Fangqi Zhu
WMPO: World Model-based Policy Optimization for Vision-Language-Action Models
Nov 12, 2025



Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have shown strong potential for general-purpose robotic manipulation, but their reliance on expert demonstrations limits their ability to learn from failures and perform self-corrections. Reinforcement learning (RL) addresses these through self-improving interactions with the physical environment, but suffers from high sample complexity on real robots. We introduce World-Model-based Policy Optimization (WMPO), a principled framework for on-policy VLA RL without interacting with the real environment. In contrast to widely used latent world models, WMPO focuses on pixel-based predictions that align the "imagined" trajectories with the VLA features pretrained with web-scale images. Crucially, WMPO enables the policy to perform on-policy GRPO that provides stronger performance than the often-used off-policy methods. Extensive experiments in both simulation and real-robot settings demonstrate that WMPO (i) substantially improves sample efficiency, (ii) achieves stronger overall performance, (iii) exhibits emergent behaviors such as self-correction, and (iv) demonstrates robust generalization and lifelong learning capabilities.
Mesh-RFT: Enhancing Mesh Generation via Fine-grained Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
May 22, 2025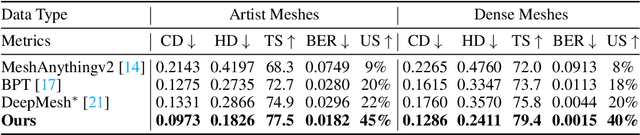
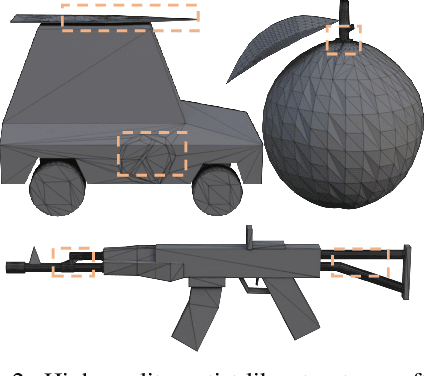
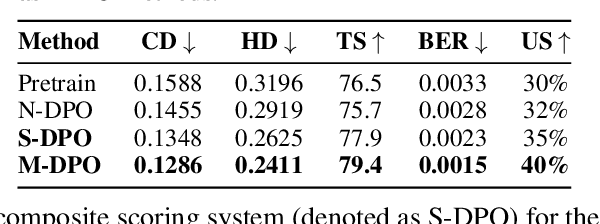
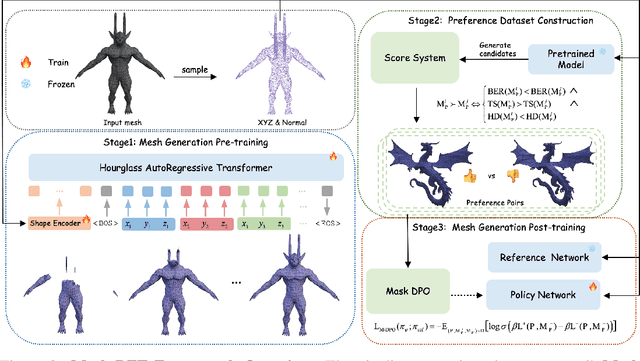
Abstract:Existing pretrained models for 3D mesh generation often suffer from data biases and produce low-quality results, while global reinforcement learning (RL) methods rely on object-level rewards that struggle to capture local structure details. To address these challenges, we present \textbf{Mesh-RFT}, a novel fine-grained reinforcement fine-tuning framework that employs Masked Direct Preference Optimization (M-DPO) to enable localized refinement via quality-aware face masking. To facilitate efficient quality evaluation, we introduce an objective topology-aware scoring system to evaluate geometric integrity and topological regularity at both object and face levels through two metrics: Boundary Edge Ratio (BER) and Topology Score (TS). By integrating these metrics into a fine-grained RL strategy, Mesh-RFT becomes the first method to optimize mesh quality at the granularity of individual faces, resolving localized errors while preserving global coherence. Experiment results show that our M-DPO approach reduces Hausdorff Distance (HD) by 24.6\% and improves Topology Score (TS) by 3.8\% over pre-trained models, while outperforming global DPO methods with a 17.4\% HD reduction and 4.9\% TS gain. These results demonstrate Mesh-RFT's ability to improve geometric integrity and topological regularity, achieving new state-of-the-art performance in production-ready mesh generation. Project Page: \href{https://hitcslj.github.io/mesh-rft/}{this https URL}.
IRASim: Learning Interactive Real-Robot Action Simulators
Jun 20, 2024



Abstract:Scalable robot learning in the real world is limited by the cost and safety issues of real robots. In addition, rolling out robot trajectories in the real world can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. In this paper, we propose to learn an interactive real-robot action simulator as an alternative. We introduce a novel method, IRASim, which leverages the power of generative models to generate extremely realistic videos of a robot arm that executes a given action trajectory, starting from an initial given frame. To validate the effectiveness of our method, we create a new benchmark, IRASim Benchmark, based on three real-robot datasets and perform extensive experiments on the benchmark. Results show that IRASim outperforms all the baseline methods and is more preferable in human evaluations. We hope that IRASim can serve as an effective and scalable approach to enhance robot learning in the real world. To promote research for generative real-robot action simulators, we open-source code, benchmark, and checkpoints at https: //gen-irasim.github.io.
Learning to Describe for Predicting Zero-shot Drug-Drug Interactions
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:Adverse drug-drug interactions~(DDIs) can compromise the effectiveness of concurrent drug administration, posing a significant challenge in healthcare. As the development of new drugs continues, the potential for unknown adverse effects resulting from DDIs becomes a growing concern. Traditional computational methods for DDI prediction may fail to capture interactions for new drugs due to the lack of knowledge. In this paper, we introduce a new problem setup as zero-shot DDI prediction that deals with the case of new drugs. Leveraging textual information from online databases like DrugBank and PubChem, we propose an innovative approach TextDDI with a language model-based DDI predictor and a reinforcement learning~(RL)-based information selector, enabling the selection of concise and pertinent text for accurate DDI prediction on new drugs. Empirical results show the benefits of the proposed approach on several settings including zero-shot and few-shot DDI prediction, and the selected texts are semantically relevant. Our code and data are available at \url{https://github.com/zhufq00/DDIs-Prediction}.
A Diffusion Model for Event Skeleton Generation
May 27, 2023



Abstract:Event skeleton generation, aiming to induce an event schema skeleton graph with abstracted event nodes and their temporal relations from a set of event instance graphs, is a critical step in the temporal complex event schema induction task. Existing methods effectively address this task from a graph generation perspective but suffer from noise-sensitive and error accumulation, e.g., the inability to correct errors while generating schema. We, therefore, propose a novel Diffusion Event Graph Model~(DEGM) to address these issues. Our DEGM is the first workable diffusion model for event skeleton generation, where the embedding and rounding techniques with a custom edge-based loss are introduced to transform a discrete event graph into learnable latent representation. Furthermore, we propose a denoising training process to maintain the model's robustness. Consequently, DEGM derives the final schema, where error correction is guaranteed by iteratively refining the latent representation during the schema generation process. Experimental results on three IED bombing datasets demonstrate that our DEGM achieves better results than other state-of-the-art baselines. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/zhufq00/EventSkeletonGeneration.
A Generative Approach for Script Event Prediction via Contrastive Fine-tuning
Dec 09, 2022



Abstract:Script event prediction aims to predict the subsequent event given the context. This requires the capability to infer the correlations between events. Recent works have attempted to improve event correlation reasoning by using pretrained language models and incorporating external knowledge~(e.g., discourse relations). Though promising results have been achieved, some challenges still remain. First, the pretrained language models adopted by current works ignore event-level knowledge, resulting in an inability to capture the correlations between events well. Second, modeling correlations between events with discourse relations is limited because it can only capture explicit correlations between events with discourse markers, and cannot capture many implicit correlations. To this end, we propose a novel generative approach for this task, in which a pretrained language model is fine-tuned with an event-centric pretraining objective and predicts the next event within a generative paradigm. Specifically, we first introduce a novel event-level blank infilling strategy as the learning objective to inject event-level knowledge into the pretrained language model, and then design a likelihood-based contrastive loss for fine-tuning the generative model. Instead of using an additional prediction layer, we perform prediction by using sequence likelihoods generated by the generative model. Our approach models correlations between events in a soft way without any external knowledge. The likelihood-based prediction eliminates the need to use additional networks to make predictions and is somewhat interpretable since it scores each word in the event. Experimental results on the multi-choice narrative cloze~(MCNC) task demonstrate that our approach achieves better results than other state-of-the-art baselines. Our code will be available at https://github.com/zhufq00/mcnc.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge