Xinyi Li
Neuromem: A Granular Decomposition of the Streaming Lifecycle in External Memory for LLMs
Feb 15, 2026Abstract:Most evaluations of External Memory Module assume a static setting: memory is built offline and queried at a fixed state. In practice, memory is streaming: new facts arrive continuously, insertions interleave with retrievals, and the memory state evolves while the model is serving queries. In this regime, accuracy and cost are governed by the full memory lifecycle, which encompasses the ingestion, maintenance, retrieval, and integration of information into generation. We present Neuromem, a scalable testbed that benchmarks External Memory Modules under an interleaved insertion-and-retrieval protocol and decomposes its lifecycle into five dimensions including memory data structure, normalization strategy, consolidation policy, query formulation strategy, and context integration mechanism. Using three representative datasets LOCOMO, LONGMEMEVAL, and MEMORYAGENTBENCH, Neuromem evaluates interchangeable variants within a shared serving stack, reporting token-level F1 and insertion/retrieval latency. Overall, we observe that performance typically degrades as memory grows across rounds, and time-related queries remain the most challenging category. The memory data structure largely determines the attainable quality frontier, while aggressive compression and generative integration mechanisms mostly shift cost between insertion and retrieval with limited accuracy gain.
Context Learning for Multi-Agent Discussion
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Multi-Agent Discussion (MAD) has garnered increasing attention very recently, where multiple LLM instances collaboratively solve problems via structured discussion. However, we find that current MAD methods easily suffer from discussion inconsistency, LLMs fail to reach a coherent solution, due to the misalignment between their individual contexts.In this paper, we introduce a multi-LLM context learning method (M2CL) that learns a context generator for each agent, capable of dynamically generating context instructions per discussion round via automatic information organization and refinement. Specifically, inspired by our theoretical insights on the context instruction, M2CL train the generators to control context coherence and output discrepancies via a carefully crafted self-adaptive mechanism.It enables LLMs to avoid premature convergence on majority noise and progressively reach the correct consensus. We evaluate M2CL on challenging tasks, including academic reasoning, embodied tasks, and mobile control. The results show that the performance of M2CL significantly surpasses existing methods by 20%--50%, while enjoying favorable transferability and computational efficiency.
CogRail: Benchmarking VLMs in Cognitive Intrusion Perception for Intelligent Railway Transportation Systems
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Accurate and early perception of potential intrusion targets is essential for ensuring the safety of railway transportation systems. However, most existing systems focus narrowly on object classification within fixed visual scopes and apply rule-based heuristics to determine intrusion status, often overlooking targets that pose latent intrusion risks. Anticipating such risks requires the cognition of spatial context and temporal dynamics for the object of interest (OOI), which presents challenges for conventional visual models. To facilitate deep intrusion perception, we introduce a novel benchmark, CogRail, which integrates curated open-source datasets with cognitively driven question-answer annotations to support spatio-temporal reasoning and prediction. Building upon this benchmark, we conduct a systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art visual-language models (VLMs) using multimodal prompts to identify their strengths and limitations in this domain. Furthermore, we fine-tune VLMs for better performance and propose a joint fine-tuning framework that integrates three core tasks, position perception, movement prediction, and threat analysis, facilitating effective adaptation of general-purpose foundation models into specialized models tailored for cognitive intrusion perception. Extensive experiments reveal that current large-scale multimodal models struggle with the complex spatial-temporal reasoning required by the cognitive intrusion perception task, underscoring the limitations of existing foundation models in this safety-critical domain. In contrast, our proposed joint fine-tuning framework significantly enhances model performance by enabling targeted adaptation to domain-specific reasoning demands, highlighting the advantages of structured multi-task learning in improving both accuracy and interpretability. Code will be available at https://github.com/Hub-Tian/CogRail.
D^3ETOR: Debate-Enhanced Pseudo Labeling and Frequency-Aware Progressive Debiasing for Weakly-Supervised Camouflaged Object Detection with Scribble Annotations
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Weakly-Supervised Camouflaged Object Detection (WSCOD) aims to locate and segment objects that are visually concealed within their surrounding scenes, relying solely on sparse supervision such as scribble annotations. Despite recent progress, existing WSCOD methods still lag far behind fully supervised ones due to two major limitations: (1) the pseudo masks generated by general-purpose segmentation models (e.g., SAM) and filtered via rules are often unreliable, as these models lack the task-specific semantic understanding required for effective pseudo labeling in COD; and (2) the neglect of inherent annotation bias in scribbles, which hinders the model from capturing the global structure of camouflaged objects. To overcome these challenges, we propose ${D}^{3}$ETOR, a two-stage WSCOD framework consisting of Debate-Enhanced Pseudo Labeling and Frequency-Aware Progressive Debiasing. In the first stage, we introduce an adaptive entropy-driven point sampling method and a multi-agent debate mechanism to enhance the capability of SAM for COD, improving the interpretability and precision of pseudo masks. In the second stage, we design FADeNet, which progressively fuses multi-level frequency-aware features to balance global semantic understanding with local detail modeling, while dynamically reweighting supervision strength across regions to alleviate scribble bias. By jointly exploiting the supervision signals from both the pseudo masks and scribble semantics, ${D}^{3}$ETOR significantly narrows the gap between weakly and fully supervised COD, achieving state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks.
${D}^{3}${ETOR}: ${D}$ebate-Enhanced Pseudo Labeling and Frequency-Aware Progressive ${D}$ebiasing for Weakly-Supervised Camouflaged Object ${D}$etection with Scribble Annotations
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Weakly-Supervised Camouflaged Object Detection (WSCOD) aims to locate and segment objects that are visually concealed within their surrounding scenes, relying solely on sparse supervision such as scribble annotations. Despite recent progress, existing WSCOD methods still lag far behind fully supervised ones due to two major limitations: (1) the pseudo masks generated by general-purpose segmentation models (e.g., SAM) and filtered via rules are often unreliable, as these models lack the task-specific semantic understanding required for effective pseudo labeling in COD; and (2) the neglect of inherent annotation bias in scribbles, which hinders the model from capturing the global structure of camouflaged objects. To overcome these challenges, we propose ${D}^{3}$ETOR, a two-stage WSCOD framework consisting of Debate-Enhanced Pseudo Labeling and Frequency-Aware Progressive Debiasing. In the first stage, we introduce an adaptive entropy-driven point sampling method and a multi-agent debate mechanism to enhance the capability of SAM for COD, improving the interpretability and precision of pseudo masks. In the second stage, we design FADeNet, which progressively fuses multi-level frequency-aware features to balance global semantic understanding with local detail modeling, while dynamically reweighting supervision strength across regions to alleviate scribble bias. By jointly exploiting the supervision signals from both the pseudo masks and scribble semantics, ${D}^{3}$ETOR significantly narrows the gap between weakly and fully supervised COD, achieving state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks.
Ghost in the Transformer: Tracing LLM Lineage with SVD-Fingerprint
Nov 17, 2025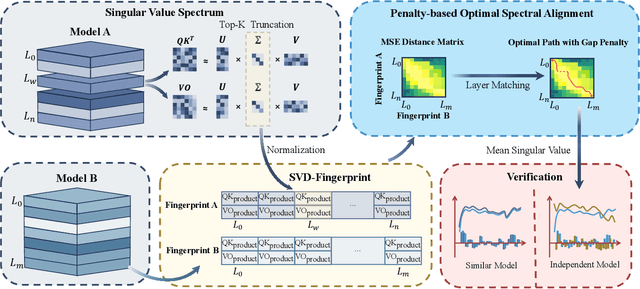
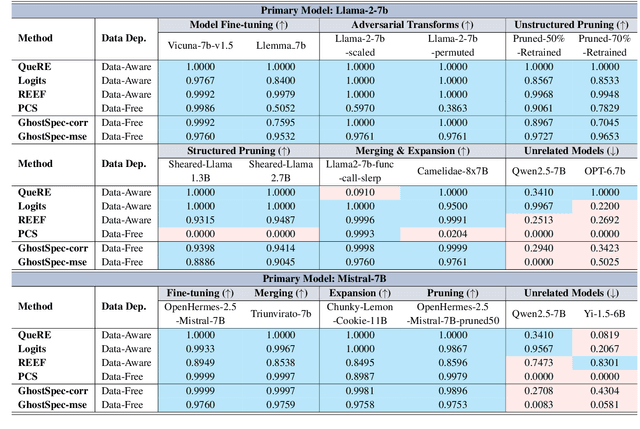
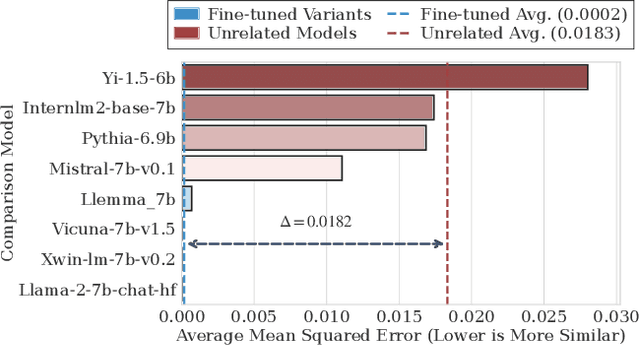
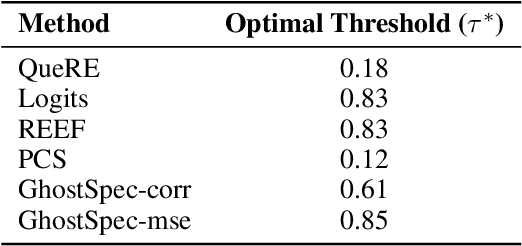
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have rapidly advanced and are widely adopted across diverse fields. Due to the substantial computational cost and data requirements of training from scratch, many developers choose to fine-tune or modify existing open-source models. While most adhere to open-source licenses, some falsely claim original training despite clear derivation from public models. This raises pressing concerns about intellectual property protection and highlights the need for reliable methods to verify model provenance. In this paper, we propose GhostSpec, a lightweight yet effective method for verifying LLM lineage without access to training data or modification of model behavior. Our approach constructs compact and robust fingerprints by applying singular value decomposition (SVD) to invariant products of internal attention weight matrices, effectively capturing the structural identity of a model. Unlike watermarking or output-based methods, GhostSpec is fully data-free, non-invasive, and computationally efficient. It demonstrates strong robustness to sequential fine-tuning, pruning, block expansion, and even adversarial transformations. Extensive experiments show that GhostSpec can reliably trace the lineage of transformed models with minimal overhead. By offering a practical solution for model verification and reuse tracking, our method contributes to the protection of intellectual property and fosters a transparent, trustworthy ecosystem for large-scale language models.
GUIDES: Guidance Using Instructor-Distilled Embeddings for Pre-trained Robot Policy Enhancement
Nov 05, 2025Abstract:Pre-trained robot policies serve as the foundation of many validated robotic systems, which encapsulate extensive embodied knowledge. However, they often lack the semantic awareness characteristic of foundation models, and replacing them entirely is impractical in many situations due to high costs and the loss of accumulated knowledge. To address this gap, we introduce GUIDES, a lightweight framework that augments pre-trained policies with semantic guidance from foundation models without requiring architectural redesign. GUIDES employs a fine-tuned vision-language model (Instructor) to generate contextual instructions, which are encoded by an auxiliary module into guidance embeddings. These embeddings are injected into the policy's latent space, allowing the legacy model to adapt to this new semantic input through brief, targeted fine-tuning. For inference-time robustness, a large language model-based Reflector monitors the Instructor's confidence and, when confidence is low, initiates a reasoning loop that analyzes execution history, retrieves relevant examples, and augments the VLM's context to refine subsequent actions. Extensive validation in the RoboCasa simulation environment across diverse policy architectures shows consistent and substantial improvements in task success rates. Real-world deployment on a UR5 robot further demonstrates that GUIDES enhances motion precision for critical sub-tasks such as grasping. Overall, GUIDES offers a practical and resource-efficient pathway to upgrade, rather than replace, validated robot policies.
Clone Deterministic 3D Worlds with Geometrically-Regularized World Models
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:A world model is an internal model that simulates how the world evolves. Given past observations and actions, it predicts the future of both the embodied agent and its environment. Accurate world models are essential for enabling agents to think, plan, and reason effectively in complex, dynamic settings. Despite rapid progress, current world models remain brittle and degrade over long horizons. We argue that a central cause is representation quality: exteroceptive inputs (e.g., images) are high-dimensional, and lossy or entangled latents make dynamics learning unnecessarily hard. We therefore ask whether improving representation learning alone can substantially improve world-model performance. In this work, we take a step toward building a truly accurate world model by addressing a fundamental yet open problem: constructing a model that can fully clone and overfit to a deterministic 3D world. We propose Geometrically-Regularized World Models (GRWM), which enforces that consecutive points along a natural sensory trajectory remain close in latent representation space. This approach yields significantly improved latent representations that align closely with the true topology of the environment. GRWM is plug-and-play, requires only minimal architectural modification, scales with trajectory length, and is compatible with diverse latent generative backbones. Across deterministic 3D settings and long-horizon prediction tasks, GRWM significantly increases rollout fidelity and stability. Analyses show that its benefits stem from learning a latent manifold with superior geometric structure. These findings support a clear takeaway: improving representation learning is a direct and useful path to robust world models, delivering reliable long-horizon predictions without enlarging the dynamics module.
TITAN: A Trajectory-Informed Technique for Adaptive Parameter Freezing in Large-Scale VQE
Sep 18, 2025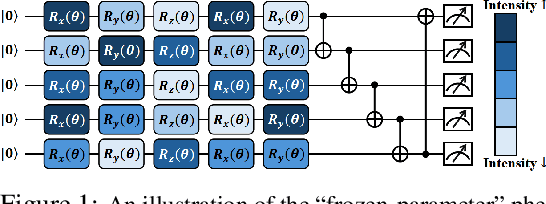
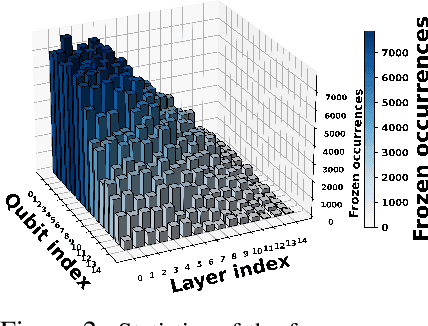
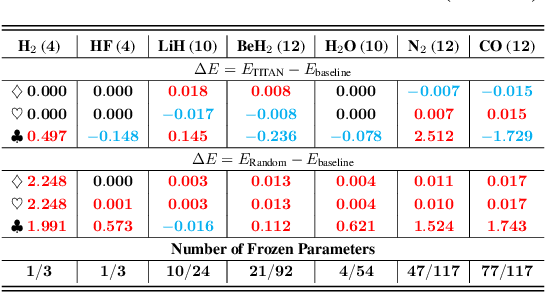
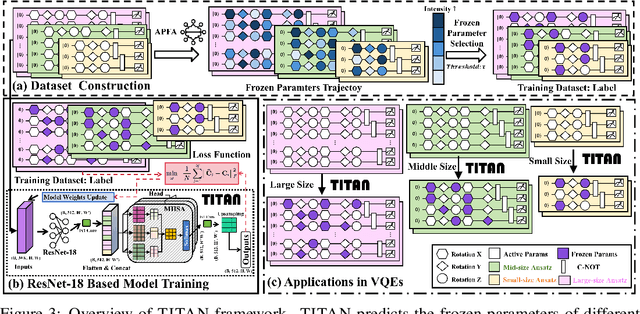
Abstract:Variational quantum Eigensolver (VQE) is a leading candidate for harnessing quantum computers to advance quantum chemistry and materials simulations, yet its training efficiency deteriorates rapidly for large Hamiltonians. Two issues underlie this bottleneck: (i) the no-cloning theorem imposes a linear growth in circuit evaluations with the number of parameters per gradient step; and (ii) deeper circuits encounter barren plateaus (BPs), leading to exponentially increasing measurement overheads. To address these challenges, here we propose a deep learning framework, dubbed Titan, which identifies and freezes inactive parameters of a given ansatze at initialization for a specific class of Hamiltonians, reducing the optimization overhead without sacrificing accuracy. The motivation of Titan starts with our empirical findings that a subset of parameters consistently has a negligible influence on training dynamics. Its design combines a theoretically grounded data construction strategy, ensuring each training example is informative and BP-resilient, with an adaptive neural architecture that generalizes across ansatze of varying sizes. Across benchmark transverse-field Ising models, Heisenberg models, and multiple molecule systems up to 30 qubits, Titan achieves up to 3 times faster convergence and 40% to 60% fewer circuit evaluations than state-of-the-art baselines, while matching or surpassing their estimation accuracy. By proactively trimming parameter space, Titan lowers hardware demands and offers a scalable path toward utilizing VQE to advance practical quantum chemistry and materials science.
Marine Chlorophyll Prediction and Driver Analysis based on LSTM-RF Hybrid Models
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Marine chlorophyll concentration is an important indicator of ecosystem health and carbon cycle strength, and its accurate prediction is crucial for red tide warning and ecological response. In this paper, we propose a LSTM-RF hybrid model that combines the advantages of LSTM and RF, which solves the deficiencies of a single model in time-series modelling and nonlinear feature portrayal. Trained with multi-source ocean data(temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen, etc.), the experimental results show that the LSTM-RF model has an R^2 of 0.5386, an MSE of 0.005806, and an MAE of 0.057147 on the test set, which is significantly better than using LSTM (R^2 = 0.0208) and RF (R^2 =0.4934) alone , respectively. The standardised treatment and sliding window approach improved the prediction accuracy of the model and provided an innovative solution for high-frequency prediction of marine ecological variables.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge