Chun Zuo
Towards Practical Defect-Focused Automated Code Review
May 23, 2025
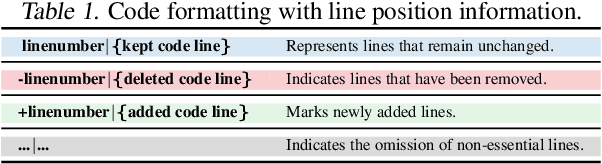
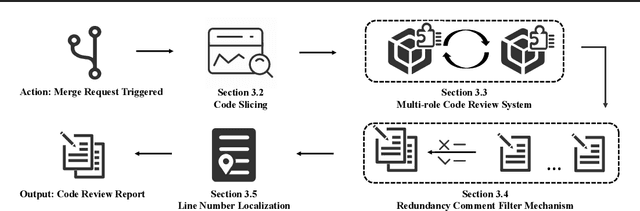
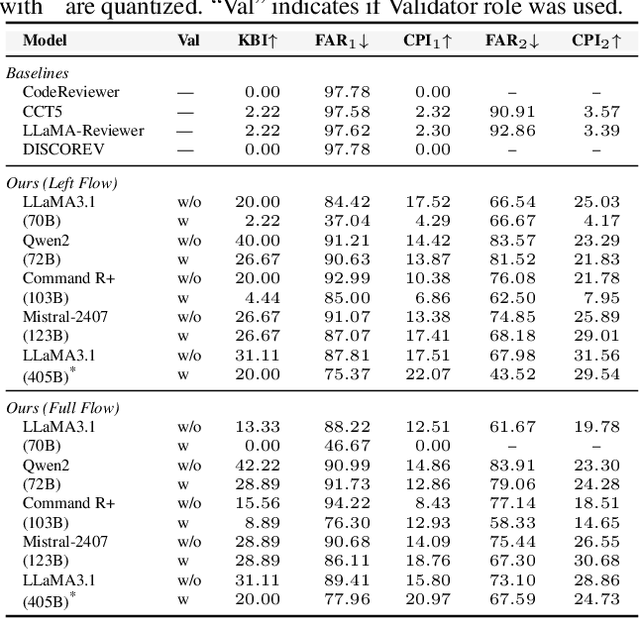
Abstract:The complexity of code reviews has driven efforts to automate review comments, but prior approaches oversimplify this task by treating it as snippet-level code-to-text generation and relying on text similarity metrics like BLEU for evaluation. These methods overlook repository context, real-world merge request evaluation, and defect detection, limiting their practicality. To address these issues, we explore the full automation pipeline within the online recommendation service of a company with nearly 400 million daily active users, analyzing industry-grade C++ codebases comprising hundreds of thousands of lines of code. We identify four key challenges: 1) capturing relevant context, 2) improving key bug inclusion (KBI), 3) reducing false alarm rates (FAR), and 4) integrating human workflows. To tackle these, we propose 1) code slicing algorithms for context extraction, 2) a multi-role LLM framework for KBI, 3) a filtering mechanism for FAR reduction, and 4) a novel prompt design for better human interaction. Our approach, validated on real-world merge requests from historical fault reports, achieves a 2x improvement over standard LLMs and a 10x gain over previous baselines. While the presented results focus on C++, the underlying framework design leverages language-agnostic principles (e.g., AST-based analysis), suggesting potential for broader applicability.
DeepCRCEval: Revisiting the Evaluation of Code Review Comment Generation
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Code review is a vital but demanding aspect of software development, generating significant interest in automating review comments. Traditional evaluation methods for these comments, primarily based on text similarity, face two major challenges: inconsistent reliability of human-authored comments in open-source projects and the weak correlation of text similarity with objectives like enhancing code quality and detecting defects. This study empirically analyzes benchmark comments using a novel set of criteria informed by prior research and developer interviews. We then similarly revisit the evaluation of existing methodologies. Our evaluation framework, DeepCRCEval, integrates human evaluators and Large Language Models (LLMs) for a comprehensive reassessment of current techniques based on the criteria set. Besides, we also introduce an innovative and efficient baseline, LLM-Reviewer, leveraging the few-shot learning capabilities of LLMs for a target-oriented comparison. Our research highlights the limitations of text similarity metrics, finding that less than 10% of benchmark comments are high quality for automation. In contrast, DeepCRCEval effectively distinguishes between high and low-quality comments, proving to be a more reliable evaluation mechanism. Incorporating LLM evaluators into DeepCRCEval significantly boosts efficiency, reducing time and cost by 88.78% and 90.32%, respectively. Furthermore, LLM-Reviewer demonstrates significant potential of focusing task real targets in comment generation.
LLaMA-Reviewer: Advancing Code Review Automation with Large Language Models through Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Sep 05, 2023



Abstract:The automation of code review activities, a long-standing pursuit in software engineering, has been primarily addressed by numerous domain-specific pre-trained models. Despite their success, these models frequently demand extensive resources for pre-training from scratch. In contrast, Large Language Models (LLMs) provide an intriguing alternative, given their remarkable capabilities when supplemented with domain-specific knowledge. However, their potential for automating code review tasks remains largely unexplored. In response to this research gap, we present LLaMA-Reviewer, an innovative framework that leverages the capabilities of LLaMA, a popular LLM, in the realm of code review. Mindful of resource constraints, this framework employs parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods, delivering high performance while using less than 1% of trainable parameters. An extensive evaluation of LLaMA-Reviewer is conducted on two diverse, publicly available datasets. Notably, even with the smallest LLaMA base model consisting of 6.7B parameters and a limited number of tuning epochs, LLaMA-Reviewer equals the performance of existing code-review-focused models. The ablation experiments provide insights into the influence of various fine-tuning process components, including input representation, instruction tuning, and different PEFT methods. To foster continuous progress in this field, the code and all PEFT-weight plugins have been made open-source.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge