Li Yang
A multitask framework for automated interpretation of multi-frame right upper quadrant ultrasound in clinical decision support
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Ultrasound is a cornerstone of emergency and hepatobiliary imaging, yet its interpretation remains highly operator-dependent and time-sensitive. Here, we present a multitask vision-language agent (VLM) developed to assist with comprehensive right upper quadrant (RUQ) ultrasound interpretation across the full diagnostic workflow. The system was trained on a large, multi-center dataset comprising a primary cohort from Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions (9,189 cases, 594,099 images) and externally validated on cohorts from Stanford University (108 cases, 3,240 images) and a major Chinese medical center (257 cases, 3,178 images). Built on the Qwen2.5-VL-7B architecture, the agent integrates frame-level visual understanding with report-grounded language reasoning to perform three tasks: (i) classification of 18 hepatobiliary and gallbladder conditions, (ii) generation of clinically coherent diagnostic reports, and (iii) surgical decision support based on ultrasound findings and clinical data. The model achieved high diagnostic accuracy across all tasks, generated reports that were indistinguishable from expert-written versions in blinded evaluations, and demonstrated superior factual accuracy and information density on content-based metrics. The agent further identified patients requiring cholecystectomy with high precision, supporting real-time decision-making. These results highlight the potential of generalist vision-language models to improve diagnostic consistency, reporting efficiency, and surgical triage in real-world ultrasound practice.
Prior-AttUNet: Retinal OCT Fluid Segmentation Based on Normal Anatomical Priors and Attention Gating
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Accurate segmentation of macular edema, a hallmark pathological feature in vision-threatening conditions such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic macular edema, is essential for clinical diagnosis and management. To overcome the challenges of segmenting fluid regions in optical coherence tomography (OCT) images-notably ambiguous boundaries and cross-device heterogeneity-this study introduces Prior-AttUNet, a segmentation model augmented with generative anatomical priors. The framework adopts a hybrid dual-path architecture that integrates a generative prior pathway with a segmentation network. A variational autoencoder supplies multi-scale normative anatomical priors, while the segmentation backbone incorporates densely connected blocks and spatial pyramid pooling modules to capture richer contextual information. Additionally, a novel triple-attention mechanism, guided by anatomical priors, dynamically modulates feature importance across decoding stages, substantially enhancing boundary delineation. Evaluated on the public RETOUCH benchmark, Prior-AttUNet achieves excellent performance across three OCT imaging devices (Cirrus, Spectralis, and Topcon), with mean Dice similarity coefficients of 93.93%, 95.18%, and 93.47%, respectively. The model maintains a low computational cost of 0.37 TFLOPs, striking an effective balance between segmentation precision and inference efficiency. These results demonstrate its potential as a reliable tool for automated clinical analysis.
DCL-SE: Dynamic Curriculum Learning for Spatiotemporal Encoding of Brain Imaging
Nov 19, 2025



Abstract:High-dimensional neuroimaging analyses for clinical diagnosis are often constrained by compromises in spatiotemporal fidelity and by the limited adaptability of large-scale, general-purpose models. To address these challenges, we introduce Dynamic Curriculum Learning for Spatiotemporal Encoding (DCL-SE), an end-to-end framework centered on data-driven spatiotemporal encoding (DaSE). We leverage Approximate Rank Pooling (ARP) to efficiently encode three-dimensional volumetric brain data into information-rich, two-dimensional dynamic representations, and then employ a dynamic curriculum learning strategy, guided by a Dynamic Group Mechanism (DGM), to progressively train the decoder, refining feature extraction from global anatomical structures to fine pathological details. Evaluated across six publicly available datasets, including Alzheimer's disease and brain tumor classification, cerebral artery segmentation, and brain age prediction, DCL-SE consistently outperforms existing methods in accuracy, robustness, and interpretability. These findings underscore the critical importance of compact, task-specific architectures in the era of large-scale pretrained networks.
Toward Autonomous and Efficient Cybersecurity: A Multi-Objective AutoML-based Intrusion Detection System
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:With increasingly sophisticated cybersecurity threats and rising demand for network automation, autonomous cybersecurity mechanisms are becoming critical for securing modern networks. The rapid expansion of Internet of Things (IoT) systems amplifies these challenges, as resource-constrained IoT devices demand scalable and efficient security solutions. In this work, an innovative Intrusion Detection System (IDS) utilizing Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) and Multi-Objective Optimization (MOO) is proposed for autonomous and optimized cyber-attack detection in modern networking environments. The proposed IDS framework integrates two primary innovative techniques: Optimized Importance and Percentage-based Automated Feature Selection (OIP-AutoFS) and Optimized Performance, Confidence, and Efficiency-based Combined Algorithm Selection and Hyperparameter Optimization (OPCE-CASH). These components optimize feature selection and model learning processes to strike a balance between intrusion detection effectiveness and computational efficiency. This work presents the first IDS framework that integrates all four AutoML stages and employs multi-objective optimization to jointly optimize detection effectiveness, efficiency, and confidence for deployment in resource-constrained systems. Experimental evaluations over two benchmark cybersecurity datasets demonstrate that the proposed MOO-AutoML IDS outperforms state-of-the-art IDSs, establishing a new benchmark for autonomous, efficient, and optimized security for networks. Designed to support IoT and edge environments with resource constraints, the proposed framework is applicable to a variety of autonomous cybersecurity applications across diverse networked environments.
Enhancing Small-Scale Dataset Expansion with Triplet-Connection-based Sample Re-Weighting
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:The performance of computer vision models in certain real-world applications, such as medical diagnosis, is often limited by the scarcity of available images. Expanding datasets using pre-trained generative models is an effective solution. However, due to the uncontrollable generation process and the ambiguity of natural language, noisy images may be generated. Re-weighting is an effective way to address this issue by assigning low weights to such noisy images. We first theoretically analyze three types of supervision for the generated images. Based on the theoretical analysis, we develop TriReWeight, a triplet-connection-based sample re-weighting method to enhance generative data augmentation. Theoretically, TriReWeight can be integrated with any generative data augmentation methods and never downgrade their performance. Moreover, its generalization approaches the optimal in the order $O(\sqrt{d\ln (n)/n})$. Our experiments validate the correctness of the theoretical analysis and demonstrate that our method outperforms the existing SOTA methods by $7.9\%$ on average over six natural image datasets and by $3.4\%$ on average over three medical datasets. We also experimentally validate that our method can enhance the performance of different generative data augmentation methods.
SAEL: Leveraging Large Language Models with Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts for Smart Contract Vulnerability Detection
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:With the increasing security issues in blockchain, smart contract vulnerability detection has become a research focus. Existing vulnerability detection methods have their limitations: 1) Static analysis methods struggle with complex scenarios. 2) Methods based on specialized pre-trained models perform well on specific datasets but have limited generalization capabilities. In contrast, general-purpose Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive ability in adapting to new vulnerability patterns. However, they often underperform on specific vulnerability types compared to methods based on specialized pre-trained models. We also observe that explanations generated by general-purpose LLMs can provide fine-grained code understanding information, contributing to improved detection performance. Inspired by these observations, we propose SAEL, an LLM-based framework for smart contract vulnerability detection. We first design targeted prompts to guide LLMs in identifying vulnerabilities and generating explanations, which serve as prediction features. Next, we apply prompt-tuning on CodeT5 and T5 to process contract code and explanations, enhancing task-specific performance. To combine the strengths of each approach, we introduce an Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts architecture. This dynamically adjusts feature weights via a Gating Network, which selects relevant features using TopK filtering and Softmax normalization, and incorporates a Multi-Head Self-Attention mechanism to enhance cross-feature relationships. This design enables effective integration of LLM predictions, explanation features, and code features through gradient optimization. The loss function jointly considers both independent feature performance and overall weighted predictions. Experiments show that SAEL outperforms existing methods across various vulnerabilities.
Interactive Hybrid Rice Breeding with Parametric Dual Projection
Jul 16, 2025



Abstract:Hybrid rice breeding crossbreeds different rice lines and cultivates the resulting hybrids in fields to select those with desirable agronomic traits, such as higher yields. Recently, genomic selection has emerged as an efficient way for hybrid rice breeding. It predicts the traits of hybrids based on their genes, which helps exclude many undesired hybrids, largely reducing the workload of field cultivation. However, due to the limited accuracy of genomic prediction models, breeders still need to combine their experience with the models to identify regulatory genes that control traits and select hybrids, which remains a time-consuming process. To ease this process, in this paper, we proposed a visual analysis method to facilitate interactive hybrid rice breeding. Regulatory gene identification and hybrid selection naturally ensemble a dual-analysis task. Therefore, we developed a parametric dual projection method with theoretical guarantees to facilitate interactive dual analysis. Based on this dual projection method, we further developed a gene visualization and a hybrid visualization to verify the identified regulatory genes and hybrids. The effectiveness of our method is demonstrated through the quantitative evaluation of the parametric dual projection method, identified regulatory genes and desired hybrids in the case study, and positive feedback from breeders.
ETT-CKGE: Efficient Task-driven Tokens for Continual Knowledge Graph Embedding
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Continual Knowledge Graph Embedding (CKGE) seeks to integrate new knowledge while preserving past information. However, existing methods struggle with efficiency and scalability due to two key limitations: (1) suboptimal knowledge preservation between snapshots caused by manually designed node/relation importance scores that ignore graph dependencies relevant to the downstream task, and (2) computationally expensive graph traversal for node/relation importance calculation, leading to slow training and high memory overhead. To address these limitations, we introduce ETT-CKGE (Efficient, Task-driven, Tokens for Continual Knowledge Graph Embedding), a novel task-guided CKGE method that leverages efficient task-driven tokens for efficient and effective knowledge transfer between snapshots. Our method introduces a set of learnable tokens that directly capture task-relevant signals, eliminating the need for explicit node scoring or traversal. These tokens serve as consistent and reusable guidance across snapshots, enabling efficient token-masked embedding alignment between snapshots. Importantly, knowledge transfer is achieved through simple matrix operations, significantly reducing training time and memory usage. Extensive experiments across six benchmark datasets demonstrate that ETT-CKGE consistently achieves superior or competitive predictive performance, while substantially improving training efficiency and scalability compared to state-of-the-art CKGE methods. The code is available at: https://github.com/lijingzhu1/ETT-CKGE/tree/main
Rethinking Continual Learning with Progressive Neural Collapse
May 30, 2025Abstract:Continual Learning (CL) seeks to build an agent that can continuously learn a sequence of tasks, where a key challenge, namely Catastrophic Forgetting, persists due to the potential knowledge interference among different tasks. On the other hand, deep neural networks (DNNs) are shown to converge to a terminal state termed Neural Collapse during training, where all class prototypes geometrically form a static simplex equiangular tight frame (ETF). These maximally and equally separated class prototypes make the ETF an ideal target for model learning in CL to mitigate knowledge interference. Thus inspired, several studies have emerged very recently to leverage a fixed global ETF in CL, which however suffers from key drawbacks, such as impracticability and limited performance.To address these challenges and fully unlock the potential of ETF in CL, we propose Progressive Neural Collapse (ProNC), a novel framework that completely removes the need of a fixed global ETF in CL. Specifically, ProNC progressively expands the ETF target in a principled way by adding new class prototypes as vertices for new tasks, ensuring maximal separability across all encountered classes with minimal shifts from the previous ETF. We next develop a new CL framework by plugging ProNC into commonly used CL algorithm designs, where distillation is further leveraged to balance between target shifting for old classes and target aligning for new classes. Extensive experiments show that our approach significantly outperforms related baselines while maintaining superior flexibility, simplicity, and efficiency.
Towards Practical Defect-Focused Automated Code Review
May 23, 2025
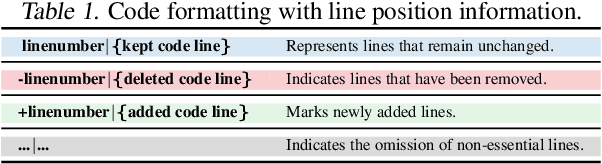
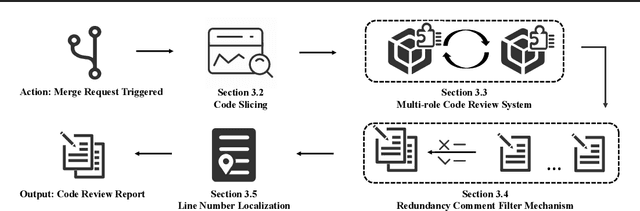
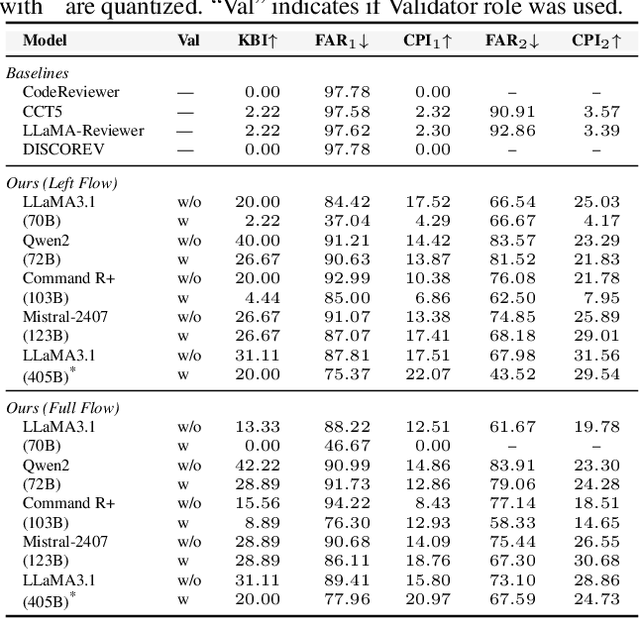
Abstract:The complexity of code reviews has driven efforts to automate review comments, but prior approaches oversimplify this task by treating it as snippet-level code-to-text generation and relying on text similarity metrics like BLEU for evaluation. These methods overlook repository context, real-world merge request evaluation, and defect detection, limiting their practicality. To address these issues, we explore the full automation pipeline within the online recommendation service of a company with nearly 400 million daily active users, analyzing industry-grade C++ codebases comprising hundreds of thousands of lines of code. We identify four key challenges: 1) capturing relevant context, 2) improving key bug inclusion (KBI), 3) reducing false alarm rates (FAR), and 4) integrating human workflows. To tackle these, we propose 1) code slicing algorithms for context extraction, 2) a multi-role LLM framework for KBI, 3) a filtering mechanism for FAR reduction, and 4) a novel prompt design for better human interaction. Our approach, validated on real-world merge requests from historical fault reports, achieves a 2x improvement over standard LLMs and a 10x gain over previous baselines. While the presented results focus on C++, the underlying framework design leverages language-agnostic principles (e.g., AST-based analysis), suggesting potential for broader applicability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge