Junfeng Guo
CertDW: Towards Certified Dataset Ownership Verification via Conformal Prediction
Jun 16, 2025



Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) rely heavily on high-quality open-source datasets (e.g., ImageNet) for their success, making dataset ownership verification (DOV) crucial for protecting public dataset copyrights. In this paper, we find existing DOV methods (implicitly) assume that the verification process is faithful, where the suspicious model will directly verify ownership by using the verification samples as input and returning their results. However, this assumption may not necessarily hold in practice and their performance may degrade sharply when subjected to intentional or unintentional perturbations. To address this limitation, we propose the first certified dataset watermark (i.e., CertDW) and CertDW-based certified dataset ownership verification method that ensures reliable verification even under malicious attacks, under certain conditions (e.g., constrained pixel-level perturbation). Specifically, inspired by conformal prediction, we introduce two statistical measures, including principal probability (PP) and watermark robustness (WR), to assess model prediction stability on benign and watermarked samples under noise perturbations. We prove there exists a provable lower bound between PP and WR, enabling ownership verification when a suspicious model's WR value significantly exceeds the PP values of multiple benign models trained on watermark-free datasets. If the number of PP values smaller than WR exceeds a threshold, the suspicious model is regarded as having been trained on the protected dataset. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets verify the effectiveness of our CertDW method and its resistance to potential adaptive attacks. Our codes are at \href{https://github.com/NcepuQiaoTing/CertDW}{GitHub}.
CoTGuard: Using Chain-of-Thought Triggering for Copyright Protection in Multi-Agent LLM Systems
May 26, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) evolve into autonomous agents capable of collaborative reasoning and task execution, multi-agent LLM systems have emerged as a powerful paradigm for solving complex problems. However, these systems pose new challenges for copyright protection, particularly when sensitive or copyrighted content is inadvertently recalled through inter-agent communication and reasoning. Existing protection techniques primarily focus on detecting content in final outputs, overlooking the richer, more revealing reasoning processes within the agents themselves. In this paper, we introduce CoTGuard, a novel framework for copyright protection that leverages trigger-based detection within Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning. Specifically, we can activate specific CoT segments and monitor intermediate reasoning steps for unauthorized content reproduction by embedding specific trigger queries into agent prompts. This approach enables fine-grained, interpretable detection of copyright violations in collaborative agent scenarios. We evaluate CoTGuard on various benchmarks in extensive experiments and show that it effectively uncovers content leakage with minimal interference to task performance. Our findings suggest that reasoning-level monitoring offers a promising direction for safeguarding intellectual property in LLM-based agent systems.
Web IP at Risk: Prevent Unauthorized Real-Time Retrieval by Large Language Models
May 19, 2025



Abstract:Protecting cyber Intellectual Property (IP) such as web content is an increasingly critical concern. The rise of large language models (LLMs) with online retrieval capabilities presents a double-edged sword that enables convenient access to information but often undermines the rights of original content creators. As users increasingly rely on LLM-generated responses, they gradually diminish direct engagement with original information sources, significantly reducing the incentives for IP creators to contribute, and leading to a saturating cyberspace with more AI-generated content. In response, we propose a novel defense framework that empowers web content creators to safeguard their web-based IP from unauthorized LLM real-time extraction by leveraging the semantic understanding capability of LLMs themselves. Our method follows principled motivations and effectively addresses an intractable black-box optimization problem. Real-world experiments demonstrated that our methods improve defense success rates from 2.5% to 88.6% on different LLMs, outperforming traditional defenses such as configuration-based restrictions.
BEV-LIO(LC): BEV Image Assisted LiDAR-Inertial Odometry with Loop Closure
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:This work introduces BEV-LIO(LC), a novel LiDAR-Inertial Odometry (LIO) framework that combines Bird's Eye View (BEV) image representations of LiDAR data with geometry-based point cloud registration and incorporates loop closure (LC) through BEV image features. By normalizing point density, we project LiDAR point clouds into BEV images, thereby enabling efficient feature extraction and matching. A lightweight convolutional neural network (CNN) based feature extractor is employed to extract distinctive local and global descriptors from the BEV images. Local descriptors are used to match BEV images with FAST keypoints for reprojection error construction, while global descriptors facilitate loop closure detection. Reprojection error minimization is then integrated with point-to-plane registration within an iterated Extended Kalman Filter (iEKF). In the back-end, global descriptors are used to create a KD-tree-indexed keyframe database for accurate loop closure detection. When a loop closure is detected, Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) computes a coarse transform from BEV image matching, which serves as the initial estimate for Iterative Closest Point (ICP). The refined transform is subsequently incorporated into a factor graph along with odometry factors, improving the global consistency of localization. Extensive experiments conducted in various scenarios with different LiDAR types demonstrate that BEV-LIO(LC) outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving competitive localization accuracy. Our code, video and supplementary materials can be found at https://github.com/HxCa1/BEV-LIO-LC.
SleeperMark: Towards Robust Watermark against Fine-Tuning Text-to-image Diffusion Models
Dec 06, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in large-scale text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models have enabled a variety of downstream applications, including style customization, subject-driven personalization, and conditional generation. As T2I models require extensive data and computational resources for training, they constitute highly valued intellectual property (IP) for their legitimate owners, yet making them incentive targets for unauthorized fine-tuning by adversaries seeking to leverage these models for customized, usually profitable applications. Existing IP protection methods for diffusion models generally involve embedding watermark patterns and then verifying ownership through generated outputs examination, or inspecting the model's feature space. However, these techniques are inherently ineffective in practical scenarios when the watermarked model undergoes fine-tuning, and the feature space is inaccessible during verification ((i.e., black-box setting). The model is prone to forgetting the previously learned watermark knowledge when it adapts to a new task. To address this challenge, we propose SleeperMark, a novel framework designed to embed resilient watermarks into T2I diffusion models. SleeperMark explicitly guides the model to disentangle the watermark information from the semantic concepts it learns, allowing the model to retain the embedded watermark while continuing to be fine-tuned to new downstream tasks. Our extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of SleeperMark across various types of diffusion models, including latent diffusion models (e.g., Stable Diffusion) and pixel diffusion models (e.g., DeepFloyd-IF), showing robustness against downstream fine-tuning and various attacks at both the image and model levels, with minimal impact on the model's generative capability. The code is available at https://github.com/taco-group/SleeperMark.
Backdoor in Seconds: Unlocking Vulnerabilities in Large Pre-trained Models via Model Editing
Oct 23, 2024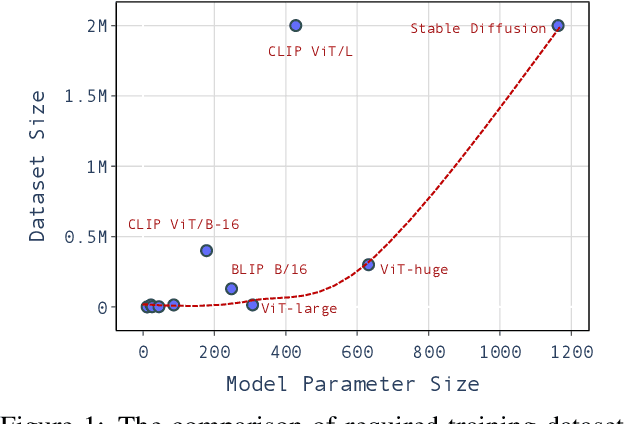
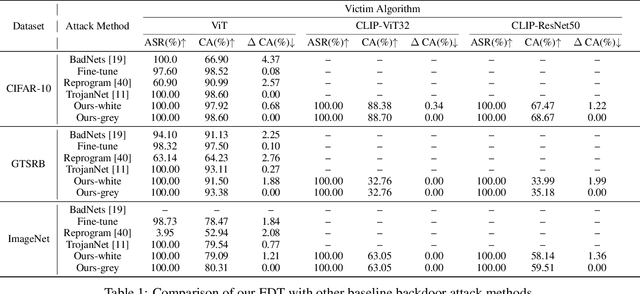
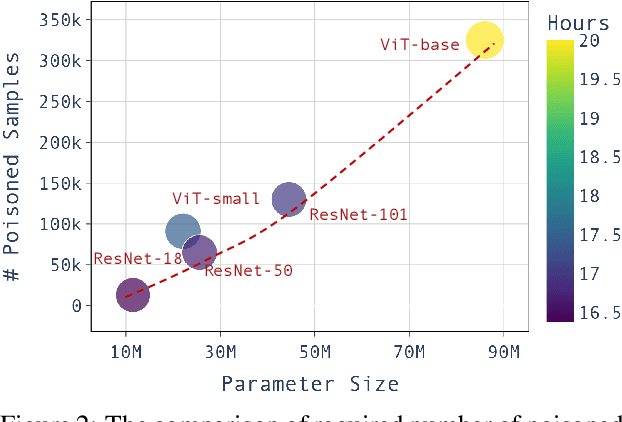
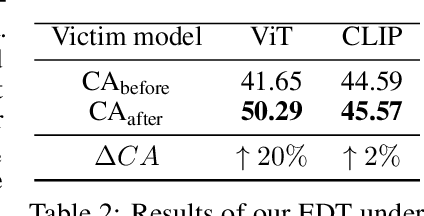
Abstract:Large pre-trained models have achieved notable success across a range of downstream tasks. However, recent research shows that a type of adversarial attack ($\textit{i.e.,}$ backdoor attack) can manipulate the behavior of machine learning models through contaminating their training dataset, posing significant threat in the real-world application of large pre-trained model, especially for those customized models. Therefore, addressing the unique challenges for exploring vulnerability of pre-trained models is of paramount importance. Through empirical studies on the capability for performing backdoor attack in large pre-trained models ($\textit{e.g.,}$ ViT), we find the following unique challenges of attacking large pre-trained models: 1) the inability to manipulate or even access large training datasets, and 2) the substantial computational resources required for training or fine-tuning these models. To address these challenges, we establish new standards for an effective and feasible backdoor attack in the context of large pre-trained models. In line with these standards, we introduce our EDT model, an \textbf{E}fficient, \textbf{D}ata-free, \textbf{T}raining-free backdoor attack method. Inspired by model editing techniques, EDT injects an editing-based lightweight codebook into the backdoor of large pre-trained models, which replaces the embedding of the poisoned image with the target image without poisoning the training dataset or training the victim model. Our experiments, conducted across various pre-trained models such as ViT, CLIP, BLIP, and stable diffusion, and on downstream tasks including image classification, image captioning, and image generation, demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Our code is available in the supplementary material.
A Watermark for Order-Agnostic Language Models
Oct 17, 2024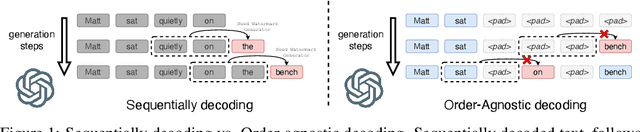
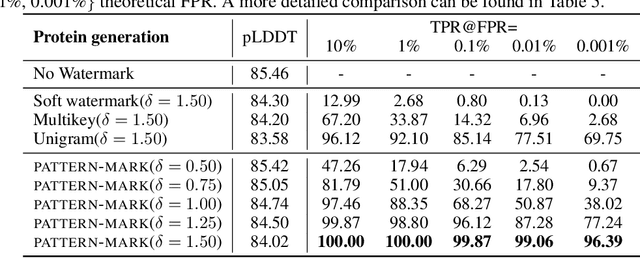
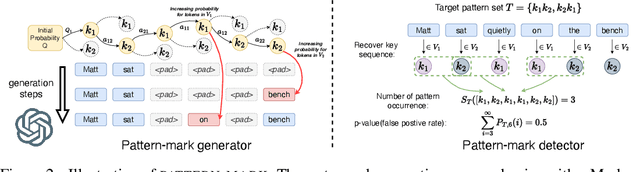

Abstract:Statistical watermarking techniques are well-established for sequentially decoded language models (LMs). However, these techniques cannot be directly applied to order-agnostic LMs, as the tokens in order-agnostic LMs are not generated sequentially. In this work, we introduce Pattern-mark, a pattern-based watermarking framework specifically designed for order-agnostic LMs. We develop a Markov-chain-based watermark generator that produces watermark key sequences with high-frequency key patterns. Correspondingly, we propose a statistical pattern-based detection algorithm that recovers the key sequence during detection and conducts statistical tests based on the count of high-frequency patterns. Our extensive evaluations on order-agnostic LMs, such as ProteinMPNN and CMLM, demonstrate Pattern-mark's enhanced detection efficiency, generation quality, and robustness, positioning it as a superior watermarking technique for order-agnostic LMs.
De-mark: Watermark Removal in Large Language Models
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:Watermarking techniques offer a promising way to identify machine-generated content via embedding covert information into the contents generated from language models (LMs). However, the robustness of the watermarking schemes has not been well explored. In this paper, we present De-mark, an advanced framework designed to remove n-gram-based watermarks effectively. Our method utilizes a novel querying strategy, termed random selection probing, which aids in assessing the strength of the watermark and identifying the red-green list within the n-gram watermark. Experiments on popular LMs, such as Llama3 and ChatGPT, demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of De-mark in watermark removal and exploitation tasks.
Distortion-free Watermarks are not Truly Distortion-free under Watermark Key Collisions
Jun 02, 2024



Abstract:Language model (LM) watermarking techniques inject a statistical signal into LM-generated content by substituting the random sampling process with pseudo-random sampling, using watermark keys as the random seed. Among these statistical watermarking approaches, distortion-free watermarks are particularly crucial because they embed watermarks into LM-generated content without compromising generation quality. However, one notable limitation of pseudo-random sampling compared to true-random sampling is that, under the same watermark keys (i.e., key collision), the results of pseudo-random sampling exhibit correlations. This limitation could potentially undermine the distortion-free property. Our studies reveal that key collisions are inevitable due to the limited availability of watermark keys, and existing distortion-free watermarks exhibit a significant distribution bias toward the original LM distribution in the presence of key collisions. Moreover, achieving a perfect distortion-free watermark is impossible as no statistical signal can be embedded under key collisions. To reduce the distribution bias caused by key collisions, we introduce a new family of distortion-free watermarks--beta-watermark. Experimental results support that the beta-watermark can effectively reduce the distribution bias under key collisions.
Few-Shot Class Incremental Learning with Attention-Aware Self-Adaptive Prompt
Mar 25, 2024



Abstract:Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) models aim to incrementally learn new classes with scarce samples while preserving knowledge of old ones. Existing FSCIL methods usually fine-tune the entire backbone, leading to overfitting and hindering the potential to learn new classes. On the other hand, recent prompt-based CIL approaches alleviate forgetting by training prompts with sufficient data in each task. In this work, we propose a novel framework named Attention-aware Self-adaptive Prompt (ASP). ASP encourages task-invariant prompts to capture shared knowledge by reducing specific information from the attention aspect. Additionally, self-adaptive task-specific prompts in ASP provide specific information and transfer knowledge from old classes to new classes with an Information Bottleneck learning objective. In summary, ASP prevents overfitting on base task and does not require enormous data in few-shot incremental tasks. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets validate that ASP consistently outperforms state-of-the-art FSCIL and prompt-based CIL methods in terms of both learning new classes and mitigating forgetting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge