Yisheng Zhong
CATNIP: LLM Unlearning via Calibrated and Tokenized Negative Preference Alignment
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Pretrained knowledge memorized in LLMs raises critical concerns over safety and privacy, which has motivated LLM Unlearning as a technique for selectively removing the influences of undesirable knowledge. Existing approaches, rooted in Gradient Ascent (GA), often degrade general domain knowledge while relying on retention data or curated contrastive pairs, which can be either impractical or data and computationally prohibitive. Negative Preference Alignment has been explored for unlearning to tackle the limitations of GA, which, however, remains confined by its choice of reference model and shows undermined performance in realistic data settings. These limitations raise two key questions: i) Can we achieve effective unlearning that quantifies model confidence in undesirable knowledge and uses it to calibrate gradient updates more precisely, thus reducing catastrophic forgetting? ii) Can we make unlearning robust to data scarcity and length variation? We answer both questions affirmatively with CATNIP (Calibrated and Tokenized Negative Preference Alignment), a principled method that rescales unlearning effects in proportion to the model's token-level confidence, thus ensuring fine-grained control over forgetting. Extensive evaluations on MUSE and WMDP benchmarks demonstrated that our work enables effective unlearning without requiring retention data or contrastive unlearning response pairs, with stronger knowledge forgetting and preservation tradeoffs than state-of-the-art methods.
DUET: Distilled LLM Unlearning from an Efficiently Contextualized Teacher
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:LLM unlearning is a technique to remove the impacts of undesirable knowledge from the model without retraining from scratch, which is indispensable towards trustworthy AI. Existing unlearning methods face significant limitations: conventional tuning-based unlearning is computationally heavy and prone to catastrophic forgetting. In contrast, in-contextualized unlearning is lightweight for precise unlearning but vulnerable to prompt removal or reverse engineering attacks. In response, we propose Distilled Unlearning from an Efficient Teacher (DUET), a novel distillation-based unlearning method that combines the merits of these two lines of work. It learns a student model to imitate the behavior of a prompt-steered teacher that effectively refuses undesirable knowledge generation while preserving general domain knowledge. Extensive evaluations on existing benchmarks with our enriched evaluation protocols demonstrate that DUET achieves higher performance in both forgetting and utility preservation, while being orders of magnitude more data-efficient than state-of-the-art unlearning methods.
Web IP at Risk: Prevent Unauthorized Real-Time Retrieval by Large Language Models
May 19, 2025



Abstract:Protecting cyber Intellectual Property (IP) such as web content is an increasingly critical concern. The rise of large language models (LLMs) with online retrieval capabilities presents a double-edged sword that enables convenient access to information but often undermines the rights of original content creators. As users increasingly rely on LLM-generated responses, they gradually diminish direct engagement with original information sources, significantly reducing the incentives for IP creators to contribute, and leading to a saturating cyberspace with more AI-generated content. In response, we propose a novel defense framework that empowers web content creators to safeguard their web-based IP from unauthorized LLM real-time extraction by leveraging the semantic understanding capability of LLMs themselves. Our method follows principled motivations and effectively addresses an intractable black-box optimization problem. Real-world experiments demonstrated that our methods improve defense success rates from 2.5% to 88.6% on different LLMs, outperforming traditional defenses such as configuration-based restrictions.
PROFL: A Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning Method with Stringent Defense Against Poisoning Attacks
Dec 02, 2023Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) faces two major issues: privacy leakage and poisoning attacks, which may seriously undermine the reliability and security of the system. Overcoming them simultaneously poses a great challenge. This is because privacy protection policies prohibit access to users' local gradients to avoid privacy leakage, while Byzantine-robust methods necessitate access to these gradients to defend against poisoning attacks. To address these problems, we propose a novel privacy-preserving Byzantine-robust FL framework PROFL. PROFL is based on the two-trapdoor additional homomorphic encryption algorithm and blinding techniques to ensure the data privacy of the entire FL process. During the defense process, PROFL first utilize secure Multi-Krum algorithm to remove malicious gradients at the user level. Then, according to the Pauta criterion, we innovatively propose a statistic-based privacy-preserving defense algorithm to eliminate outlier interference at the feature level and resist impersonation poisoning attacks with stronger concealment. Detailed theoretical analysis proves the security and efficiency of the proposed method. We conducted extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets, and PROFL improved accuracy by 39% to 75% across different attack settings compared to similar privacy-preserving robust methods, demonstrating its significant advantage in robustness.
Policy Evaluation and Seeking for Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning via Best Response
Jun 20, 2020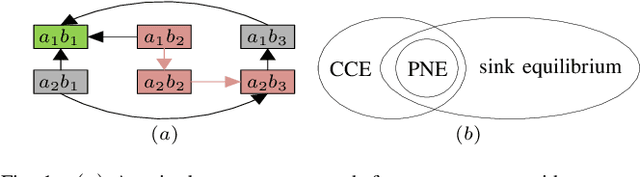
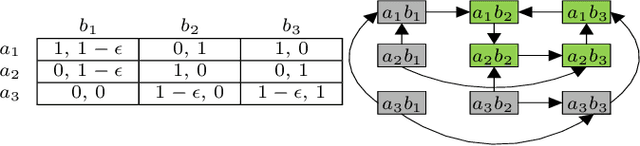
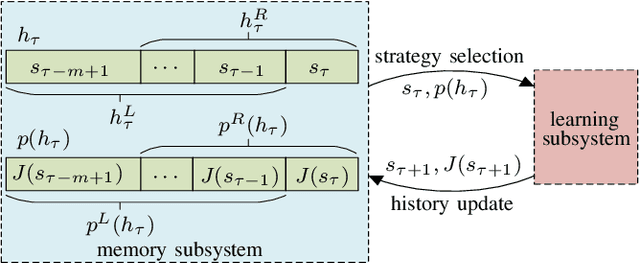
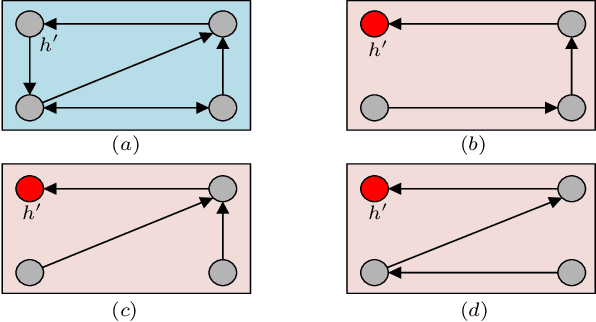
Abstract:This paper introduces two metrics (cycle-based and memory-based metrics), grounded on a dynamical game-theoretic solution concept called sink equilibrium, for the evaluation, ranking, and computation of policies in multi-agent learning. We adopt strict best response dynamics (SBRD) to model selfish behaviors at a meta-level for multi-agent reinforcement learning. Our approach can deal with dynamical cyclical behaviors (unlike approaches based on Nash equilibria and Elo ratings), and is more compatible with single-agent reinforcement learning than alpha-rank which relies on weakly better responses. We first consider settings where the difference between largest and second largest underlying metric has a known lower bound. With this knowledge we propose a class of perturbed SBRD with the following property: only policies with maximum metric are observed with nonzero probability for a broad class of stochastic games with finite memory. We then consider settings where the lower bound for the difference is unknown. For this setting, we propose a class of perturbed SBRD such that the metrics of the policies observed with nonzero probability differ from the optimal by any given tolerance. The proposed perturbed SBRD addresses the opponent-induced non-stationarity by fixing the strategies of others for the learning agent, and uses empirical game-theoretic analysis to estimate payoffs for each strategy profile obtained due to the perturbation.
Person Re-Identification by Unsupervised Video Matching
Nov 28, 2016
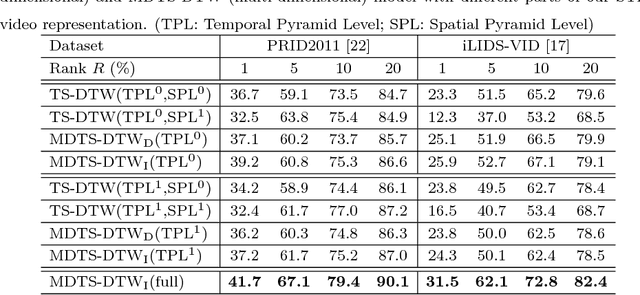

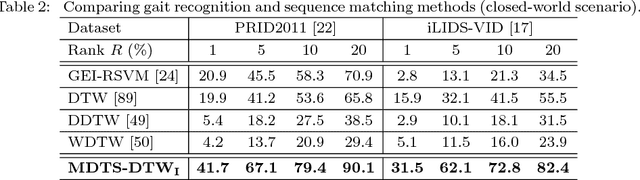
Abstract:Most existing person re-identification (ReID) methods rely only on the spatial appearance information from either one or multiple person images, whilst ignore the space-time cues readily available in video or image-sequence data. Moreover, they often assume the availability of exhaustively labelled cross-view pairwise data for every camera pair, making them non-scalable to ReID applications in real-world large scale camera networks. In this work, we introduce a novel video based person ReID method capable of accurately matching people across views from arbitrary unaligned image-sequences without any labelled pairwise data. Specifically, we introduce a new space-time person representation by encoding multiple granularities of spatio-temporal dynamics in form of time series. Moreover, a Time Shift Dynamic Time Warping (TS-DTW) model is derived for performing automatically alignment whilst achieving data selection and matching between inherently inaccurate and incomplete sequences in a unified way. We further extend the TS-DTW model for accommodating multiple feature-sequences of an image-sequence in order to fuse information from different descriptions. Crucially, this model does not require pairwise labelled training data (i.e. unsupervised) therefore readily scalable to large scale camera networks of arbitrary camera pairs without the need for exhaustive data annotation for every camera pair. We show the effectiveness and advantages of the proposed method by extensive comparisons with related state-of-the-art approaches using two benchmarking ReID datasets, PRID2011 and iLIDS-VID.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge