Firouz Badrkhani Ajaei
Pruning-Based TinyML Optimization of Machine Learning Models for Anomaly Detection in Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure
Mar 19, 2025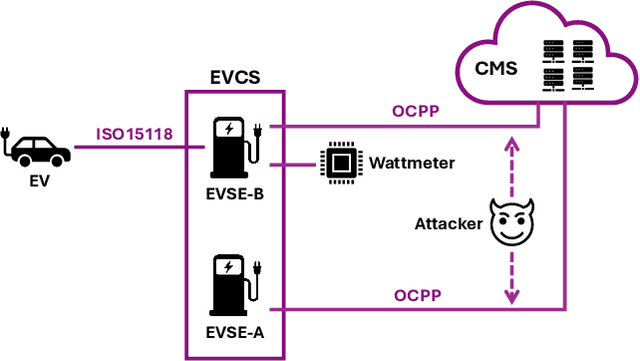
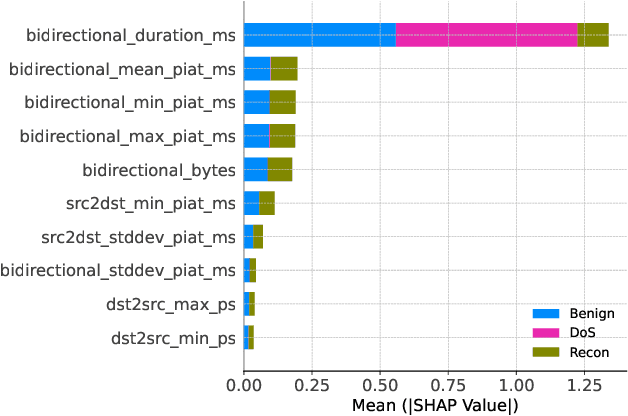
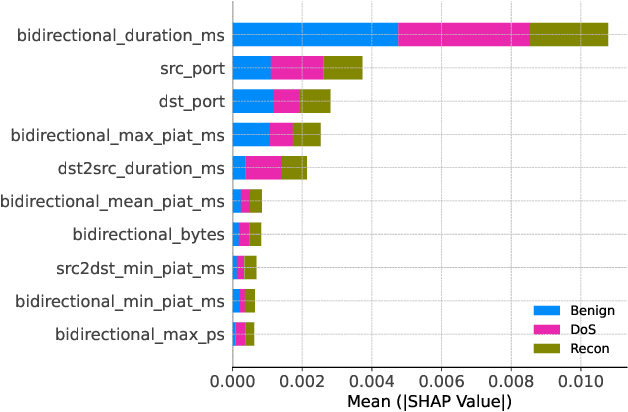
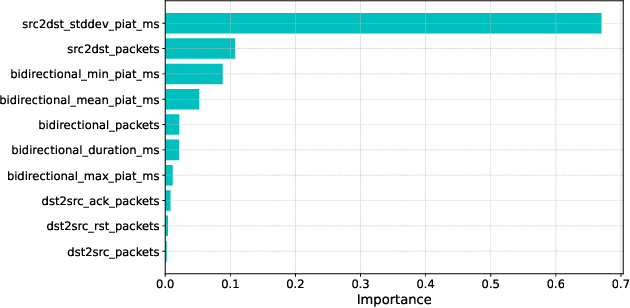
Abstract:With the growing need for real-time processing on IoT devices, optimizing machine learning (ML) models' size, latency, and computational efficiency is essential. This paper investigates a pruning method for anomaly detection in resource-constrained environments, specifically targeting Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure (EVCI). Using the CICEVSE2024 dataset, we trained and optimized three models-Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), and XGBoost-through hyperparameter tuning with Optuna, further refining them using SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP)-based feature selection (FS) and unstructured pruning techniques. The optimized models achieved significant reductions in model size and inference times, with only a marginal impact on their performance. Notably, our findings indicate that, in the context of EVCI, pruning and FS can enhance computational efficiency while retaining critical anomaly detection capabilities.
On TinyML and Cybersecurity: Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Use Case
Apr 29, 2024



Abstract:As technology advances, the use of Machine Learning (ML) in cybersecurity is becoming increasingly crucial to tackle the growing complexity of cyber threats. While traditional ML models can enhance cybersecurity, their high energy and resource demands limit their applications, leading to the emergence of Tiny Machine Learning (TinyML) as a more suitable solution for resource-constrained environments. TinyML is widely applied in areas such as smart homes, healthcare, and industrial automation. TinyML focuses on optimizing ML algorithms for small, low-power devices, enabling intelligent data processing directly on edge devices. This paper provides a comprehensive review of common challenges of TinyML techniques, such as power consumption, limited memory, and computational constraints; it also explores potential solutions to these challenges, such as energy harvesting, computational optimization techniques, and transfer learning for privacy preservation. On the other hand, this paper discusses TinyML's applications in advancing cybersecurity for Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructures (EVCIs) as a representative use case. It presents an experimental case study that enhances cybersecurity in EVCI using TinyML, evaluated against traditional ML in terms of reduced delay and memory usage, with a slight trade-off in accuracy. Additionally, the study includes a practical setup using the ESP32 microcontroller in the PlatformIO environment, which provides a hands-on assessment of TinyML's application in cybersecurity for EVCI.
Deep Learning for High-Impedance Fault Detection: Convolutional Autoencoders
Jun 24, 2021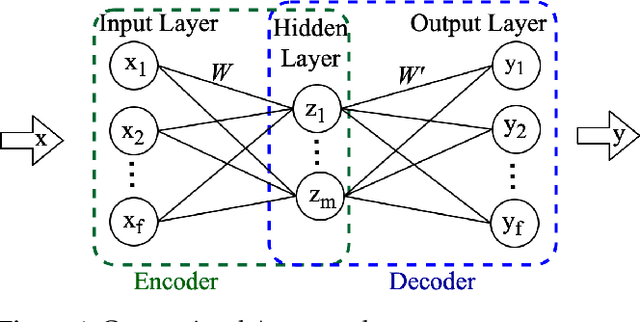
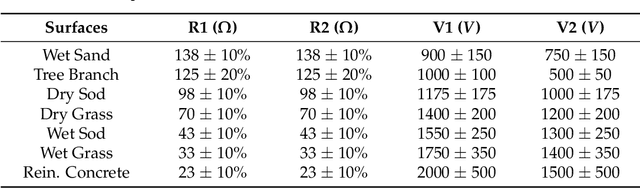
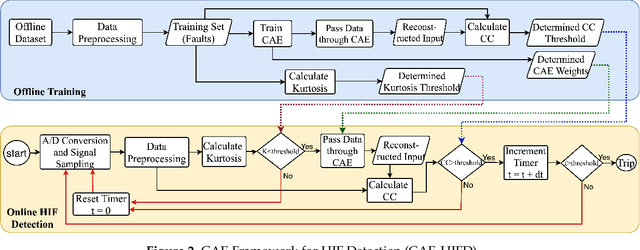
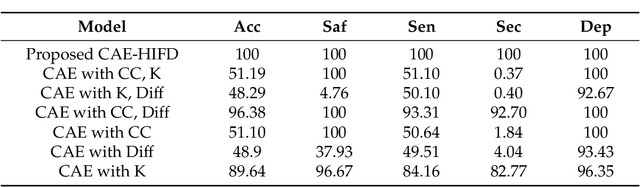
Abstract:High-impedance faults (HIF) are difficult to detect because of their low current amplitude and highly diverse characteristics. In recent years, machine learning (ML) has been gaining popularity in HIF detection because ML techniques learn patterns from data and successfully detect HIFs. However, as these methods are based on supervised learning, they fail to reliably detect any scenario, fault or non-fault, not present in the training data. Consequently, this paper takes advantage of unsupervised learning and proposes a convolutional autoencoder framework for HIF detection (CAE-HIFD). Contrary to the conventional autoencoders that learn from normal behavior, the convolutional autoencoder (CAE) in CAE-HIFD learns only from the HIF signals eliminating the need for presence of diverse non-HIF scenarios in the CAE training. CAE distinguishes HIFs from non-HIF operating conditions by employing cross-correlation. To discriminate HIFs from transient disturbances such as capacitor or load switching, CAE-HIFD uses kurtosis, a statistical measure of the probability distribution shape. The performance evaluation studies conducted using the IEEE 13-node test feeder indicate that the CAE-HIFD reliably detects HIFs, outperforms the state-of-the-art HIF detection techniques, and is robust against noise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge