Abdallah Shami
Toward Autonomous and Efficient Cybersecurity: A Multi-Objective AutoML-based Intrusion Detection System
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:With increasingly sophisticated cybersecurity threats and rising demand for network automation, autonomous cybersecurity mechanisms are becoming critical for securing modern networks. The rapid expansion of Internet of Things (IoT) systems amplifies these challenges, as resource-constrained IoT devices demand scalable and efficient security solutions. In this work, an innovative Intrusion Detection System (IDS) utilizing Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) and Multi-Objective Optimization (MOO) is proposed for autonomous and optimized cyber-attack detection in modern networking environments. The proposed IDS framework integrates two primary innovative techniques: Optimized Importance and Percentage-based Automated Feature Selection (OIP-AutoFS) and Optimized Performance, Confidence, and Efficiency-based Combined Algorithm Selection and Hyperparameter Optimization (OPCE-CASH). These components optimize feature selection and model learning processes to strike a balance between intrusion detection effectiveness and computational efficiency. This work presents the first IDS framework that integrates all four AutoML stages and employs multi-objective optimization to jointly optimize detection effectiveness, efficiency, and confidence for deployment in resource-constrained systems. Experimental evaluations over two benchmark cybersecurity datasets demonstrate that the proposed MOO-AutoML IDS outperforms state-of-the-art IDSs, establishing a new benchmark for autonomous, efficient, and optimized security for networks. Designed to support IoT and edge environments with resource constraints, the proposed framework is applicable to a variety of autonomous cybersecurity applications across diverse networked environments.
TinyDrive: Multiscale Visual Question Answering with Selective Token Routing for Autonomous Driving
May 21, 2025Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) employed for visual question-answering (VQA) in autonomous driving often require substantial computational resources that pose a challenge for their deployment in resource-constrained vehicles. To address this challenge, we introduce TinyDrive, a lightweight yet effective VLM for multi-view VQA in driving scenarios. Our model comprises two key components including a multiscale vision encoder and a dual-level prioritization mechanism for tokens and sequences. The multiscale encoder facilitates the processing of multi-view images at diverse resolutions through scale injection and cross-scale gating to generate enhanced visual representations. At the token level, we design a token routing mechanism that dynamically selects and process the most informative tokens based on learned importance scores. At the sequence level, we propose integrating normalized loss, uncertainty estimates, and a diversity metric to formulate sequence scores that rank and preserve samples within a sequence priority buffer. Samples with higher scores are more frequently selected for training. TinyDrive is first evaluated on our custom-curated VQA dataset, and it is subsequently tested on the public DriveLM benchmark, where it achieves state-of-the-art language understanding performance. Notably, it achieves relative improvements of 11.1% and 35.4% in BLEU-4 and METEOR scores, respectively, despite having a significantly smaller parameter count.
Pruning-Based TinyML Optimization of Machine Learning Models for Anomaly Detection in Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure
Mar 19, 2025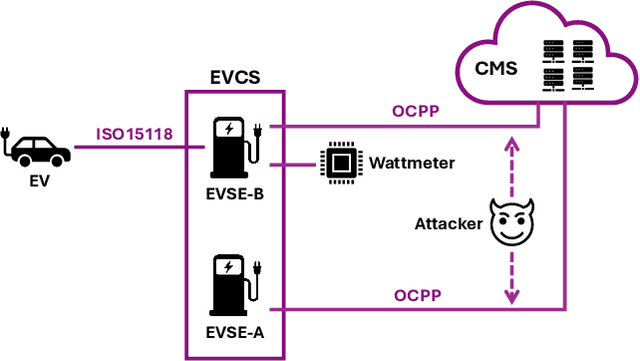
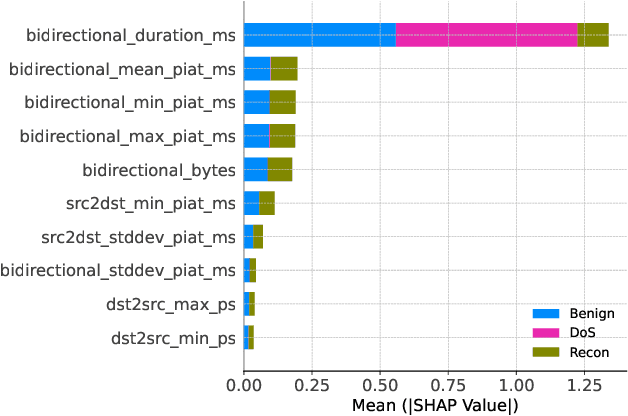
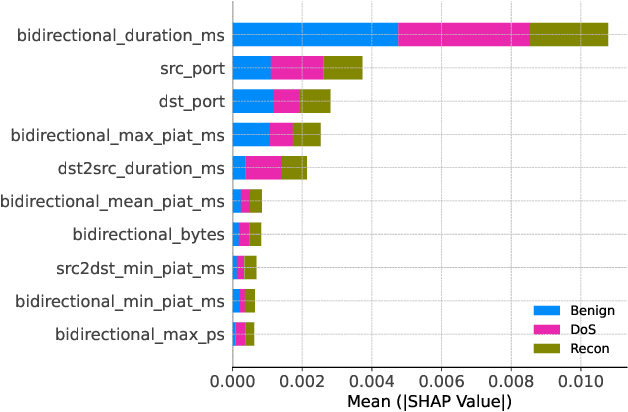
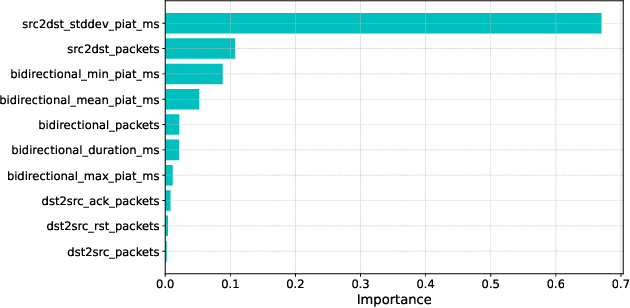
Abstract:With the growing need for real-time processing on IoT devices, optimizing machine learning (ML) models' size, latency, and computational efficiency is essential. This paper investigates a pruning method for anomaly detection in resource-constrained environments, specifically targeting Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure (EVCI). Using the CICEVSE2024 dataset, we trained and optimized three models-Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), and XGBoost-through hyperparameter tuning with Optuna, further refining them using SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP)-based feature selection (FS) and unstructured pruning techniques. The optimized models achieved significant reductions in model size and inference times, with only a marginal impact on their performance. Notably, our findings indicate that, in the context of EVCI, pruning and FS can enhance computational efficiency while retaining critical anomaly detection capabilities.
Enabling AutoML for Zero-Touch Network Security: Use-Case Driven Analysis
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:Zero-Touch Networks (ZTNs) represent a state-of-the-art paradigm shift towards fully automated and intelligent network management, enabling the automation and intelligence required to manage the complexity, scale, and dynamic nature of next-generation (6G) networks. ZTNs leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to enhance operational efficiency, support intelligent decision-making, and ensure effective resource allocation. However, the implementation of ZTNs is subject to security challenges that need to be resolved to achieve their full potential. In particular, two critical challenges arise: the need for human expertise in developing AI/ML-based security mechanisms, and the threat of adversarial attacks targeting AI/ML models. In this survey paper, we provide a comprehensive review of current security issues in ZTNs, emphasizing the need for advanced AI/ML-based security mechanisms that require minimal human intervention and protect AI/ML models themselves. Furthermore, we explore the potential of Automated ML (AutoML) technologies in developing robust security solutions for ZTNs. Through case studies, we illustrate practical approaches to securing ZTNs against both conventional and AI/ML-specific threats, including the development of autonomous intrusion detection systems and strategies to combat Adversarial ML (AML) attacks. The paper concludes with a discussion of the future research directions for the development of ZTN security approaches.
* Published in IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management (TNSM); Code is available at Github link: https://github.com/Western-OC2-Lab/AutoML-and-Adversarial-Attack-Defense-for-Zero-Touch-Network-Security
Towards Zero Touch Networks: Cross-Layer Automated Security Solutions for 6G Wireless Networks
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:The transition from 5G to 6G mobile networks necessitates network automation to meet the escalating demands for high data rates, ultra-low latency, and integrated technology. Recently, Zero-Touch Networks (ZTNs), driven by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), are designed to automate the entire lifecycle of network operations with minimal human intervention, presenting a promising solution for enhancing automation in 5G/6G networks. However, the implementation of ZTNs brings forth the need for autonomous and robust cybersecurity solutions, as ZTNs rely heavily on automation. AI/ML algorithms are widely used to develop cybersecurity mechanisms, but require substantial specialized expertise and encounter model drift issues, posing significant challenges in developing autonomous cybersecurity measures. Therefore, this paper proposes an automated security framework targeting Physical Layer Authentication (PLA) and Cross-Layer Intrusion Detection Systems (CLIDS) to address security concerns at multiple Internet protocol layers. The proposed framework employs drift-adaptive online learning techniques and a novel enhanced Successive Halving (SH)-based Automated ML (AutoML) method to automatically generate optimized ML models for dynamic networking environments. Experimental results illustrate that the proposed framework achieves high performance on the public Radio Frequency (RF) fingerprinting and the Canadian Institute for CICIDS2017 datasets, showcasing its effectiveness in addressing PLA and CLIDS tasks within dynamic and complex networking environments. Furthermore, the paper explores open challenges and research directions in the 5G/6G cybersecurity domain. This framework represents a significant advancement towards fully autonomous and secure 6G networks, paving the way for future innovations in network automation and cybersecurity.
Network Resource Optimization for ML-Based UAV Condition Monitoring with Vibration Analysis
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:As smart cities begin to materialize, the role of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and their reliability becomes increasingly important. One aspect of reliability relates to Condition Monitoring (CM), where Machine Learning (ML) models are leveraged to identify abnormal and adverse conditions. Given the resource-constrained nature of next-generation edge networks, the utilization of precious network resources must be minimized. This work explores the optimization of network resources for ML-based UAV CM frameworks. The developed framework uses experimental data and varies the feature extraction aggregation interval to optimize ML model selection. Additionally, by leveraging dimensionality reduction techniques, there is a 99.9% reduction in network resource consumption.
Towards Autonomous Cybersecurity: An Intelligent AutoML Framework for Autonomous Intrusion Detection
Sep 05, 2024



Abstract:The rapid evolution of mobile networks from 5G to 6G has necessitated the development of autonomous network management systems, such as Zero-Touch Networks (ZTNs). However, the increased complexity and automation of these networks have also escalated cybersecurity risks. Existing Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs) leveraging traditional Machine Learning (ML) techniques have shown effectiveness in mitigating these risks, but they often require extensive manual effort and expert knowledge. To address these challenges, this paper proposes an Automated Machine Learning (AutoML)-based autonomous IDS framework towards achieving autonomous cybersecurity for next-generation networks. To achieve autonomous intrusion detection, the proposed AutoML framework automates all critical procedures of the data analytics pipeline, including data pre-processing, feature engineering, model selection, hyperparameter tuning, and model ensemble. Specifically, it utilizes a Tabular Variational Auto-Encoder (TVAE) method for automated data balancing, tree-based ML models for automated feature selection and base model learning, Bayesian Optimization (BO) for hyperparameter optimization, and a novel Optimized Confidence-based Stacking Ensemble (OCSE) method for automated model ensemble. The proposed AutoML-based IDS was evaluated on two public benchmark network security datasets, CICIDS2017 and 5G-NIDD, and demonstrated improved performance compared to state-of-the-art cybersecurity methods. This research marks a significant step towards fully autonomous cybersecurity in next-generation networks, potentially revolutionizing network security applications.
Decentralized Semantic Traffic Control in AVs Using RL and DQN for Dynamic Roadblocks
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous Vehicles (AVs), furnished with sensors capable of capturing essential vehicle dynamics such as speed, acceleration, and precise location, possess the capacity to execute intelligent maneuvers, including lane changes, in anticipation of approaching roadblocks. Nevertheless, the sheer volume of sensory data and the processing necessary to derive informed decisions can often overwhelm the vehicles, rendering them unable to handle the task independently. Consequently, a common approach in traffic scenarios involves transmitting the data to servers for processing, a practice that introduces challenges, particularly in situations demanding real-time processing. In response to this challenge, we present a novel DL-based semantic traffic control system that entrusts semantic encoding responsibilities to the vehicles themselves. This system processes driving decisions obtained from a Reinforcement Learning (RL) agent, streamlining the decision-making process. Specifically, our framework envisions scenarios where abrupt roadblocks materialize due to factors such as road maintenance, accidents, or vehicle repairs, necessitating vehicles to make determinations concerning lane-keeping or lane-changing actions to navigate past these obstacles. To formulate this scenario mathematically, we employ a Markov Decision Process (MDP) and harness the Deep Q Learning (DQN) algorithm to unearth viable solutions.
Joint Instantaneous Amplitude-Frequency Analysis of Vibration Signals for Vibration-Based Condition Monitoring of Rolling Bearings
May 14, 2024Abstract:Vibrations of damaged bearings are manifested as modulations in the amplitude of the generated vibration signal, making envelope analysis an effective approach for discriminating between healthy and abnormal vibration patterns. Motivated by this, we introduce a low-complexity method for vibration-based condition monitoring (VBCM) of rolling bearings based on envelope analysis. In the proposed method, the instantaneous amplitude (envelope) and instantaneous frequency of the vibration signal are jointly utilized to facilitate three novel envelope representations: instantaneous amplitude-frequency mapping (IAFM), instantaneous amplitude-frequency correlation (IAFC), and instantaneous energy-frequency distribution (IEFD). Maintaining temporal information, these representations effectively capture energy-frequency variations that are unique to the condition of the bearing, thereby enabling the extraction of discriminative features with high sensitivity to variations in operational conditions. Accordingly, six new highly discriminative features are engineered from these representations, capturing and characterizing their shapes. The experimental results show outstanding performance in detecting and diagnosing various fault types, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed method in capturing unique variations in energy and frequency between healthy and faulty bearings. Moreover, the proposed method has moderate computational complexity, meeting the requirements of real-time applications. Further, the Python code of the proposed method is made public to support collaborative research efforts and ensure the reproducibility of the presented work
On TinyML and Cybersecurity: Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Use Case
Apr 29, 2024



Abstract:As technology advances, the use of Machine Learning (ML) in cybersecurity is becoming increasingly crucial to tackle the growing complexity of cyber threats. While traditional ML models can enhance cybersecurity, their high energy and resource demands limit their applications, leading to the emergence of Tiny Machine Learning (TinyML) as a more suitable solution for resource-constrained environments. TinyML is widely applied in areas such as smart homes, healthcare, and industrial automation. TinyML focuses on optimizing ML algorithms for small, low-power devices, enabling intelligent data processing directly on edge devices. This paper provides a comprehensive review of common challenges of TinyML techniques, such as power consumption, limited memory, and computational constraints; it also explores potential solutions to these challenges, such as energy harvesting, computational optimization techniques, and transfer learning for privacy preservation. On the other hand, this paper discusses TinyML's applications in advancing cybersecurity for Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructures (EVCIs) as a representative use case. It presents an experimental case study that enhances cybersecurity in EVCI using TinyML, evaluated against traditional ML in terms of reduced delay and memory usage, with a slight trade-off in accuracy. Additionally, the study includes a practical setup using the ESP32 microcontroller in the PlatformIO environment, which provides a hands-on assessment of TinyML's application in cybersecurity for EVCI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge