Guofu Liao
A Survey of Zero-Knowledge Proof Based Verifiable Machine Learning
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:As machine learning technologies advance rapidly across various domains, concerns over data privacy and model security have grown significantly. These challenges are particularly pronounced when models are trained and deployed on cloud platforms or third-party servers due to the computational resource limitations of users' end devices. In response, zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) technology has emerged as a promising solution, enabling effective validation of model performance and authenticity in both training and inference processes without disclosing sensitive data. Thus, ZKP ensures the verifiability and security of machine learning models, making it a valuable tool for privacy-preserving AI. Although some research has explored the verifiable machine learning solutions that exploit ZKP, a comprehensive survey and summary of these efforts remain absent. This survey paper aims to bridge this gap by reviewing and analyzing all the existing Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning (ZKML) research from June 2017 to December 2024. We begin by introducing the concept of ZKML and outlining its ZKP algorithmic setups under three key categories: verifiable training, verifiable inference, and verifiable testing. Next, we provide a comprehensive categorization of existing ZKML research within these categories and analyze the works in detail. Furthermore, we explore the implementation challenges faced in this field and discuss the improvement works to address these obstacles. Additionally, we highlight several commercial applications of ZKML technology. Finally, we propose promising directions for future advancements in this domain.
Chats-Grid: An Iterative Retrieval Q&A Optimization Scheme Leveraging Large Model and Retrieval Enhancement Generation in smart grid
Feb 21, 2025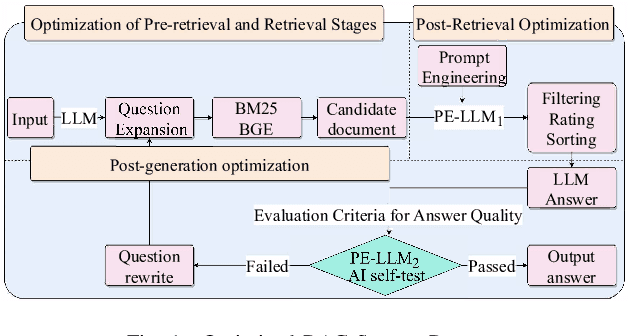
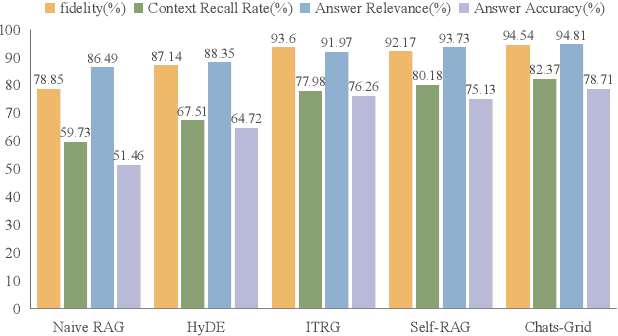
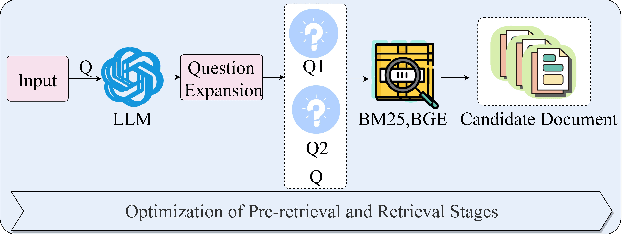
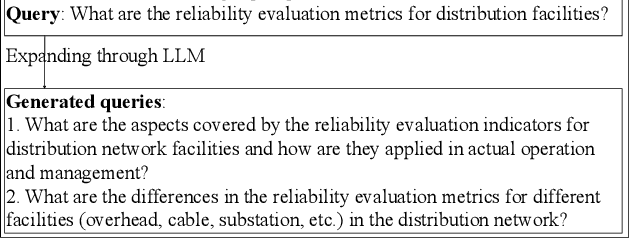
Abstract:With rapid advancements in artificial intelligence, question-answering (Q&A) systems have become essential in intelligent search engines, virtual assistants, and customer service platforms. However, in dynamic domains like smart grids, conventional retrieval-augmented generation(RAG) Q&A systems face challenges such as inadequate retrieval quality, irrelevant responses, and inefficiencies in handling large-scale, real-time data streams. This paper proposes an optimized iterative retrieval-based Q&A framework called Chats-Grid tailored for smart grid environments. In the pre-retrieval phase, Chats-Grid advanced query expansion ensures comprehensive coverage of diverse data sources, including sensor readings, meter records, and control system parameters. During retrieval, Best Matching 25(BM25) sparse retrieval and BAAI General Embedding(BGE) dense retrieval in Chats-Grid are combined to process vast, heterogeneous datasets effectively. Post-retrieval, a fine-tuned large language model uses prompt engineering to assess relevance, filter irrelevant results, and reorder documents based on contextual accuracy. The model further generates precise, context-aware answers, adhering to quality criteria and employing a self-checking mechanism for enhanced reliability. Experimental results demonstrate Chats-Grid's superiority over state-of-the-art methods in fidelity, contextual recall, relevance, and accuracy by 2.37%, 2.19%, and 3.58% respectively. This framework advances smart grid management by improving decision-making and user interactions, fostering resilient and adaptive smart grid infrastructures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge