Zhiming Cui
Adapting Foundation Model for Dental Caries Detection with Dual-View Co-Training
Aug 28, 2025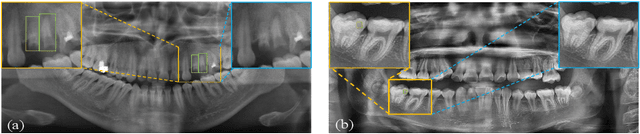
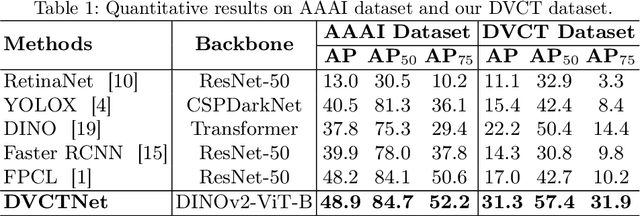
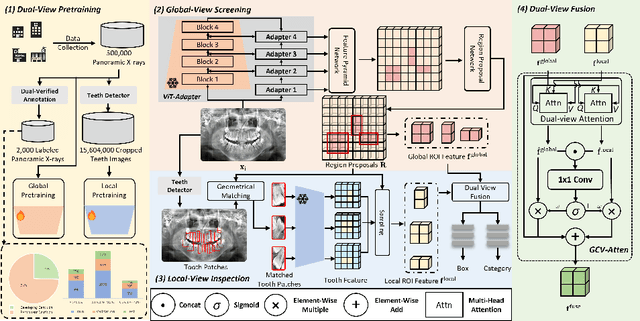
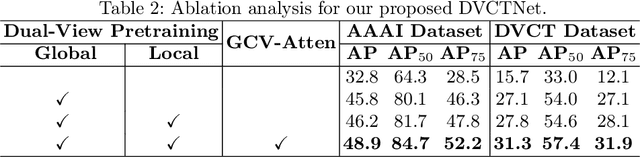
Abstract:Accurate dental caries detection from panoramic X-rays plays a pivotal role in preventing lesion progression. However, current detection methods often yield suboptimal accuracy due to subtle contrast variations and diverse lesion morphology of dental caries. In this work, inspired by the clinical workflow where dentists systematically combine whole-image screening with detailed tooth-level inspection, we present DVCTNet, a novel Dual-View Co-Training network for accurate dental caries detection. Our DVCTNet starts with employing automated tooth detection to establish two complementary views: a global view from panoramic X-ray images and a local view from cropped tooth images. We then pretrain two vision foundation models separately on the two views. The global-view foundation model serves as the detection backbone, generating region proposals and global features, while the local-view model extracts detailed features from corresponding cropped tooth patches matched by the region proposals. To effectively integrate information from both views, we introduce a Gated Cross-View Attention (GCV-Atten) module that dynamically fuses dual-view features, enhancing the detection pipeline by integrating the fused features back into the detection model for final caries detection. To rigorously evaluate our DVCTNet, we test it on a public dataset and further validate its performance on a newly curated, high-precision dental caries detection dataset, annotated using both intra-oral images and panoramic X-rays for double verification. Experimental results demonstrate DVCTNet's superior performance against existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on both datasets, indicating the clinical applicability of our method. Our code and labeled dataset are available at https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/DVCTNet.
3D MedDiffusion: A 3D Medical Diffusion Model for Controllable and High-quality Medical Image Generation
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:The generation of medical images presents significant challenges due to their high-resolution and three-dimensional nature. Existing methods often yield suboptimal performance in generating high-quality 3D medical images, and there is currently no universal generative framework for medical imaging. In this paper, we introduce the 3D Medical Diffusion (3D MedDiffusion) model for controllable, high-quality 3D medical image generation. 3D MedDiffusion incorporates a novel, highly efficient Patch-Volume Autoencoder that compresses medical images into latent space through patch-wise encoding and recovers back into image space through volume-wise decoding. Additionally, we design a new noise estimator to capture both local details and global structure information during diffusion denoising process. 3D MedDiffusion can generate fine-detailed, high-resolution images (up to 512x512x512) and effectively adapt to various downstream tasks as it is trained on large-scale datasets covering CT and MRI modalities and different anatomical regions (from head to leg). Experimental results demonstrate that 3D MedDiffusion surpasses state-of-the-art methods in generative quality and exhibits strong generalizability across tasks such as sparse-view CT reconstruction, fast MRI reconstruction, and data augmentation.
4DRGS: 4D Radiative Gaussian Splatting for Efficient 3D Vessel Reconstruction from Sparse-View Dynamic DSA Images
Dec 17, 2024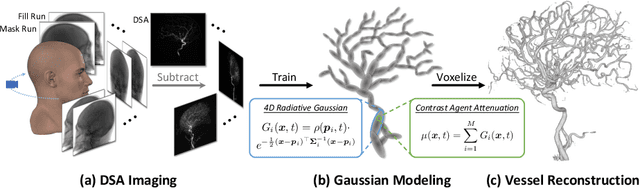

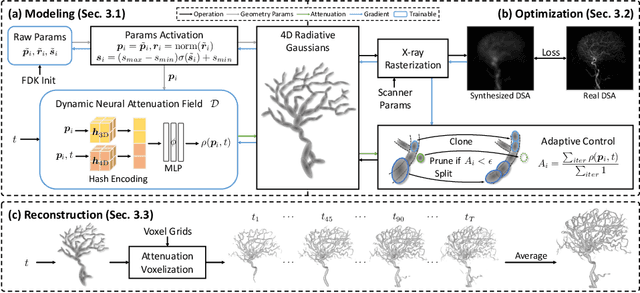

Abstract:Reconstructing 3D vessel structures from sparse-view dynamic digital subtraction angiography (DSA) images enables accurate medical assessment while reducing radiation exposure. Existing methods often produce suboptimal results or require excessive computation time. In this work, we propose 4D radiative Gaussian splatting (4DRGS) to achieve high-quality reconstruction efficiently. In detail, we represent the vessels with 4D radiative Gaussian kernels. Each kernel has time-invariant geometry parameters, including position, rotation, and scale, to model static vessel structures. The time-dependent central attenuation of each kernel is predicted from a compact neural network to capture the temporal varying response of contrast agent flow. We splat these Gaussian kernels to synthesize DSA images via X-ray rasterization and optimize the model with real captured ones. The final 3D vessel volume is voxelized from the well-trained kernels. Moreover, we introduce accumulated attenuation pruning and bounded scaling activation to improve reconstruction quality. Extensive experiments on real-world patient data demonstrate that 4DRGS achieves impressive results in 5 minutes training, which is 32x faster than the state-of-the-art method. This underscores the potential of 4DRGS for real-world clinics.
Align3R: Aligned Monocular Depth Estimation for Dynamic Videos
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Recent developments in monocular depth estimation methods enable high-quality depth estimation of single-view images but fail to estimate consistent video depth across different frames. Recent works address this problem by applying a video diffusion model to generate video depth conditioned on the input video, which is training-expensive and can only produce scale-invariant depth values without camera poses. In this paper, we propose a novel video-depth estimation method called Align3R to estimate temporal consistent depth maps for a dynamic video. Our key idea is to utilize the recent DUSt3R model to align estimated monocular depth maps of different timesteps. First, we fine-tune the DUSt3R model with additional estimated monocular depth as inputs for the dynamic scenes. Then, we apply optimization to reconstruct both depth maps and camera poses. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Align3R estimates consistent video depth and camera poses for a monocular video with superior performance than baseline methods.
VQ-SGen: A Vector Quantized Stroke Representation for Sketch Generation
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:This paper presents VQ-SGen, a novel algorithm for high-quality sketch generation. Recent approaches have often framed the task as pixel-based generation either as a whole or part-by-part, neglecting the intrinsic and contextual relationships among individual strokes, such as the shape and spatial positioning of both proximal and distant strokes. To overcome these limitations, we propose treating each stroke within a sketch as an entity and introducing a vector-quantized (VQ) stroke representation for fine-grained sketch generation. Our method follows a two-stage framework - in the first stage, we decouple each stroke's shape and location information to ensure the VQ representation prioritizes stroke shape learning. In the second stage, we feed the precise and compact representation into an auto-decoding Transformer to incorporate stroke semantics, positions, and shapes into the generation process. By utilizing tokenized stroke representation, our approach generates strokes with high fidelity and facilitates novel applications, such as conditional generation and semantic-aware stroke editing. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate our method surpasses existing state-of-the-art techniques, underscoring its effectiveness. The code and model will be made publicly available upon publication.
TeethDreamer: 3D Teeth Reconstruction from Five Intra-oral Photographs
Jul 16, 2024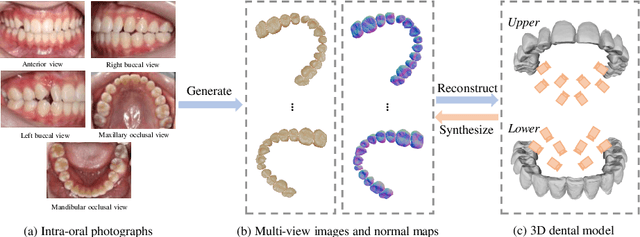
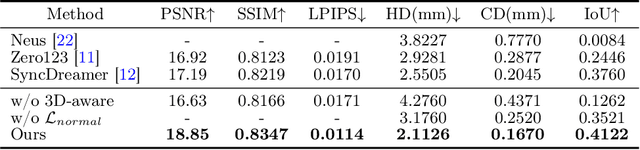
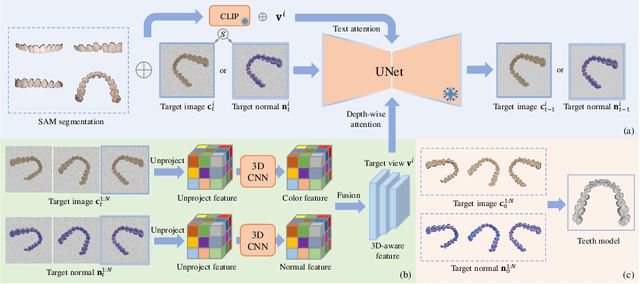
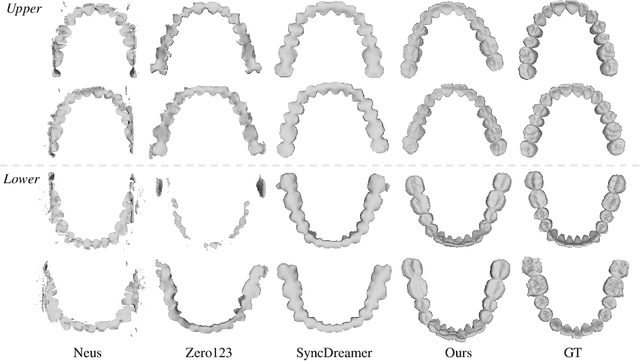
Abstract:Orthodontic treatment usually requires regular face-to-face examinations to monitor dental conditions of the patients. When in-person diagnosis is not feasible, an alternative is to utilize five intra-oral photographs for remote dental monitoring. However, it lacks of 3D information, and how to reconstruct 3D dental models from such sparse view photographs is a challenging problem. In this study, we propose a 3D teeth reconstruction framework, named TeethDreamer, aiming to restore the shape and position of the upper and lower teeth. Given five intra-oral photographs, our approach first leverages a large diffusion model's prior knowledge to generate novel multi-view images with known poses to address sparse inputs and then reconstructs high-quality 3D teeth models by neural surface reconstruction. To ensure the 3D consistency across generated views, we integrate a 3D-aware feature attention mechanism in the reverse diffusion process. Moreover, a geometry-aware normal loss is incorporated into the teeth reconstruction process to enhance geometry accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method over current state-of-the-arts, giving the potential to monitor orthodontic treatment remotely. Our code is available at https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/TeethDreamer
Cephalometric Landmark Detection across Ages with Prototypical Network
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Automated cephalometric landmark detection is crucial in real-world orthodontic diagnosis. Current studies mainly focus on only adult subjects, neglecting the clinically crucial scenario presented by adolescents whose landmarks often exhibit significantly different appearances compared to adults. Hence, an open question arises about how to develop a unified and effective detection algorithm across various age groups, including adolescents and adults. In this paper, we propose CeLDA, the first work for Cephalometric Landmark Detection across Ages. Our method leverages a prototypical network for landmark detection by comparing image features with landmark prototypes. To tackle the appearance discrepancy of landmarks between age groups, we design new strategies for CeLDA to improve prototype alignment and obtain a holistic estimation of landmark prototypes from a large set of training images. Moreover, a novel prototype relation mining paradigm is introduced to exploit the anatomical relations between the landmark prototypes. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of CeLDA in detecting cephalometric landmarks on both adult and adolescent subjects. To our knowledge, this is the first effort toward developing a unified solution and dataset for cephalometric landmark detection across age groups. Our code and dataset will be made public on https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/Cephalometric-Landmark-Detection-across-Ages-with-Prototypical-Network
3D Vessel Reconstruction from Sparse-View Dynamic DSA Images via Vessel Probability Guided Attenuation Learning
May 17, 2024



Abstract:Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) is one of the gold standards in vascular disease diagnosing. With the help of contrast agent, time-resolved 2D DSA images deliver comprehensive insights into blood flow information and can be utilized to reconstruct 3D vessel structures. Current commercial DSA systems typically demand hundreds of scanning views to perform reconstruction, resulting in substantial radiation exposure. However, sparse-view DSA reconstruction, aimed at reducing radiation dosage, is still underexplored in the research community. The dynamic blood flow and insufficient input of sparse-view DSA images present significant challenges to the 3D vessel reconstruction task. In this study, we propose to use a time-agnostic vessel probability field to solve this problem effectively. Our approach, termed as vessel probability guided attenuation learning, represents the DSA imaging as a complementary weighted combination of static and dynamic attenuation fields, with the weights derived from the vessel probability field. Functioning as a dynamic mask, vessel probability provides proper gradients for both static and dynamic fields adaptive to different scene types. This mechanism facilitates a self-supervised decomposition between static backgrounds and dynamic contrast agent flow, and significantly improves the reconstruction quality. Our model is trained by minimizing the disparity between synthesized projections and real captured DSA images. We further employ two training strategies to improve our reconstruction quality: (1) coarse-to-fine progressive training to achieve better geometry and (2) temporal perturbed rendering loss to enforce temporal consistency. Experimental results have demonstrated superior quality on both 3D vessel reconstruction and 2D view synthesis.
CLIP in Medical Imaging: A Comprehensive Survey
Dec 26, 2023



Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP), a simple yet effective pre-training paradigm, successfully introduces text supervision to vision models. It has shown promising results across various tasks, attributable to its generalizability and interpretability. The use of CLIP has recently gained increasing interest in the medical imaging domain, serving both as a pre-training paradigm for aligning medical vision and language, and as a critical component in diverse clinical tasks. With the aim of facilitating a deeper understanding of this promising direction, this survey offers an in-depth exploration of the CLIP paradigm within the domain of medical imaging, regarding both refined CLIP pre-training and CLIP-driven applications. In this study, We (1) start with a brief introduction to the fundamentals of CLIP methodology. (2) Then, we investigate the adaptation of CLIP pre-training in the medical domain, focusing on how to optimize CLIP given characteristics of medical images and reports. (3) Furthermore, we explore the practical utilization of CLIP pre-trained models in various tasks, including classification, dense prediction, and cross-modal tasks. (4) Finally, we discuss existing limitations of CLIP in the context of medical imaging and propose forward-looking directions to address the demands of medical imaging domain. We expect that this comprehensive survey will provide researchers in the field of medical image analysis with a holistic understanding of the CLIP paradigm and its potential implications. The project page can be found on https://github.com/zhaozh10/Awesome-CLIP-in-Medical-Imaging.
3D Structure-guided Network for Tooth Alignment in 2D Photograph
Oct 17, 2023Abstract:Orthodontics focuses on rectifying misaligned teeth (i.e., malocclusions), affecting both masticatory function and aesthetics. However, orthodontic treatment often involves complex, lengthy procedures. As such, generating a 2D photograph depicting aligned teeth prior to orthodontic treatment is crucial for effective dentist-patient communication and, more importantly, for encouraging patients to accept orthodontic intervention. In this paper, we propose a 3D structure-guided tooth alignment network that takes 2D photographs as input (e.g., photos captured by smartphones) and aligns the teeth within the 2D image space to generate an orthodontic comparison photograph featuring aesthetically pleasing, aligned teeth. Notably, while the process operates within a 2D image space, our method employs 3D intra-oral scanning models collected in clinics to learn about orthodontic treatment, i.e., projecting the pre- and post-orthodontic 3D tooth structures onto 2D tooth contours, followed by a diffusion model to learn the mapping relationship. Ultimately, the aligned tooth contours are leveraged to guide the generation of a 2D photograph with aesthetically pleasing, aligned teeth and realistic textures. We evaluate our network on various facial photographs, demonstrating its exceptional performance and strong applicability within the orthodontic industry.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge