Sheng Yue
FORLER: Federated Offline Reinforcement Learning with Q-Ensemble and Actor Rectification
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:In Internet-of-Things systems, federated learning has advanced online reinforcement learning (RL) by enabling parallel policy training without sharing raw data. However, interacting with real environments online can be risky and costly, motivating offline federated RL (FRL), where local devices learn from fixed datasets. Despite its promise, offline FRL may break down under low-quality, heterogeneous data. Offline RL tends to get stuck in local optima, and in FRL, one device's suboptimal policy can degrade the aggregated model, i.e., policy pollution. We present FORLER, combining Q-ensemble aggregation on the server with actor rectification on devices. The server robustly merges device Q-functions to curb policy pollution and shift heavy computation off resource-constrained hardware without compromising privacy. Locally, actor rectification enriches policy gradients via a zeroth-order search for high-Q actions plus a bespoke regularizer that nudges the policy toward them. A $δ$-periodic strategy further reduces local computation. We theoretically provide safe policy improvement performance guarantees. Extensive experiments show FORLER consistently outperforms strong baselines under varying data quality and heterogeneity.
Context Learning for Multi-Agent Discussion
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Multi-Agent Discussion (MAD) has garnered increasing attention very recently, where multiple LLM instances collaboratively solve problems via structured discussion. However, we find that current MAD methods easily suffer from discussion inconsistency, LLMs fail to reach a coherent solution, due to the misalignment between their individual contexts.In this paper, we introduce a multi-LLM context learning method (M2CL) that learns a context generator for each agent, capable of dynamically generating context instructions per discussion round via automatic information organization and refinement. Specifically, inspired by our theoretical insights on the context instruction, M2CL train the generators to control context coherence and output discrepancies via a carefully crafted self-adaptive mechanism.It enables LLMs to avoid premature convergence on majority noise and progressively reach the correct consensus. We evaluate M2CL on challenging tasks, including academic reasoning, embodied tasks, and mobile control. The results show that the performance of M2CL significantly surpasses existing methods by 20%--50%, while enjoying favorable transferability and computational efficiency.
Less is More: Clustered Cross-Covariance Control for Offline RL
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:A fundamental challenge in offline reinforcement learning is distributional shift. Scarce data or datasets dominated by out-of-distribution (OOD) areas exacerbate this issue. Our theoretical analysis and experiments show that the standard squared error objective induces a harmful TD cross covariance. This effect amplifies in OOD areas, biasing optimization and degrading policy learning. To counteract this mechanism, we develop two complementary strategies: partitioned buffer sampling that restricts updates to localized replay partitions, attenuates irregular covariance effects, and aligns update directions, yielding a scheme that is easy to integrate with existing implementations, namely Clustered Cross-Covariance Control for TD (C^4). We also introduce an explicit gradient-based corrective penalty that cancels the covariance induced bias within each update. We prove that buffer partitioning preserves the lower bound property of the maximization objective, and that these constraints mitigate excessive conservatism in extreme OOD areas without altering the core behavior of policy constrained offline reinforcement learning. Empirically, our method showcases higher stability and up to 30% improvement in returns over prior methods, especially with small datasets and splits that emphasize OOD areas.
AugFL: Augmenting Federated Learning with Pretrained Models
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has garnered widespread interest in recent years. However, owing to strict privacy policies or limited storage capacities of training participants such as IoT devices, its effective deployment is often impeded by the scarcity of training data in practical decentralized learning environments. In this paper, we study enhancing FL with the aid of (large) pre-trained models (PMs), that encapsulate wealthy general/domain-agnostic knowledge, to alleviate the data requirement in conducting FL from scratch. Specifically, we consider a networked FL system formed by a central server and distributed clients. First, we formulate the PM-aided personalized FL as a regularization-based federated meta-learning problem, where clients join forces to learn a meta-model with knowledge transferred from a private PM stored at the server. Then, we develop an inexact-ADMM-based algorithm, AugFL, to optimize the problem with no need to expose the PM or incur additional computational costs to local clients. Further, we establish theoretical guarantees for AugFL in terms of communication complexity, adaptation performance, and the benefit of knowledge transfer in general non-convex cases. Extensive experiments corroborate the efficacy and superiority of AugFL over existing baselines.
OLLIE: Imitation Learning from Offline Pretraining to Online Finetuning
May 29, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we study offline-to-online Imitation Learning (IL) that pretrains an imitation policy from static demonstration data, followed by fast finetuning with minimal environmental interaction. We find the na\"ive combination of existing offline IL and online IL methods tends to behave poorly in this context, because the initial discriminator (often used in online IL) operates randomly and discordantly against the policy initialization, leading to misguided policy optimization and $\textit{unlearning}$ of pretraining knowledge. To overcome this challenge, we propose a principled offline-to-online IL method, named $\texttt{OLLIE}$, that simultaneously learns a near-expert policy initialization along with an $\textit{aligned discriminator initialization}$, which can be seamlessly integrated into online IL, achieving smooth and fast finetuning. Empirically, $\texttt{OLLIE}$ consistently and significantly outperforms the baseline methods in $\textbf{20}$ challenging tasks, from continuous control to vision-based domains, in terms of performance, demonstration efficiency, and convergence speed. This work may serve as a foundation for further exploration of pretraining and finetuning in the context of IL.
Federated Offline Policy Optimization with Dual Regularization
May 29, 2024Abstract:Federated Reinforcement Learning (FRL) has been deemed as a promising solution for intelligent decision-making in the era of Artificial Internet of Things. However, existing FRL approaches often entail repeated interactions with the environment during local updating, which can be prohibitively expensive or even infeasible in many real-world domains. To overcome this challenge, this paper proposes a novel offline federated policy optimization algorithm, named $\texttt{DRPO}$, which enables distributed agents to collaboratively learn a decision policy only from private and static data without further environmental interactions. $\texttt{DRPO}$ leverages dual regularization, incorporating both the local behavioral policy and the global aggregated policy, to judiciously cope with the intrinsic two-tier distributional shifts in offline FRL. Theoretical analysis characterizes the impact of the dual regularization on performance, demonstrating that by achieving the right balance thereof, $\texttt{DRPO}$ can effectively counteract distributional shifts and ensure strict policy improvement in each federative learning round. Extensive experiments validate the significant performance gains of $\texttt{DRPO}$ over baseline methods.
How to Leverage Diverse Demonstrations in Offline Imitation Learning
May 29, 2024
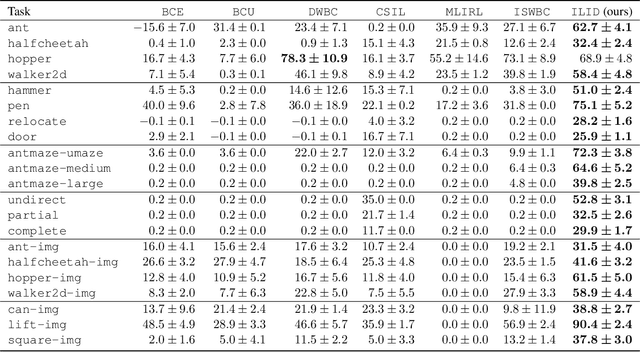
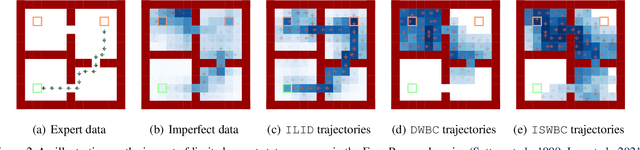
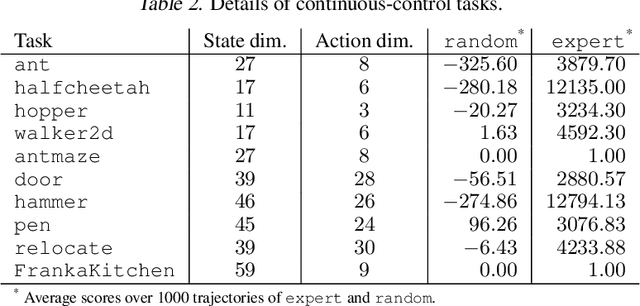
Abstract:Offline Imitation Learning (IL) with imperfect demonstrations has garnered increasing attention owing to the scarcity of expert data in many real-world domains. A fundamental problem in this scenario is how to extract positive behaviors from noisy data. In general, current approaches to the problem select data building on state-action similarity to given expert demonstrations, neglecting precious information in (potentially abundant) $\textit{diverse}$ state-actions that deviate from expert ones. In this paper, we introduce a simple yet effective data selection method that identifies positive behaviors based on their resultant states -- a more informative criterion enabling explicit utilization of dynamics information and effective extraction of both expert and beneficial diverse behaviors. Further, we devise a lightweight behavior cloning algorithm capable of leveraging the expert and selected data correctly. In the experiments, we evaluate our method on a suite of complex and high-dimensional offline IL benchmarks, including continuous-control and vision-based tasks. The results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming existing methods on $\textbf{20/21}$ benchmarks, typically by $\textbf{2-5x}$, while maintaining a comparable runtime to Behavior Cloning ($\texttt{BC}$).
Momentum-Based Federated Reinforcement Learning with Interaction and Communication Efficiency
May 29, 2024
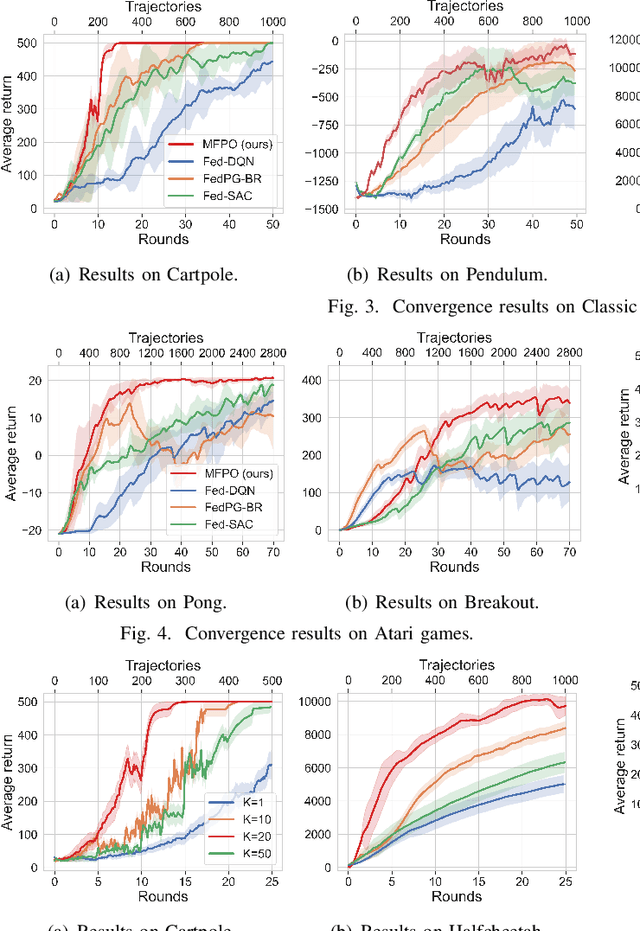
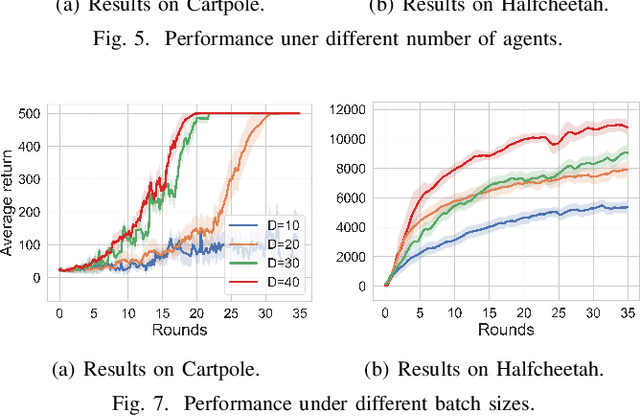
Abstract:Federated Reinforcement Learning (FRL) has garnered increasing attention recently. However, due to the intrinsic spatio-temporal non-stationarity of data distributions, the current approaches typically suffer from high interaction and communication costs. In this paper, we introduce a new FRL algorithm, named $\texttt{MFPO}$, that utilizes momentum, importance sampling, and additional server-side adjustment to control the shift of stochastic policy gradients and enhance the efficiency of data utilization. We prove that by proper selection of momentum parameters and interaction frequency, $\texttt{MFPO}$ can achieve $\tilde{\mathcal{O}}(H N^{-1}\epsilon^{-3/2})$ and $\tilde{\mathcal{O}}(\epsilon^{-1})$ interaction and communication complexities ($N$ represents the number of agents), where the interaction complexity achieves linear speedup with the number of agents, and the communication complexity aligns the best achievable of existing first-order FL algorithms. Extensive experiments corroborate the substantial performance gains of $\texttt{MFPO}$ over existing methods on a suite of complex and high-dimensional benchmarks.
CLARE: Conservative Model-Based Reward Learning for Offline Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Feb 21, 2023


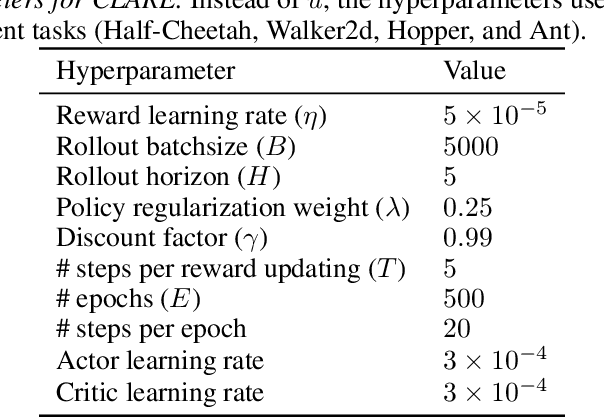
Abstract:This work aims to tackle a major challenge in offline Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL), namely the reward extrapolation error, where the learned reward function may fail to explain the task correctly and misguide the agent in unseen environments due to the intrinsic covariate shift. Leveraging both expert data and lower-quality diverse data, we devise a principled algorithm (namely CLARE) that solves offline IRL efficiently via integrating "conservatism" into a learned reward function and utilizing an estimated dynamics model. Our theoretical analysis provides an upper bound on the return gap between the learned policy and the expert policy, based on which we characterize the impact of covariate shift by examining subtle two-tier tradeoffs between the exploitation (on both expert and diverse data) and exploration (on the estimated dynamics model). We show that CLARE can provably alleviate the reward extrapolation error by striking the right exploitation-exploration balance therein. Extensive experiments corroborate the significant performance gains of CLARE over existing state-of-the-art algorithms on MuJoCo continuous control tasks (especially with a small offline dataset), and the learned reward is highly instructive for further learning.
Efficient Federated Meta-Learning over Multi-Access Wireless Networks
Sep 01, 2021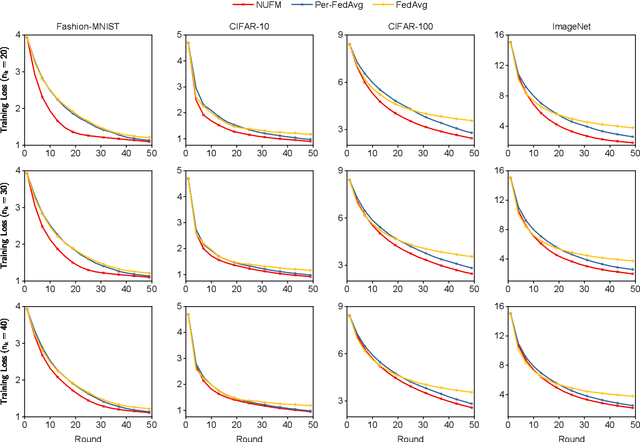
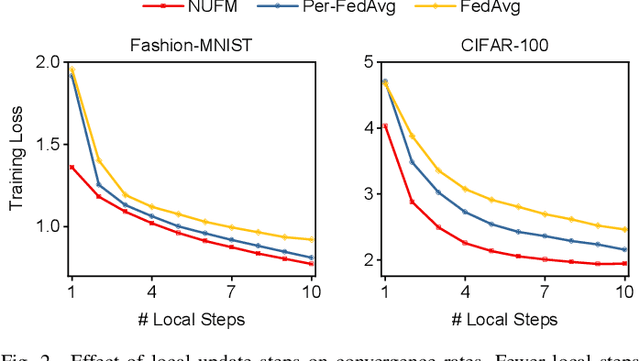
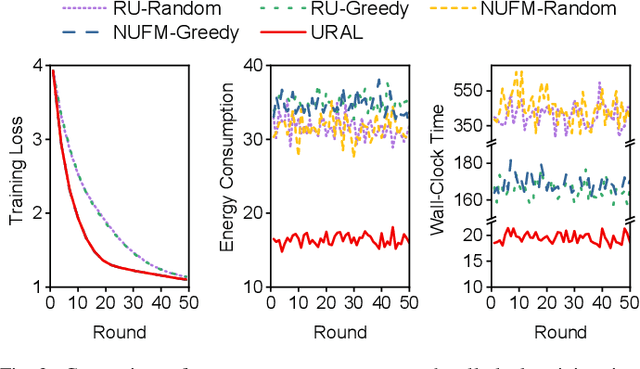
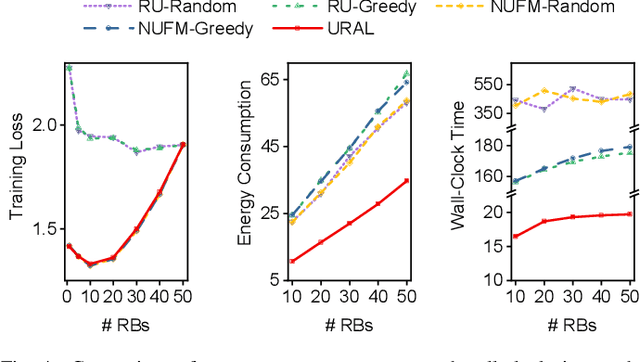
Abstract:Federated meta-learning (FML) has emerged as a promising paradigm to cope with the data limitation and heterogeneity challenges in today's edge learning arena. However, its performance is often limited by slow convergence and corresponding low communication efficiency. In addition, since the available radio spectrum and IoT devices' energy capacity are usually insufficient, it is crucial to control the resource allocation and energy consumption when deploying FML in practical wireless networks. To overcome the challenges, in this paper, we rigorously analyze each device's contribution to the global loss reduction in each round and develop an FML algorithm (called NUFM) with a non-uniform device selection scheme to accelerate the convergence. After that, we formulate a resource allocation problem integrating NUFM in multi-access wireless systems to jointly improve the convergence rate and minimize the wall-clock time along with energy cost. By deconstructing the original problem step by step, we devise a joint device selection and resource allocation strategy to solve the problem with theoretical guarantees. Further, we show that the computational complexity of NUFM can be reduced from $O(d^2)$ to $O(d)$ (with the model dimension $d$) via combining two first-order approximation techniques. Extensive simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed methods in comparison with existing baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge