reasoning?
Mar 29, 2025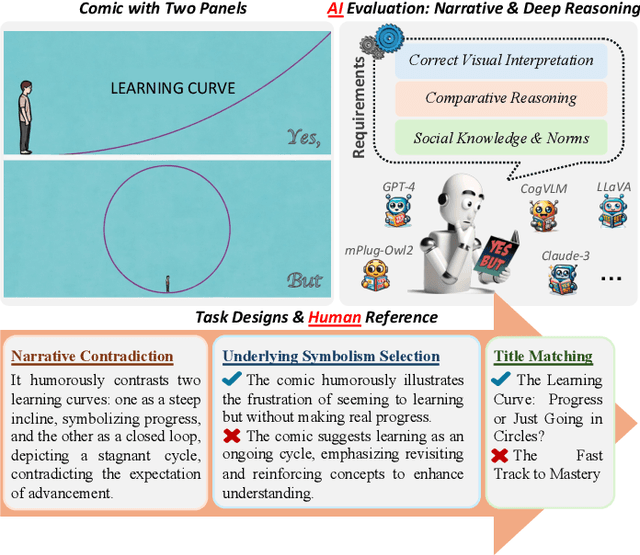

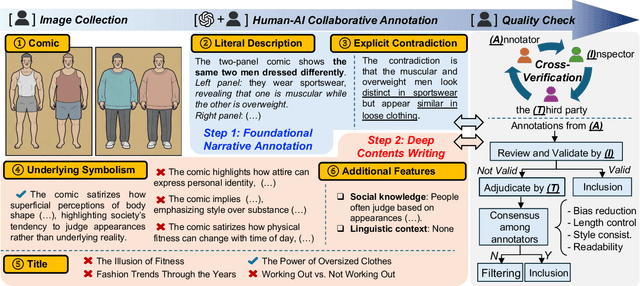

Abstract:Understanding humor-particularly when it involves complex, contradictory narratives that require comparative reasoning-remains a significant challenge for large vision-language models (VLMs). This limitation hinders AI's ability to engage in human-like reasoning and cultural expression. In this paper, we investigate this challenge through an in-depth analysis of comics that juxtapose panels to create humor through contradictions. We introduce the YesBut (V2), a novel benchmark with 1,262 comic images from diverse multilingual and multicultural contexts, featuring comprehensive annotations that capture various aspects of narrative understanding. Using this benchmark, we systematically evaluate a wide range of VLMs through four complementary tasks spanning from surface content comprehension to deep narrative reasoning, with particular emphasis on comparative reasoning between contradictory elements. Our extensive experiments reveal that even the most advanced models significantly underperform compared to humans, with common failures in visual perception, key element identification, comparative analysis and hallucinations. We further investigate text-based training strategies and social knowledge augmentation methods to enhance model performance. Our findings not only highlight critical weaknesses in VLMs' understanding of cultural and creative expressions but also provide pathways toward developing context-aware models capable of deeper narrative understanding though comparative reasoning.
Segment then Splat: A Unified Approach for 3D Open-Vocabulary Segmentation based on Gaussian Splatting
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:Open-vocabulary querying in 3D space is crucial for enabling more intelligent perception in applications such as robotics, autonomous systems, and augmented reality. However, most existing methods rely on 2D pixel-level parsing, leading to multi-view inconsistencies and poor 3D object retrieval. Moreover, they are limited to static scenes and struggle with dynamic scenes due to the complexities of motion modeling. In this paper, we propose Segment then Splat, a 3D-aware open vocabulary segmentation approach for both static and dynamic scenes based on Gaussian Splatting. Segment then Splat reverses the long established approach of "segmentation after reconstruction" by dividing Gaussians into distinct object sets before reconstruction. Once the reconstruction is complete, the scene is naturally segmented into individual objects, achieving true 3D segmentation. This approach not only eliminates Gaussian-object misalignment issues in dynamic scenes but also accelerates the optimization process, as it eliminates the need for learning a separate language field. After optimization, a CLIP embedding is assigned to each object to enable open-vocabulary querying. Extensive experiments on various datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method in both static and dynamic scenarios.
BARD-GS: Blur-Aware Reconstruction of Dynamic Scenes via Gaussian Splatting
Mar 20, 2025



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has shown remarkable potential for static scene reconstruction, and recent advancements have extended its application to dynamic scenes. However, the quality of reconstructions depends heavily on high-quality input images and precise camera poses, which are not that trivial to fulfill in real-world scenarios. Capturing dynamic scenes with handheld monocular cameras, for instance, typically involves simultaneous movement of both the camera and objects within a single exposure. This combined motion frequently results in image blur that existing methods cannot adequately handle. To address these challenges, we introduce BARD-GS, a novel approach for robust dynamic scene reconstruction that effectively handles blurry inputs and imprecise camera poses. Our method comprises two main components: 1) camera motion deblurring and 2) object motion deblurring. By explicitly decomposing motion blur into camera motion blur and object motion blur and modeling them separately, we achieve significantly improved rendering results in dynamic regions. In addition, we collect a real-world motion blur dataset of dynamic scenes to evaluate our approach. Extensive experiments demonstrate that BARD-GS effectively reconstructs high-quality dynamic scenes under realistic conditions, significantly outperforming existing methods.
CAUSAL3D: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Causal Learning from Visual Data
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:True intelligence hinges on the ability to uncover and leverage hidden causal relations. Despite significant progress in AI and computer vision (CV), there remains a lack of benchmarks for assessing models' abilities to infer latent causality from complex visual data. In this paper, we introduce \textsc{\textbf{Causal3D}}, a novel and comprehensive benchmark that integrates structured data (tables) with corresponding visual representations (images) to evaluate causal reasoning. Designed within a systematic framework, Causal3D comprises 19 3D-scene datasets capturing diverse causal relations, views, and backgrounds, enabling evaluations across scenes of varying complexity. We assess multiple state-of-the-art methods, including classical causal discovery, causal representation learning, and large/vision-language models (LLMs/VLMs). Our experiments show that as causal structures grow more complex without prior knowledge, performance declines significantly, highlighting the challenges even advanced methods face in complex causal scenarios. Causal3D serves as a vital resource for advancing causal reasoning in CV and fostering trustworthy AI in critical domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge