Sen Lin
Constraint-Rectified Training for Efficient Chain-of-Thought
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) has significantly enhanced the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), especially when combined with reinforcement learning (RL) based post-training methods. While longer reasoning traces can improve answer quality and unlock abilities such as self-correction, they also incur high inference costs and often introduce redundant steps, known as overthinking. Recent research seeks to develop efficient reasoning strategies that balance reasoning length and accuracy, either through length-aware reward design or prompt-based calibration. However, these heuristic-based approaches may suffer from severe accuracy drop and be very sensitive to hyperparameters. To address these problems, we introduce CRT (Constraint-Rectified Training), a principled post-training framework based on reference-guarded constrained optimization, yielding a more stable and interpretable formulation for efficient reasoning. CRT alternates between minimizing reasoning length and rectifying accuracy only when performance falls below the reference, enabling stable and effective pruning of redundant reasoning. We further extend CRT with a two-stage training scheme that first discovers the shortest reliable reasoning patterns and then refines accuracy under a learnt length budget, preventing the re-emergence of verbose CoT. Our comprehensive evaluation shows that this framework consistently reduces token usage while maintaining answer quality at a robust and reliable level. Further analysis reveals that CRT improves reasoning efficiency not only by shortening responses but also by reducing internal language redundancy, leading to a new evaluation metric. Moreover, CRT-based training naturally yields a sequence of intermediate checkpoints that span a spectrum of explanation lengths while preserving correctness, enabling fine-grained control over reasoning verbosity without retraining.
Reward Modeling for Reinforcement Learning-Based LLM Reasoning: Design, Challenges, and Evaluation
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate transformative potential, yet their reasoning remains inconsistent and unreliable. Reinforcement learning (RL)-based fine-tuning is a key mechanism for improvement, but its effectiveness is fundamentally governed by reward design. Despite its importance, the relationship between reward modeling and core LLM challenges--such as evaluation bias, hallucination, distribution shift, and efficient learning--remains poorly understood. This work argues that reward modeling is not merely an implementation detail but a central architect of reasoning alignment, shaping what models learn, how they generalize, and whether their outputs can be trusted. We introduce Reasoning-Aligned Reinforcement Learning (RARL), a unifying framework that systematizes diverse reward paradigms for multi-step reasoning. Within this framework, we present a taxonomy of reward mechanisms, analyze reward hacking as a pervasive failure mode, and examine how reward signals unify challenges ranging from inference-time scaling to hallucination mitigation. We further critically evaluate existing benchmarks, highlighting vulnerabilities such as data contamination and reward misalignment, and outline directions for more robust evaluation. By integrating fragmented research threads and clarifying the interplay between reward design and fundamental reasoning capabilities, this work provides a foundational roadmap for building reasoning models that are robust, verifiable, and trustworthy.
Mixture-of-Transformers Learn Faster: A Theoretical Study on Classification Problems
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models improve transformer efficiency but lack a unified theoretical explanation, especially when both feed-forward and attention layers are allowed to specialize. To this end, we study the Mixture-of-Transformers (MoT), a tractable theoretical framework in which each transformer block acts as an expert governed by a continuously trained gating network. This design allows us to isolate and study the core learning dynamics of expert specialization and attention alignment. In particular, we develop a three-stage training algorithm with continuous training of the gating network, and show that each transformer expert specializes in a distinct class of tasks and that the gating network accurately routes data samples to the correct expert. Our analysis shows how expert specialization reduces gradient conflicts and makes each subtask strongly convex. We prove that the training drives the expected prediction loss to near zero in $O(\log(\epsilon^{-1}))$ iteration steps, significantly improving over the $O(\epsilon^{-1})$ rate for a single transformer. We further validate our theoretical findings through extensive real-data experiments, demonstrating the practical effectiveness of MoT. Together, these results offer the first unified theoretical account of transformer-level specialization and learning dynamics, providing practical guidance for designing efficient large-scale models.
Rethinking Continual Learning with Progressive Neural Collapse
May 30, 2025Abstract:Continual Learning (CL) seeks to build an agent that can continuously learn a sequence of tasks, where a key challenge, namely Catastrophic Forgetting, persists due to the potential knowledge interference among different tasks. On the other hand, deep neural networks (DNNs) are shown to converge to a terminal state termed Neural Collapse during training, where all class prototypes geometrically form a static simplex equiangular tight frame (ETF). These maximally and equally separated class prototypes make the ETF an ideal target for model learning in CL to mitigate knowledge interference. Thus inspired, several studies have emerged very recently to leverage a fixed global ETF in CL, which however suffers from key drawbacks, such as impracticability and limited performance.To address these challenges and fully unlock the potential of ETF in CL, we propose Progressive Neural Collapse (ProNC), a novel framework that completely removes the need of a fixed global ETF in CL. Specifically, ProNC progressively expands the ETF target in a principled way by adding new class prototypes as vertices for new tasks, ensuring maximal separability across all encountered classes with minimal shifts from the previous ETF. We next develop a new CL framework by plugging ProNC into commonly used CL algorithm designs, where distillation is further leveraged to balance between target shifting for old classes and target aligning for new classes. Extensive experiments show that our approach significantly outperforms related baselines while maintaining superior flexibility, simplicity, and efficiency.
Outlook Towards Deployable Continual Learning for Particle Accelerators
Apr 04, 2025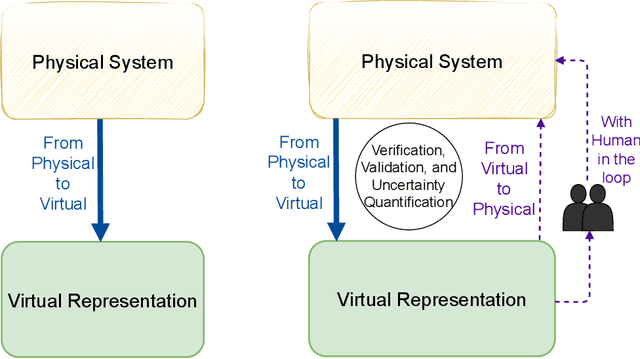
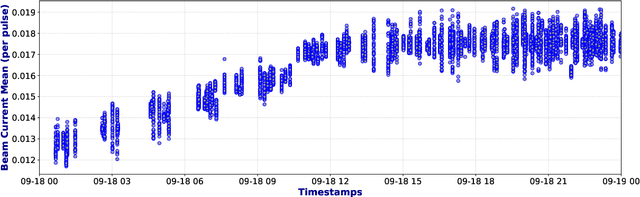
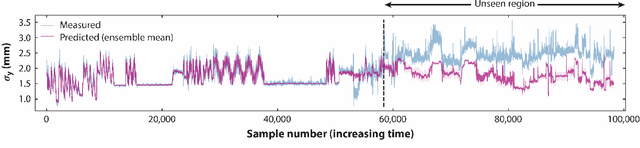
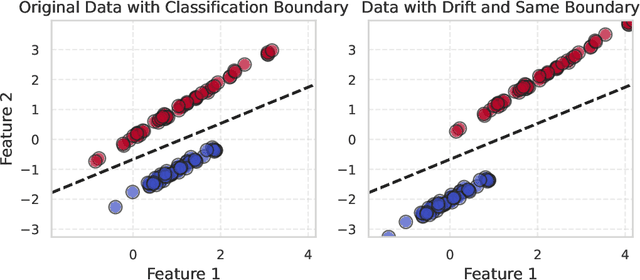
Abstract:Particle Accelerators are high power complex machines. To ensure uninterrupted operation of these machines, thousands of pieces of equipment need to be synchronized, which requires addressing many challenges including design, optimization and control, anomaly detection and machine protection. With recent advancements, Machine Learning (ML) holds promise to assist in more advance prognostics, optimization, and control. While ML based solutions have been developed for several applications in particle accelerators, only few have reached deployment and even fewer to long term usage, due to particle accelerator data distribution drifts caused by changes in both measurable and non-measurable parameters. In this paper, we identify some of the key areas within particle accelerators where continual learning can allow maintenance of ML model performance with distribution drifts. Particularly, we first discuss existing applications of ML in particle accelerators, and their limitations due to distribution drift. Next, we review existing continual learning techniques and investigate their potential applications to address data distribution drifts in accelerators. By identifying the opportunities and challenges in applying continual learning, this paper seeks to open up the new field and inspire more research efforts towards deployable continual learning for particle accelerators.
A Comprehensive Survey of Mixture-of-Experts: Algorithms, Theory, and Applications
Mar 10, 2025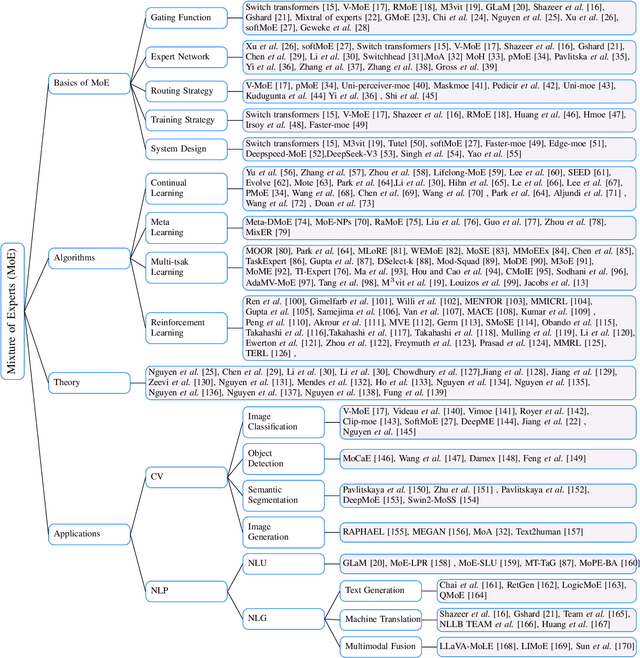
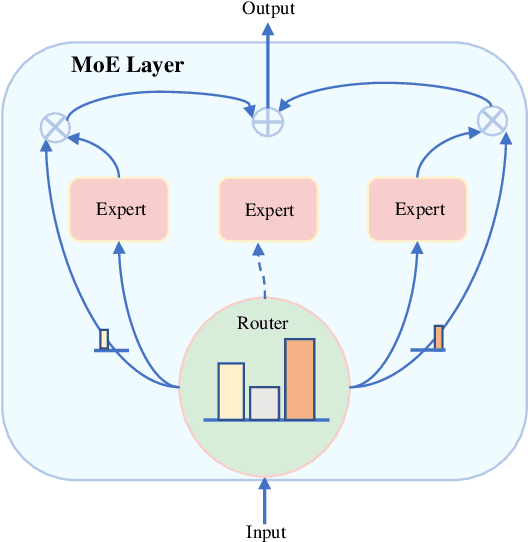
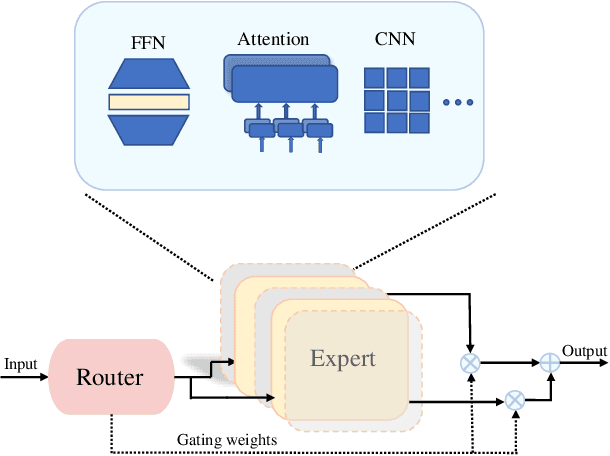
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) has achieved astonishing successes in many domains, especially with the recent breakthroughs in the development of foundational large models. These large models, leveraging their extensive training data, provide versatile solutions for a wide range of downstream tasks. However, as modern datasets become increasingly diverse and complex, the development of large AI models faces two major challenges: (1) the enormous consumption of computational resources and deployment difficulties, and (2) the difficulty in fitting heterogeneous and complex data, which limits the usability of the models. Mixture of Experts (MoE) models has recently attracted much attention in addressing these challenges, by dynamically selecting and activating the most relevant sub-models to process input data. It has been shown that MoEs can significantly improve model performance and efficiency with fewer resources, particularly excelling in handling large-scale, multimodal data. Given the tremendous potential MoE has demonstrated across various domains, it is urgent to provide a comprehensive summary of recent advancements of MoEs in many important fields. Existing surveys on MoE have their limitations, e.g., being outdated or lacking discussion on certain key areas, and we aim to address these gaps. In this paper, we first introduce the basic design of MoE, including gating functions, expert networks, routing mechanisms, training strategies, and system design. We then explore the algorithm design of MoE in important machine learning paradigms such as continual learning, meta-learning, multi-task learning, and reinforcement learning. Additionally, we summarize theoretical studies aimed at understanding MoE and review its applications in computer vision and natural language processing. Finally, we discuss promising future research directions.
Marvel: Accelerating Safe Online Reinforcement Learning with Finetuned Offline Policy
Dec 05, 2024
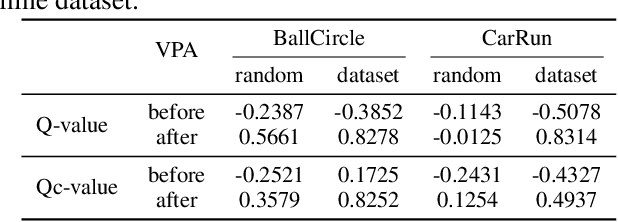

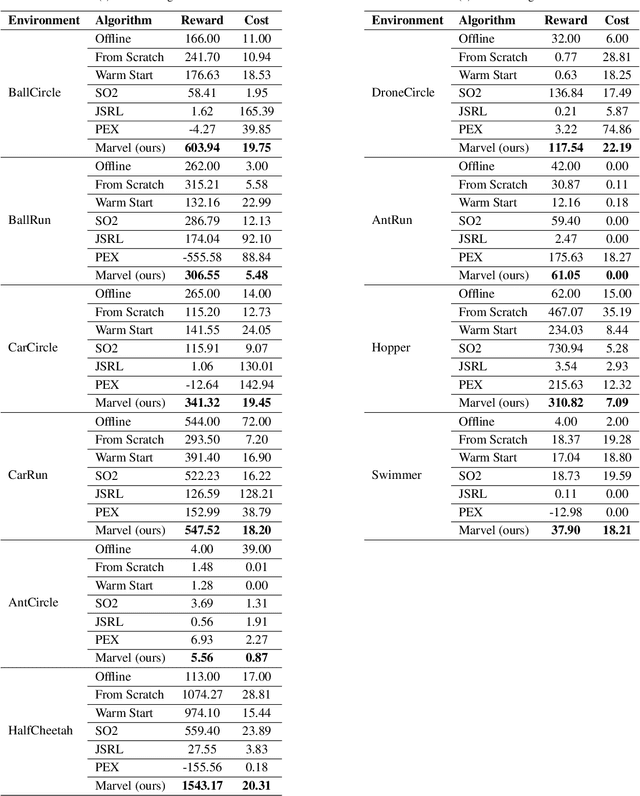
Abstract:The high costs and risks involved in extensive environment interactions hinder the practical application of current online safe reinforcement learning (RL) methods. While offline safe RL addresses this by learning policies from static datasets, the performance therein is usually limited due to reliance on data quality and challenges with out-of-distribution (OOD) actions. Inspired by recent successes in offline-to-online (O2O) RL, it is crucial to explore whether offline safe RL can be leveraged to facilitate faster and safer online policy learning, a direction that has yet to be fully investigated. To fill this gap, we first demonstrate that naively applying existing O2O algorithms from standard RL would not work well in the safe RL setting due to two unique challenges: \emph{erroneous Q-estimations}, resulted from offline-online objective mismatch and offline cost sparsity, and \emph{Lagrangian mismatch}, resulted from difficulties in aligning Lagrange multipliers between offline and online policies. To address these challenges, we introduce \textbf{Marvel}, a novel framework for O2O safe RL, comprising two key components that work in concert: \emph{Value Pre-Alignment} to align the Q-functions with the underlying truth before online learning, and \emph{Adaptive PID Control} to effectively adjust the Lagrange multipliers during online finetuning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Marvel significantly outperforms existing baselines in both reward maximization and safety constraint satisfaction. By introducing the first policy-finetuning based framework for O2O safe RL, which is compatible with many offline and online safe RL methods, our work has the great potential to advance the field towards more efficient and practical safe RL solutions.
Unlearning Trojans in Large Language Models: A Comparison Between Natural Language and Source Code
Aug 22, 2024Abstract:This work investigates the application of Machine Unlearning (MU) for mitigating the impact of trojans embedded in conventional large language models of natural language (Text-LLMs) and large language models of code (Code-LLMs) We propose a novel unlearning approach, LYA, that leverages both gradient ascent and elastic weight consolidation, a Fisher Information Matrix (FIM) based regularization technique, to unlearn trojans from poisoned models. We compare the effectiveness of LYA against conventional techniques like fine-tuning, retraining, and vanilla gradient ascent. The subject models we investigate are BERT and CodeBERT, for sentiment analysis and code defect detection tasks, respectively. Our findings demonstrate that the combination of gradient ascent and FIM-based regularization, as done in LYA, outperforms existing methods in removing the trojan's influence from the poisoned model, while preserving its original functionality. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that compares and contrasts MU of trojans in LLMs, in the NL and Coding domain.
Theory on Mixture-of-Experts in Continual Learning
Jun 24, 2024



Abstract:Continual learning (CL) has garnered significant attention because of its ability to adapt to new tasks that arrive over time. Catastrophic forgetting (of old tasks) has been identified as a major issue in CL, as the model adapts to new tasks. The Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model has recently been shown to effectively mitigate catastrophic forgetting in CL, by employing a gating network to sparsify and distribute diverse tasks among multiple experts. However, there is a lack of theoretical analysis of MoE and its impact on the learning performance in CL. This paper provides the first theoretical results to characterize the impact of MoE in CL via the lens of overparameterized linear regression tasks. We establish the benefit of MoE over a single expert by proving that the MoE model can diversify its experts to specialize in different tasks, while its router learns to select the right expert for each task and balance the loads across all experts. Our study further suggests an intriguing fact that the MoE in CL needs to terminate the update of the gating network after sufficient training rounds to attain system convergence, which is not needed in the existing MoE studies that do not consider the continual task arrival. Furthermore, we provide explicit expressions for the expected forgetting and overall generalization error to characterize the benefit of MoE in the learning performance in CL. Interestingly, adding more experts requires additional rounds before convergence, which may not enhance the learning performance. Finally, we conduct experiments on both synthetic and real datasets to extend these insights from linear models to deep neural networks (DNNs), which also shed light on the practical algorithm design for MoE in CL.
OLLIE: Imitation Learning from Offline Pretraining to Online Finetuning
May 29, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we study offline-to-online Imitation Learning (IL) that pretrains an imitation policy from static demonstration data, followed by fast finetuning with minimal environmental interaction. We find the na\"ive combination of existing offline IL and online IL methods tends to behave poorly in this context, because the initial discriminator (often used in online IL) operates randomly and discordantly against the policy initialization, leading to misguided policy optimization and $\textit{unlearning}$ of pretraining knowledge. To overcome this challenge, we propose a principled offline-to-online IL method, named $\texttt{OLLIE}$, that simultaneously learns a near-expert policy initialization along with an $\textit{aligned discriminator initialization}$, which can be seamlessly integrated into online IL, achieving smooth and fast finetuning. Empirically, $\texttt{OLLIE}$ consistently and significantly outperforms the baseline methods in $\textbf{20}$ challenging tasks, from continuous control to vision-based domains, in terms of performance, demonstration efficiency, and convergence speed. This work may serve as a foundation for further exploration of pretraining and finetuning in the context of IL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge