Ju Ren
Context Learning for Multi-Agent Discussion
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Multi-Agent Discussion (MAD) has garnered increasing attention very recently, where multiple LLM instances collaboratively solve problems via structured discussion. However, we find that current MAD methods easily suffer from discussion inconsistency, LLMs fail to reach a coherent solution, due to the misalignment between their individual contexts.In this paper, we introduce a multi-LLM context learning method (M2CL) that learns a context generator for each agent, capable of dynamically generating context instructions per discussion round via automatic information organization and refinement. Specifically, inspired by our theoretical insights on the context instruction, M2CL train the generators to control context coherence and output discrepancies via a carefully crafted self-adaptive mechanism.It enables LLMs to avoid premature convergence on majority noise and progressively reach the correct consensus. We evaluate M2CL on challenging tasks, including academic reasoning, embodied tasks, and mobile control. The results show that the performance of M2CL significantly surpasses existing methods by 20%--50%, while enjoying favorable transferability and computational efficiency.
Less is More: Clustered Cross-Covariance Control for Offline RL
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:A fundamental challenge in offline reinforcement learning is distributional shift. Scarce data or datasets dominated by out-of-distribution (OOD) areas exacerbate this issue. Our theoretical analysis and experiments show that the standard squared error objective induces a harmful TD cross covariance. This effect amplifies in OOD areas, biasing optimization and degrading policy learning. To counteract this mechanism, we develop two complementary strategies: partitioned buffer sampling that restricts updates to localized replay partitions, attenuates irregular covariance effects, and aligns update directions, yielding a scheme that is easy to integrate with existing implementations, namely Clustered Cross-Covariance Control for TD (C^4). We also introduce an explicit gradient-based corrective penalty that cancels the covariance induced bias within each update. We prove that buffer partitioning preserves the lower bound property of the maximization objective, and that these constraints mitigate excessive conservatism in extreme OOD areas without altering the core behavior of policy constrained offline reinforcement learning. Empirically, our method showcases higher stability and up to 30% improvement in returns over prior methods, especially with small datasets and splits that emphasize OOD areas.
AgentProg: Empowering Long-Horizon GUI Agents with Program-Guided Context Management
Dec 11, 2025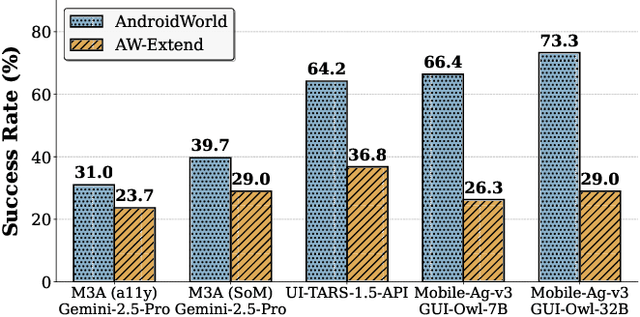

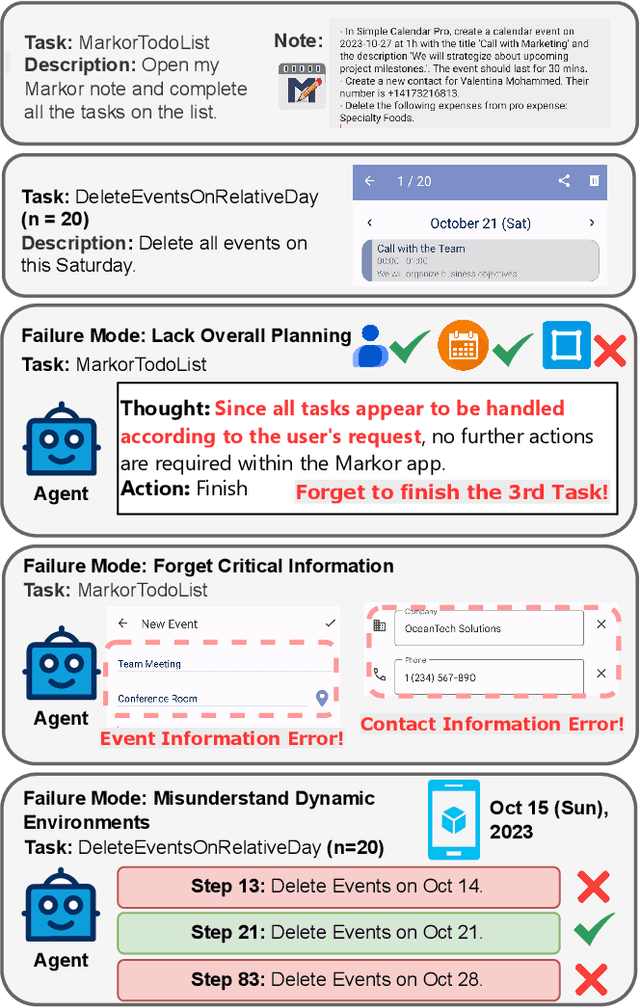

Abstract:The rapid development of mobile GUI agents has stimulated growing research interest in long-horizon task automation. However, building agents for these tasks faces a critical bottleneck: the reliance on ever-expanding interaction history incurs substantial context overhead. Existing context management and compression techniques often fail to preserve vital semantic information, leading to degraded task performance. We propose AgentProg, a program-guided approach for agent context management that reframes the interaction history as a program with variables and control flow. By organizing information according to the structure of program, this structure provides a principled mechanism to determine which information should be retained and which can be discarded. We further integrate a global belief state mechanism inspired by Belief MDP framework to handle partial observability and adapt to unexpected environmental changes. Experiments on AndroidWorld and our extended long-horizon task suite demonstrate that AgentProg has achieved the state-of-the-art success rates on these benchmarks. More importantly, it maintains robust performance on long-horizon tasks while baseline methods experience catastrophic degradation. Our system is open-sourced at https://github.com/MobileLLM/AgentProg.
Wideband RF Radiance Field Modeling Using Frequency-embedded 3D Gaussian Splatting
May 27, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an innovative frequency-embedded 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) algorithm for wideband radio-frequency (RF) radiance field modeling, offering an advancement over the existing works limited to single-frequency modeling. Grounded in fundamental physics, we uncover the complex relationship between EM wave propagation behaviors and RF frequencies. Inspired by this, we design an EM feature network with attenuation and radiance modules to learn the complex relationships between RF frequencies and the key properties of each 3D Gaussian, specifically the attenuation factor and RF signal intensity. By training the frequency-embedded 3DGS model, we can efficiently reconstruct RF radiance fields at arbitrary unknown frequencies within a given 3D environment. Finally, we propose a large-scale power angular spectrum (PAS) dataset containing 50000 samples ranging from 1 to 100 GHz in 6 indoor environments, and conduct extensive experiments to verify the effectiveness of our method. Our approach achieves an average Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) up to 0.72, and a significant improvement up to 17.8% compared to the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods trained on individual test frequencies. Additionally, our method achieves an SSIM of 0.70 without prior training on these frequencies, which represents only a 2.8% performance drop compared to models trained with full PAS data. This demonstrates our model's capability to estimate PAS at unknown frequencies. For related code and datasets, please refer to https://github.com/sim-2-real/Wideband3DGS.
ConCISE: Confidence-guided Compression in Step-by-step Efficient Reasoning
May 08, 2025Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) perform strongly in complex reasoning tasks via Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting, but often suffer from verbose outputs caused by redundant content, increasing computational overhead, and degrading user experience. Existing compression methods either operate post-hoc pruning, risking disruption to reasoning coherence, or rely on sampling-based selection, which fails to intervene effectively during generation. In this work, we introduce a confidence-guided perspective to explain the emergence of redundant reflection in LRMs, identifying two key patterns: Confidence Deficit, where the model reconsiders correct steps due to low internal confidence, and Termination Delay, where reasoning continues even after reaching a confident answer. Based on this analysis, we propose ConCISE (Confidence-guided Compression In Step-by-step Efficient Reasoning), a framework that simplifies reasoning chains by reinforcing the model's confidence during inference, thus preventing the generation of redundant reflection steps. It integrates Confidence Injection to stabilize intermediate steps and Early Stopping to terminate reasoning when confidence is sufficient. Extensive experiments demonstrate that fine-tuning LRMs on ConCISE-generated data yields significantly shorter outputs, reducing length by up to approximately 50% under SimPO, while maintaining high task accuracy. ConCISE consistently outperforms existing baselines across multiple reasoning benchmarks.
Scaling Up On-Device LLMs via Active-Weight Swapping Between DRAM and Flash
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly being deployed on mobile devices, but the limited DRAM capacity constrains the deployable model size. This paper introduces ActiveFlow, the first LLM inference framework that can achieve adaptive DRAM usage for modern LLMs (not ReLU-based), enabling the scaling up of deployable model sizes. The framework is based on the novel concept of active weight DRAM-flash swapping and incorporates three novel techniques: (1) Cross-layer active weights preloading. It uses the activations from the current layer to predict the active weights of several subsequent layers, enabling computation and data loading to overlap, as well as facilitating large I/O transfers. (2) Sparsity-aware self-distillation. It adjusts the active weights to align with the dense-model output distribution, compensating for approximations introduced by contextual sparsity. (3) Active weight DRAM-flash swapping pipeline. It orchestrates the DRAM space allocation among the hot weight cache, preloaded active weights, and computation-involved weights based on available memory. Results show ActiveFlow achieves the performance-cost Pareto frontier compared to existing efficiency optimization methods.
AugFL: Augmenting Federated Learning with Pretrained Models
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has garnered widespread interest in recent years. However, owing to strict privacy policies or limited storage capacities of training participants such as IoT devices, its effective deployment is often impeded by the scarcity of training data in practical decentralized learning environments. In this paper, we study enhancing FL with the aid of (large) pre-trained models (PMs), that encapsulate wealthy general/domain-agnostic knowledge, to alleviate the data requirement in conducting FL from scratch. Specifically, we consider a networked FL system formed by a central server and distributed clients. First, we formulate the PM-aided personalized FL as a regularization-based federated meta-learning problem, where clients join forces to learn a meta-model with knowledge transferred from a private PM stored at the server. Then, we develop an inexact-ADMM-based algorithm, AugFL, to optimize the problem with no need to expose the PM or incur additional computational costs to local clients. Further, we establish theoretical guarantees for AugFL in terms of communication complexity, adaptation performance, and the benefit of knowledge transfer in general non-convex cases. Extensive experiments corroborate the efficacy and superiority of AugFL over existing baselines.
LeMo: Enabling LEss Token Involvement for MOre Context Fine-tuning
Jan 15, 2025



Abstract:The escalating demand for long-context applications has intensified the necessity of extending the LLM context windows. Despite recent fine-tuning approaches successfully expanding context lengths, their high memory footprints, especially for activations, present a critical practical limitation. Current parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods prioritize reducing parameter update overhead over addressing activation memory constraints. Similarly, existing sparsity mechanisms improve computational efficiency but overlook activation memory optimization due to the phenomenon of Shadowy Activation. In this paper, we propose LeMo, the first LLM fine-tuning system that explores and exploits a new token-level sparsity mechanism inherent in long-context scenarios, termed Contextual Token Sparsity. LeMo minimizes redundant token involvement by assessing the informativeness of token embeddings while preserving model accuracy. Specifically, LeMo introduces three key techniques: (1) Token Elimination, dynamically identifying and excluding redundant tokens across varying inputs and layers. (2) Pattern Prediction, utilizing well-trained predictors to approximate token sparsity patterns with minimal overhead. (3) Kernel Optimization, employing permutation-free and segment-based strategies to boost system performance. We implement LeMo as an end-to-end fine-tuning system compatible with various LLM architectures and other optimization techniques. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that LeMo reduces memory consumption by up to 1.93x and achieves up to 1.36x speedups, outperforming state-of-the-art fine-tuning systems.
Enabling Cardiac Monitoring using In-ear Ballistocardiogram on COTS Wireless Earbuds
Jan 12, 2025Abstract:The human ear offers a unique opportunity for cardiac monitoring due to its physiological and practical advantages. However, existing earable solutions require additional hardware and complex processing, posing challenges for commercial True Wireless Stereo (TWS) earbuds which are limited by their form factor and resources. In this paper, we propose TWSCardio, a novel system that repurposes the IMU sensors in TWS earbuds for cardiac monitoring. Our key finding is that these sensors can capture in-ear ballistocardiogram (BCG) signals. TWSCardio reuses the unstable Bluetooth channel to stream the IMU data to a smartphone for BCG processing. It incorporates a signal enhancement framework to address issues related to missing data and low sampling rate, while mitigating motion artifacts by fusing multi-axis information. Furthermore, it employs a region-focused signal reconstruction method to translate the multi-axis in-ear BCG signals into fine-grained seismocardiogram (SCG) signals. We have implemented TWSCardio as an efficient real-time app. Our experiments on 100 subjects verify that TWSCardio can accurately reconstruct cardiac signals while showing resilience to motion artifacts, missing data, and low sampling rates. Our case studies further demonstrate that TWSCardio can support diverse cardiac monitoring applications.
MobiFuse: A High-Precision On-device Depth Perception System with Multi-Data Fusion
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:We present MobiFuse, a high-precision depth perception system on mobile devices that combines dual RGB and Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras. To achieve this, we leverage physical principles from various environmental factors to propose the Depth Error Indication (DEI) modality, characterizing the depth error of ToF and stereo-matching. Furthermore, we employ a progressive fusion strategy, merging geometric features from ToF and stereo depth maps with depth error features from the DEI modality to create precise depth maps. Additionally, we create a new ToF-Stereo depth dataset, RealToF, to train and validate our model. Our experiments demonstrate that MobiFuse excels over baselines by significantly reducing depth measurement errors by up to 77.7%. It also showcases strong generalization across diverse datasets and proves effectiveness in two downstream tasks: 3D reconstruction and 3D segmentation. The demo video of MobiFuse in real-life scenarios is available at the de-identified YouTube link(https://youtu.be/jy-Sp7T1LVs).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge